Abstract
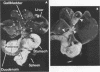
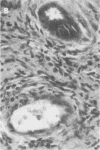
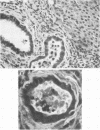
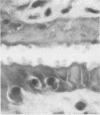
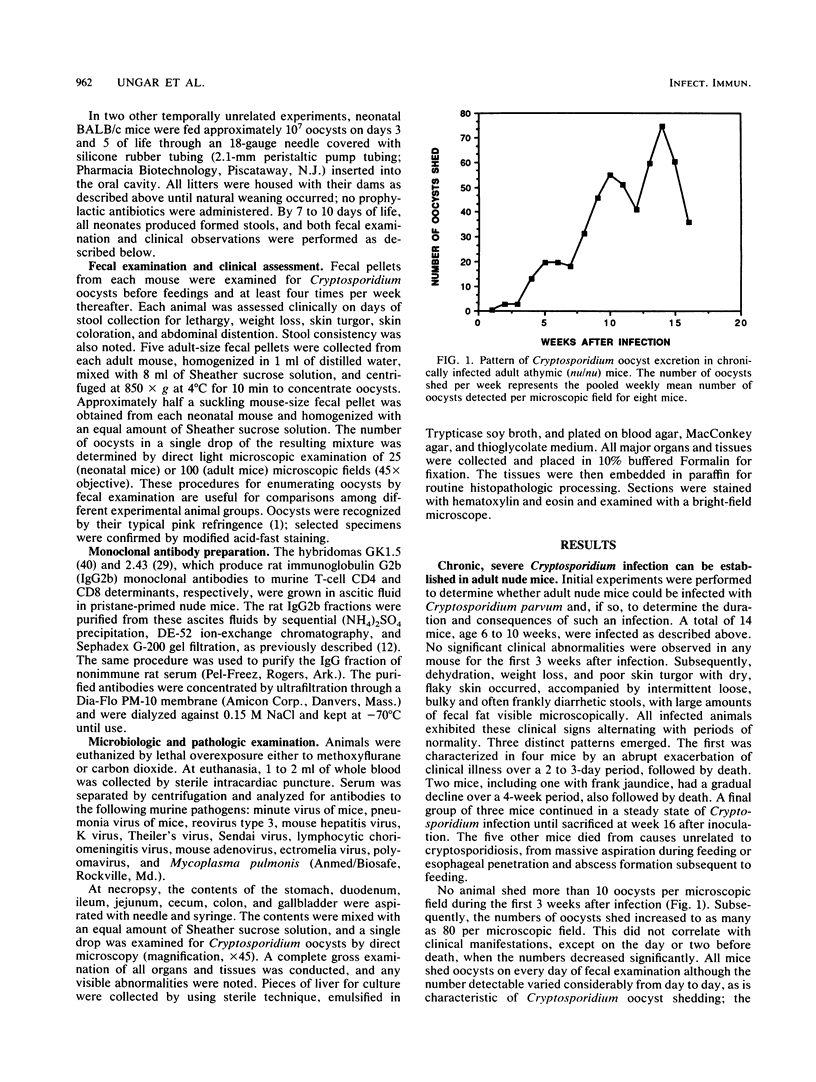
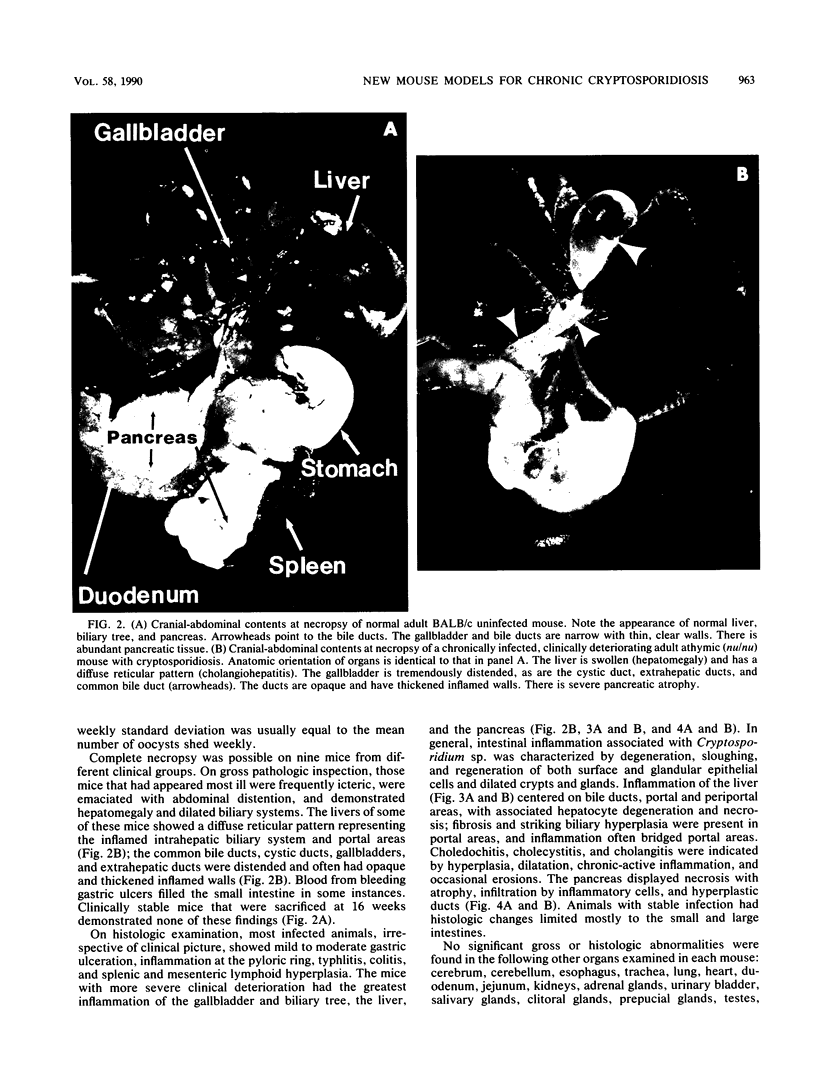
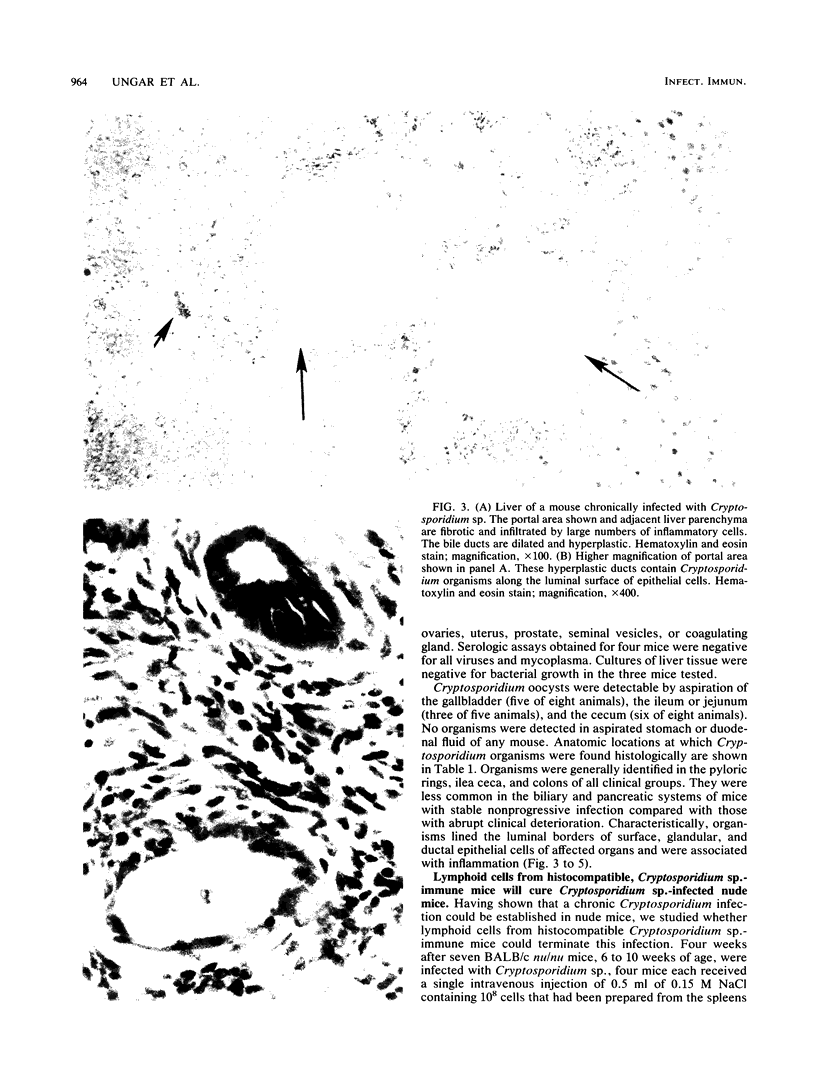
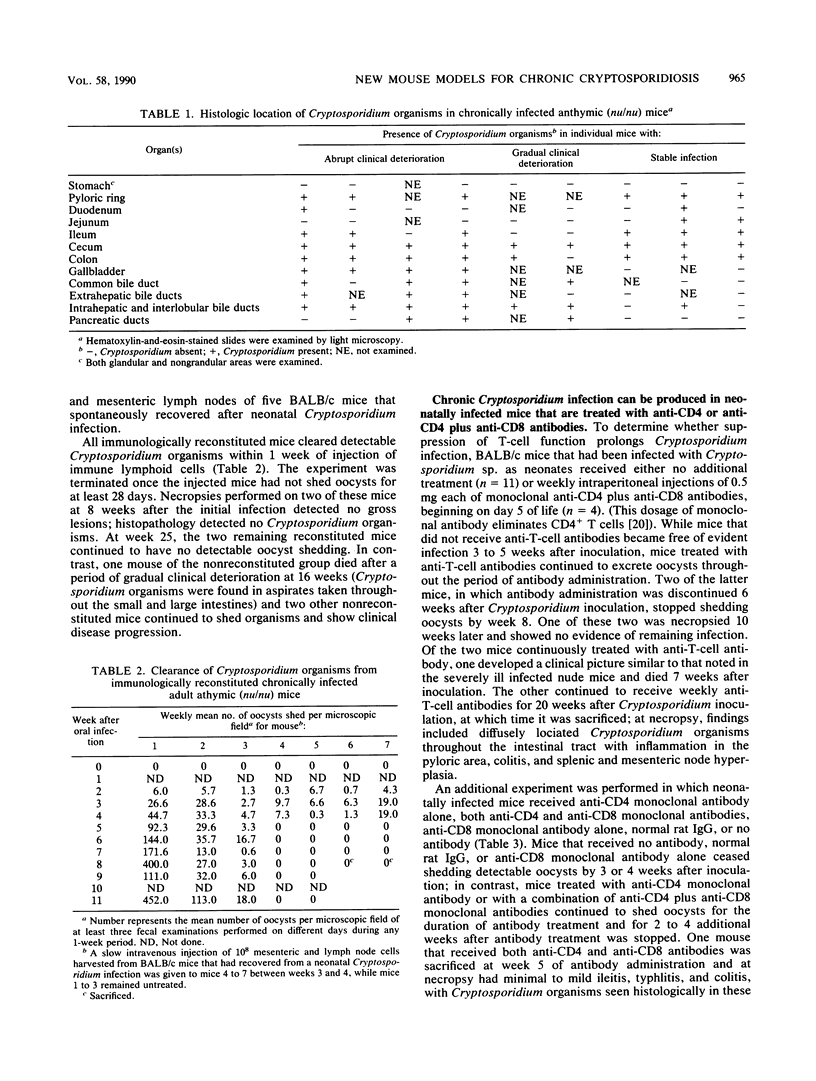
Cryptosporidium sp. causes fulminant diarrhea and chronic infection in immunocompromised, particularly human immunodeficiency virus-infected, persons. The lack of in vitro cultivation and a suitable animal model has limited development of effective treatment. We describe two new mouse models of chronic symptomatic cryptosporidiosis in adult athymic mice and in T-cell subset-depleted mice. A progressive infection, fatal within 4 months, occurred in most adult athymic mice; a few developed stable infections. Symptoms included dehydration, weight loss, intermittent diarrhea, and jaundice. Pathologic abnormalities and organisms localized in the intestine in stable infections but involved the hepatobiliary tree and pancreas in others. Lymphoid cells from histocompatible, Cryptosporidium sp.-immune mice cured infected nude mice. Identical infections occurred in neonatally infected BALB/c mice treated with anti-CD4 monoclonal antibodies alone or also with anti-CD8 monoclonal antibodies; the mice were cured when the monoclonal antibody treatments were stopped. These models will be useful in definition of the immune defects that permit chronic cryptosporidiosis to develop and in assessment of treatment modalities.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxby D., Blundell N. Recognition and laboratory characteristics of an atypical oocyst of Cryptosporidium. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1038–1045. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur P., Lemeteil D., Ballet J. J. Rat model for human cryptosporidiosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):1037–1039. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.1037-1039.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly G. M., Dryden M. S., Shanson D. C., Gazzard B. G. Cryptosporidial diarrhoea in AIDS and its treatment. Gut. 1988 May;29(5):593–597. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.5.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford F. G., Vermund S. H. Human cryptosporidiosis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1988;16(2):113–159. doi: 10.3109/10408418809104469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Current W. L., Haynes T. B. Complete development of Cryptosporidium in cell culture. Science. 1984 May 11;224(4649):603–605. doi: 10.1126/science.6710159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Current W. L., Long P. L. Development of human and calf Cryptosporidium in chicken embryos. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1108–1113. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Current W. L., Reese N. C. A comparison of endogenous development of three isolates of Cryptosporidium in suckling mice. J Protozool. 1986 Feb;33(1):98–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dias R. M., Mangini A. C., Torres D. M., Corrêa M. O., Lupetti N., Corrêa F. M., Chieffi P. P. Cryptosporidiosis among patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) in the county of São Paulo, Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1988 Jul-Aug;30(4):310–312. doi: 10.1590/s0036-46651988000400011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman M. J., Oldfield E. C. Severe cryptosporidiosis in an immunocompetent host. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Aug;148(8):1873–1874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernest J. A., Blagburn B. L., Lindsay D. S., Current W. L. Infection dynamics of Cryptosporidium parvum (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporiidae) in neonatal mice (Mus musculus). J Parasitol. 1986 Oct;72(5):796–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayer R., Ungar B. L. Cryptosporidium spp. and cryptosporidiosis. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):458–483. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.458-483.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelman F. D., Kessler S. W., Mushinski J. F., Potter M. IgD-secreting murine plasmacytomas: identification and partial characterization of two IgD myeloma proteins. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):680–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross T. L., Wheat J., Bartlett M., O'Connor K. W. AIDS and multiple system involvement with cryptosporidium. Am J Gastroenterol. 1986 Jun;81(6):456–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harp J. A., Wannemuehler M. W., Woodmansee D. B., Moon H. W. Susceptibility of germfree or antibiotic-treated adult mice to Cryptosporidium parvum. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2006–2010. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2006-2010.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins S. P., Thomas R. P., Teasdale C. Acute pancreatitis: a new finding in cryptosporidium enteritis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Feb 21;294(6570):483–484. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6570.483-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J., Moon H. W., Woodmansee D. B. Persistent Cryptosporidium infection in congenitally athymic (nude) mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):856–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.856-859.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth M. F., Carlson J. R., Ermak T. H. Clearance of Giardia muris infection requires helper/inducer T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1743–1748. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokipii L., Jokipii A. M. Timing of symptoms and oocyst excretion in human cryptosporidiosis. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 25;315(26):1643–1647. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612253152604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn D. G., Garfinkle J. M., Klonoff D. C., Pembrook L. J., Morrow D. J. Cryptosporidial and cytomegaloviral hepatitis and cholecystitis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1987 Sep;111(9):879–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katona I. M., Urban J. F., Jr, Finkelman F. D. The role of L3T4+ and Lyt-2+ T cells in the IgE response and immunity to Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3206–3211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Druckman D. A., Vernon A., Quinn T. C., Polk B. F., Modlin J. F., Yolken R. H., Bartlett J. G. Prevalence of enteric pathogens in homosexual men with and without acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1988 Apr;94(4):984–993. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90557-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebler E. M., Pohlenz J. F., Woodmansee D. B. Experimental intrauterine infection of adult BALB/c mice with Cryptosporidium sp. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):255–259. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.255-259.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulis S. J., Honig C. L., Soave R., Govoni A. F., Mouradian J. A., Jacobson I. M. Biliary tract obstruction in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Aug;105(2):207–210. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-2-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navin T. R., Hardy A. M. Cryptosporidiosis in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):150–150. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehg J. E., Hancock M. L., Woodmansee D. B. Characterization of a dexamethasone-treated rat model of cryptosporidial infection. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1406–1407. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehg J. E., Hancock M. L., Woodmansee D. B. Characterization of cyclophosphamide-rat model of cryptosporidiosis. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2669–2674. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2669-2674.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson I. C., Mitchell G. F. Giardiasis in mice. I. Prolonged infections in certain mouse strains and hypothymic (nude) mice. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jul;75(1):42–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. E., Joysey H. S., Hesketh P., Grencis R. K., Wakelin D. Mediation of immunity to Eimeria vermiformis in mice by L3T4+ T cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1760–1765. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1760-1765.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. IgG or IgM monoclonal antibodies reactive with different determinants on the molecular complex bearing Lyt 2 antigen block T cell-mediated cytolysis in the absence of complement. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2665–2672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneiderman D. J., Cello J. P., Laing F. C. Papillary stenosis and sclerosing cholangitis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Apr;106(4):546–549. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-4-546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood D., Angus K. W., Snodgrass D. R., Tzipori S. Experimental cryptosporidiosis in laboratory mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):471–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.471-475.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Lane H. C., Gill V. J., Manischewitz J. F., Quinnan G. V., Fauci A. S., Masur H. Intestinal infections in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Etiology and response to therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Mar;108(3):328–333. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-3-328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soave R., Armstrong D. Cryptosporidium and cryptosporidiosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):1012–1023. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehr-Green J. K., McCaig L., Remsen H. M., Rains C. S., Fox M., Juranek D. D. Shedding of oocysts in immunocompetent individuals infected with Cryptosporidium. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Mar;36(2):338–342. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. P., Frank D. M., Mahmoud A. A. Thymus dependency of host resistance to Giardia muris infection: studies in nude mice. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):680–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar B. L., Soave R., Fayer R., Nash T. E. Enzyme immunoassay detection of immunoglobulin M and G antibodies to Cryptosporidium in immunocompetent and immunocompromised persons. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):570–578. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer T. L., Waldor M. K., Steinman L., Conley F. K. Depletion of T-4+ lymphocytes with monoclonal antibody reactivates toxoplasmosis in the central nervous system: a model of superinfection in AIDS. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3737–3741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Kappler J., Dialynas D. P., Fitch F. W. Evidence implicating L3T4 in class II MHC antigen reactivity; monoclonal antibody GK1.5 (anti-L3T4a) blocks class II MHC antigen-specific proliferation, release of lymphokines, and binding by cloned murine helper T lymphocyte lines. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2178–2183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]