Abstract
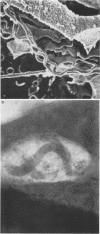
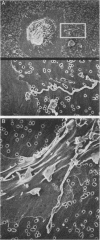
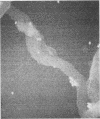
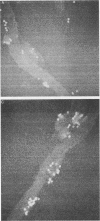
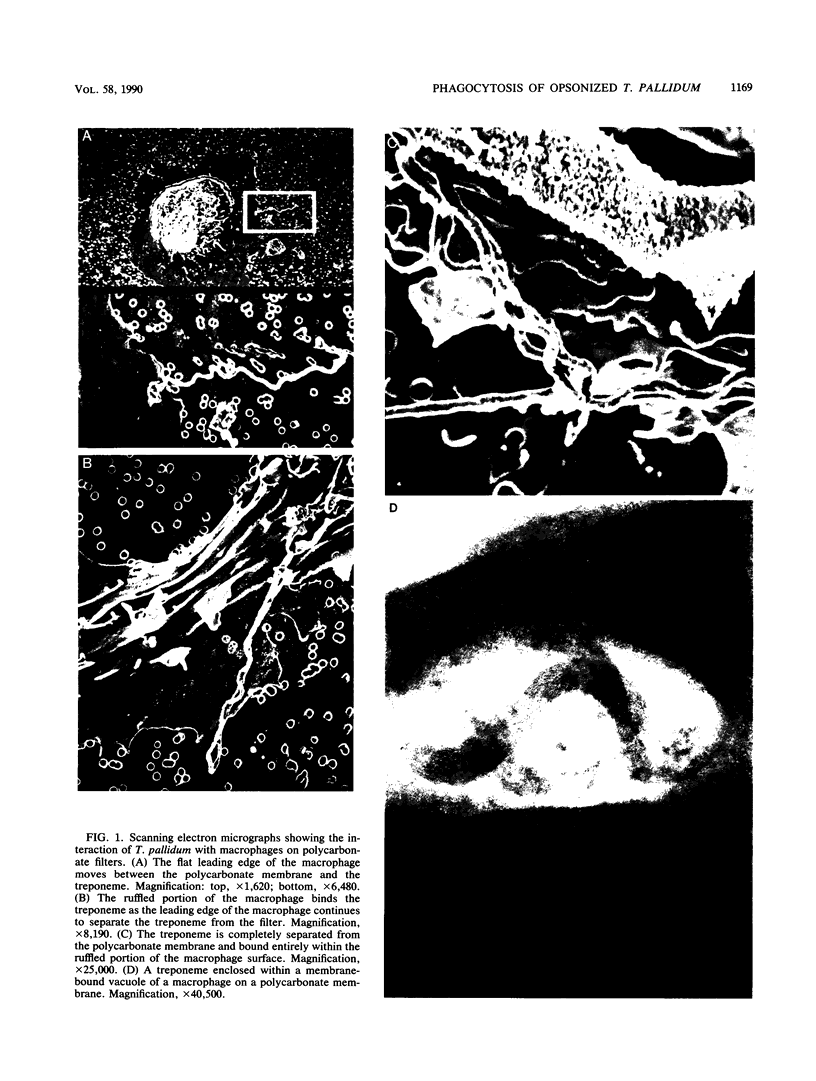
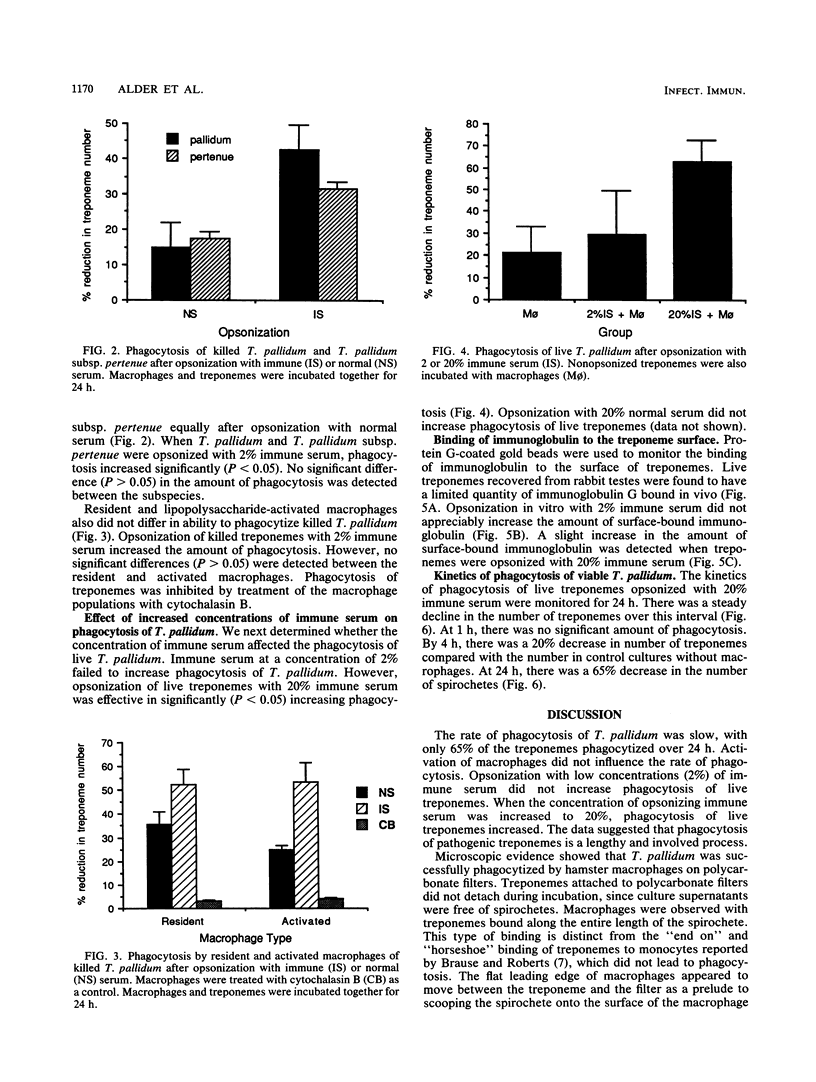
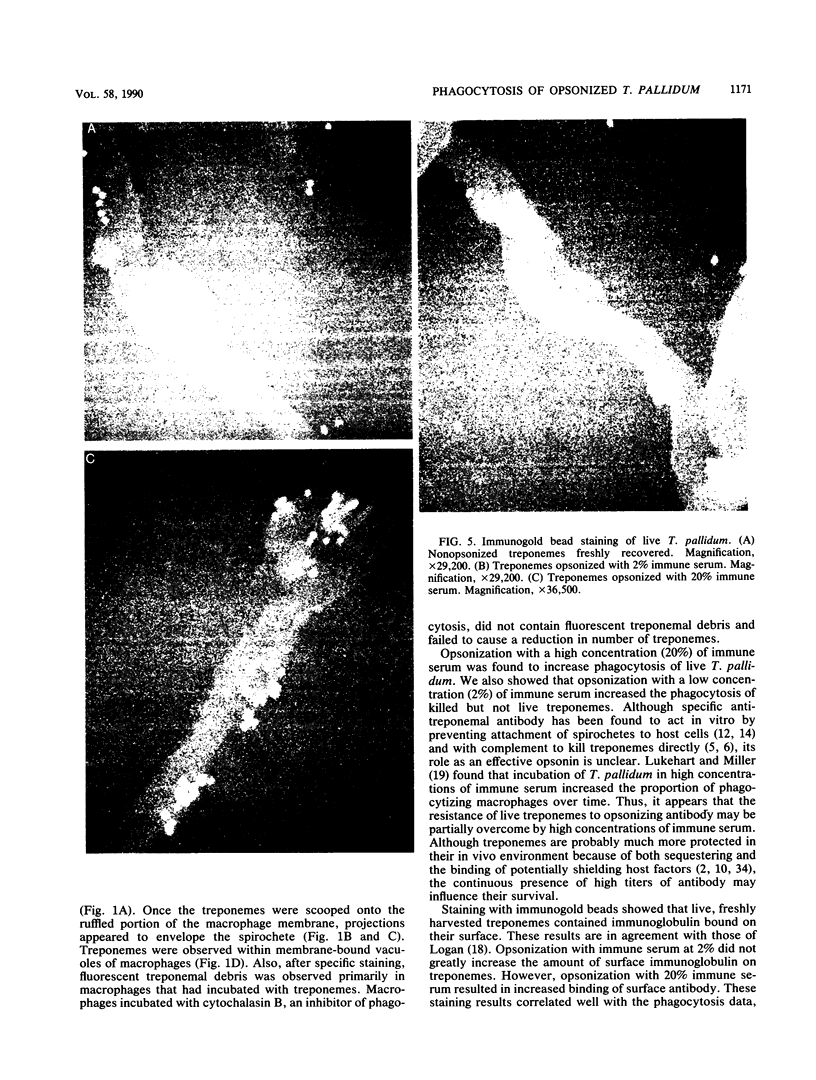
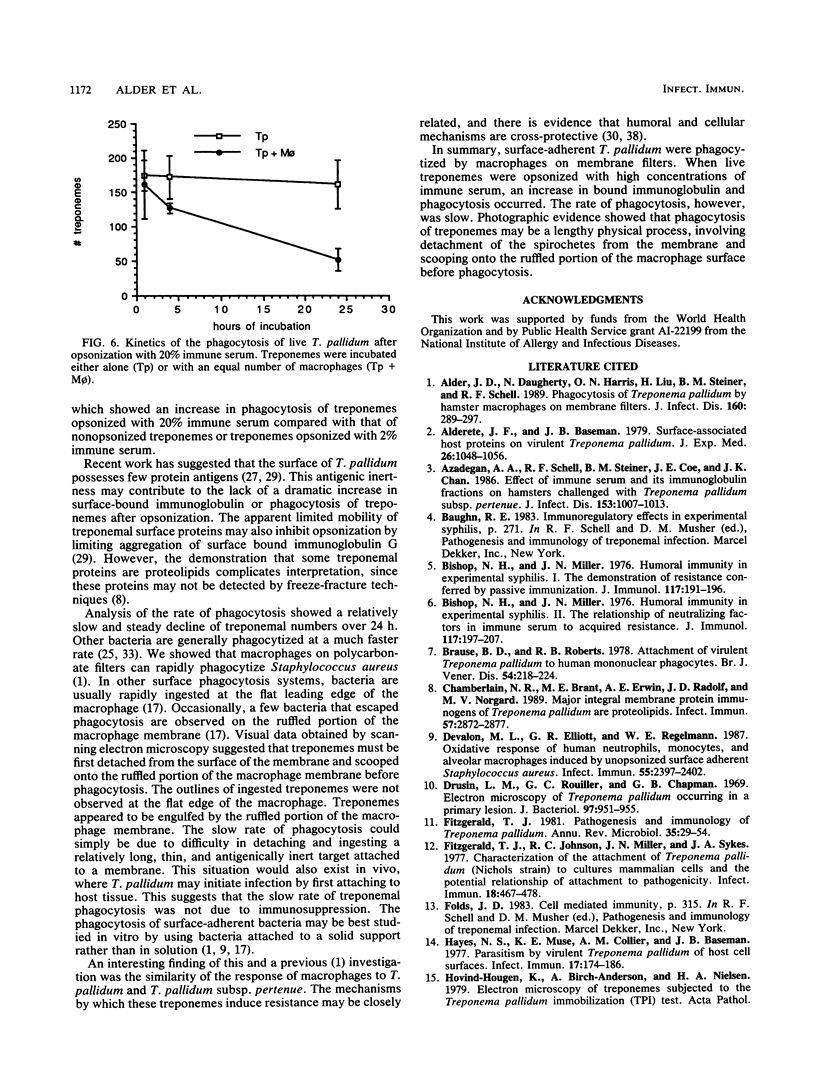
Macrophages were found to phagocytize Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum attached to polycarbonate filters. This environment simulated the in vivo interaction of surface-adherent treponemes with macrophages. The phagocytosis of T. pallidum subsp. pallidum was found to proceed slowly. Heat-killed T. pallidum subsp. pallidum were susceptible to opsonization with 2% immune serum, whereas live treponemes were resistant to this concentration of antibody. High concentrations of immune serum were found to increase phagocytosis of the spirochetes. Live T. pallidum subsp. pallidum had bound limited quantities of immunoglobulin G in vivo, and only opsonization with 20% immune serum resulted in a detectable increase in surface-bound immunoglobulin in vitro. Kinetic studies suggested a steady rate of phagocytosis that is considerably slower than with other bacteria. Scanning electron microscopy studies of the phagocytizing macrophages showed that the treponemes were detached from the membrane filters and scooped onto the ruffled portion of the macrophage surface. This lengthy physical process, along with the lack of a dramatic increase in ingestion after opsonization, may account for the slow rate of phagocytosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alder J. D., Daugherty N., Harris O. N., Liu H., Steiner B. M., Schell R. F. Phagocytosis of Treponema pallidum pertenue by hamster macrophages on membrane filters. J Infect Dis. 1989 Aug;160(2):289–297. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface-associated host proteins on virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1048–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1048-1056.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azadegan A. A., Schell R. F., Steiner B. M., Coe J. E., Chan J. K. Effect of immune serum and its immunoglobulin fractions on hamsters challenged with Treponema pallidum ssp. pertenue. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1007–1013. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop N. H., Miller J. N. Humoral immunity in experimental syphilis. I. The demonstration of resistance conferred by passive immunization. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):191–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop N. H., Miller J. N. Humoral immunity in experimental syphilis. II. The relationship of neutralizing factors in immune serum to acquired resistance. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):197–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brause B. D., Roberts R. B. Attachment of virulent Treponema pallidum to human mononuclear phagocytes. Br J Vener Dis. 1978 Aug;54(4):218–224. doi: 10.1136/sti.54.4.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., Brandt M. E., Erwin A. L., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Major integral membrane protein immunogens of Treponema pallidum are proteolipids. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2872–2877. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2872-2877.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusin L. M., Rouiller G. C., Chapman G. B. Electron microscopy of Treponema pallidum occurring in a human primary lesion. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):951–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.951-955.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Characterization of the attachment of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) to cultured mammalian cells and the potential relationship of attachment to pathogenicity. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):467–478. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.467-478.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J. Pathogenesis and immunology of Treponema pallidum. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:29–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes N. S., Muse K. E., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Parasitism by virulent Treponema pallidum of host cell surfaces. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):174–186. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.174-186.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovind-Hougen K., Birch-Andersen A., Nielsen H. A. Electron microscopy of treponemes subjected to the Treponema pallidum immobilization (TPI) test. II. Immunoelectron microscopy. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1979 Aug;87C(4):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovind-Hougen K., Nielsen H. A., Birch-Andersen A. Electron microscopy of treponemes subjected to the Treponema pallidum immobilization (TPI) test. I. Comparison of immunoimmobilized cells and control cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1979 Jun;87C(3):217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. A., Hoidal J. R., Garlich D. J., Clawson C. C., Quie P. G., Peterson P. K. Opsonin-independent phagocytosis of surface-adherent bacteria by human alveolar macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Dec;36(6):689–701. doi: 10.1002/jlb.36.6.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan L. C. Rabbit globulin and antiglobulin factors associated with Treponema pallidum growth in rabbits. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Dec;50(6):421–427. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.6.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Miller J. N. Demonstration of the in vitro phagocytosis of Treponema pallidum by rabbit peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2014–2024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. N. Immunity in experimental syphilis. VI. Successful vaccination of rabbits with Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain, attenuated by -irradiation. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1206–1215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Miller J. N. Cloning and expression of Treponema pallidum (Nichols) antigen genes in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):435–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.435-445.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell J. A., Pawley J. B. Preparation of experimental animal tissue for SEM. Scan Electron Microsc. 1980;(Pt 2):1–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovcinnikov N. M., Delektorskij V. V. Electron microscopy of phagocytosis in syphilis and yaws. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Aug;48(4):227–248. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.4.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Legionella pneumophila is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1377–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W. Avoidance of host defences by Treponema pallidum in situ and on extraction from infected rabbit testes. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Sep;126(1):69–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-126-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Chamberlain N. R., Clausell A., Norgard M. V. Identification and localization of integral membrane proteins of virulent Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum by phase partitioning with the nonionic detergent triton X-114. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):490–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.490-498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Fehniger T. E., Silverblatt F. J., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. The surface of virulent Treponema pallidum: resistance to antibody binding in the absence of complement and surface association of recombinant antigen 4D. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):579–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.579-585.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V., Schulz W. W. Outer membrane ultrastructure explains the limited antigenicity of virulent Treponema pallidum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2051–2055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell R. F., Azadegan A. A., Nitskansky S. G., LeFrock J. L. Acquired resistance of hamsters to challenge with homologous and heterologous virulent treponemes. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):617–621. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.617-621.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell R. F., Le Frock J. L., Babu J. P., Chan J. K. Use of CB hamsters in the study of Treponema pertenue. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Oct;55(5):316–319. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.5.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Baker-Zander S., Powell H. C. Experimental syphilitic orchitis in rabbits: ultrastructural appearance of Treponema pallidum during phagocytosis and dissolution by macrophages in vivo. Lab Invest. 1982 Apr;46(4):355–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz R. P., Naai D., Vogel C. W., Yeager H., Jr Differences in uptake of mycobacteria by human monocytes: a role for complement. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2223–2227. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2223-2227.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes J. A., Miller J. N., Kalan A. J. Treponema pallidum within cells of a primary chancre from a human female. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Feb;50(1):40–44. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER T. B., HOLLANDER D. H. Studies on the mechanism of action of cortisone in experimental syphilis. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1954 Sep;38(5):371–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor D. R., Azadegan A. A., Schell R. F., Lefrock J. L. Inhibition of macrophage C3b-mediated ingestion by syphilitic hamster T cell-enriched fractions. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2698–2705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomai M. A., Elmquist B. J., Warmka S. M., Fitzgerald T. J. Macrophage-mediated suppression of con A-induced IL-2 production in spleen cells from syphilitic rabbits. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):309–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]