Abstract
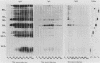
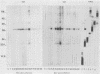
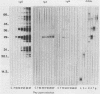
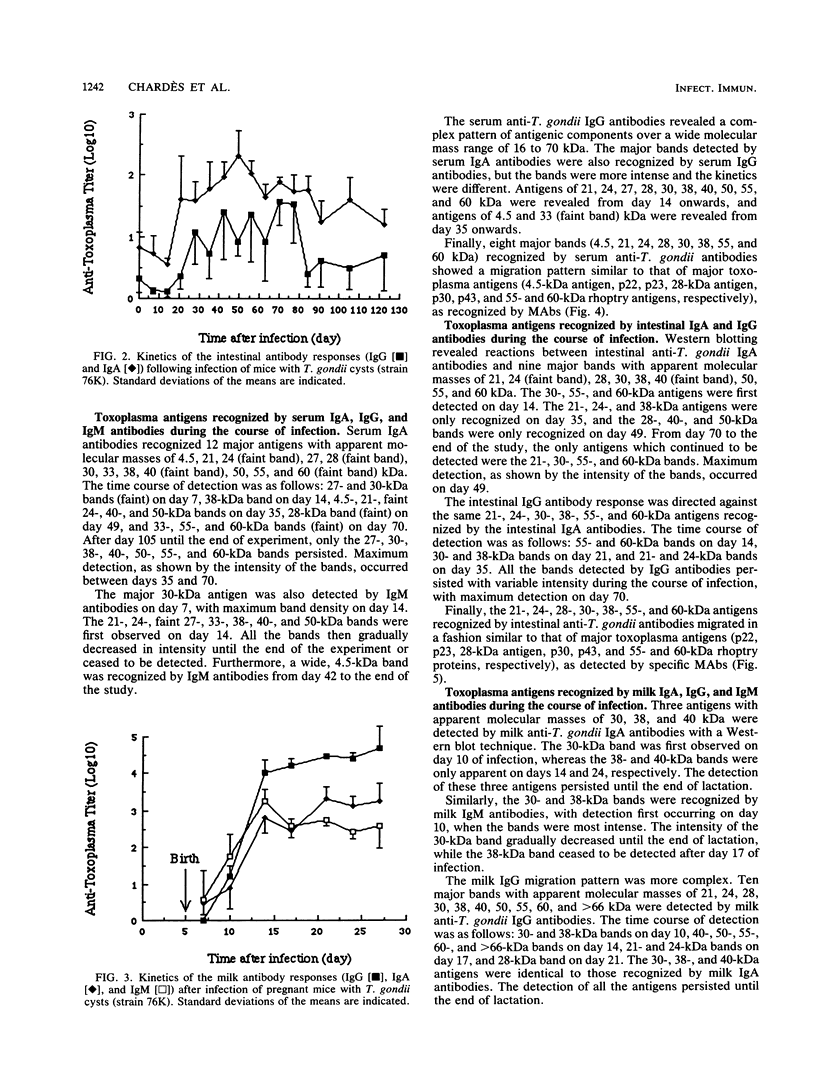
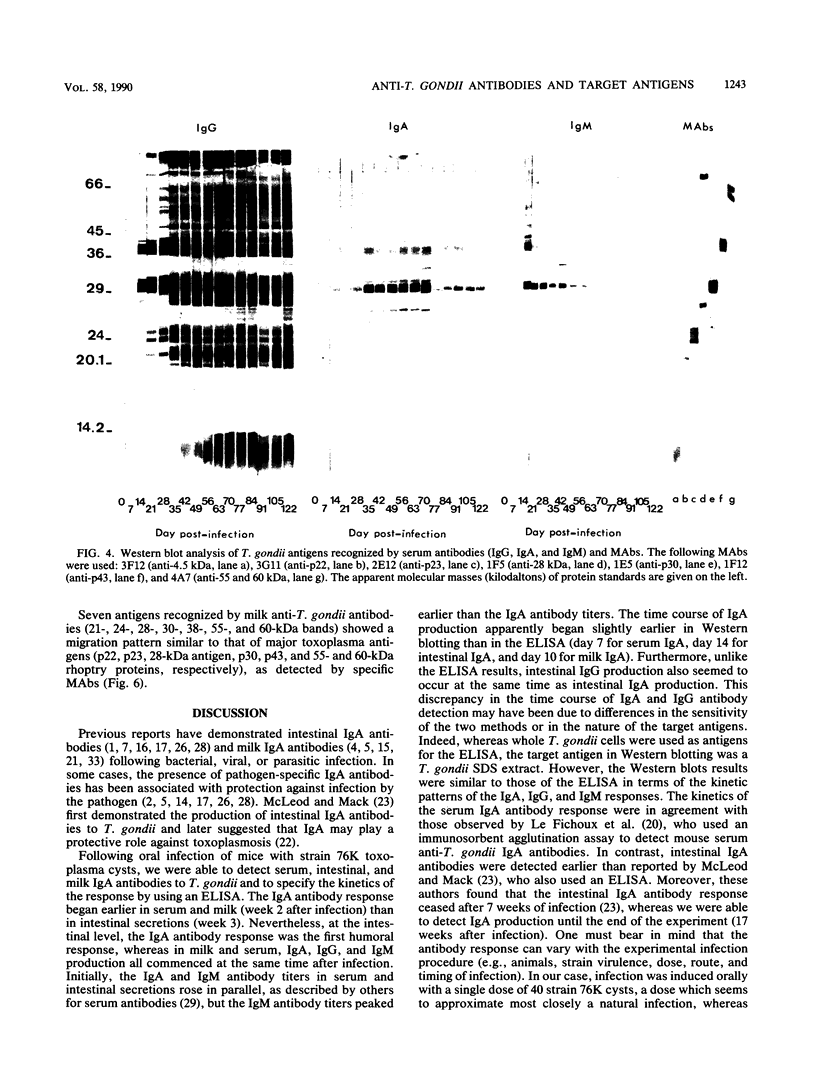
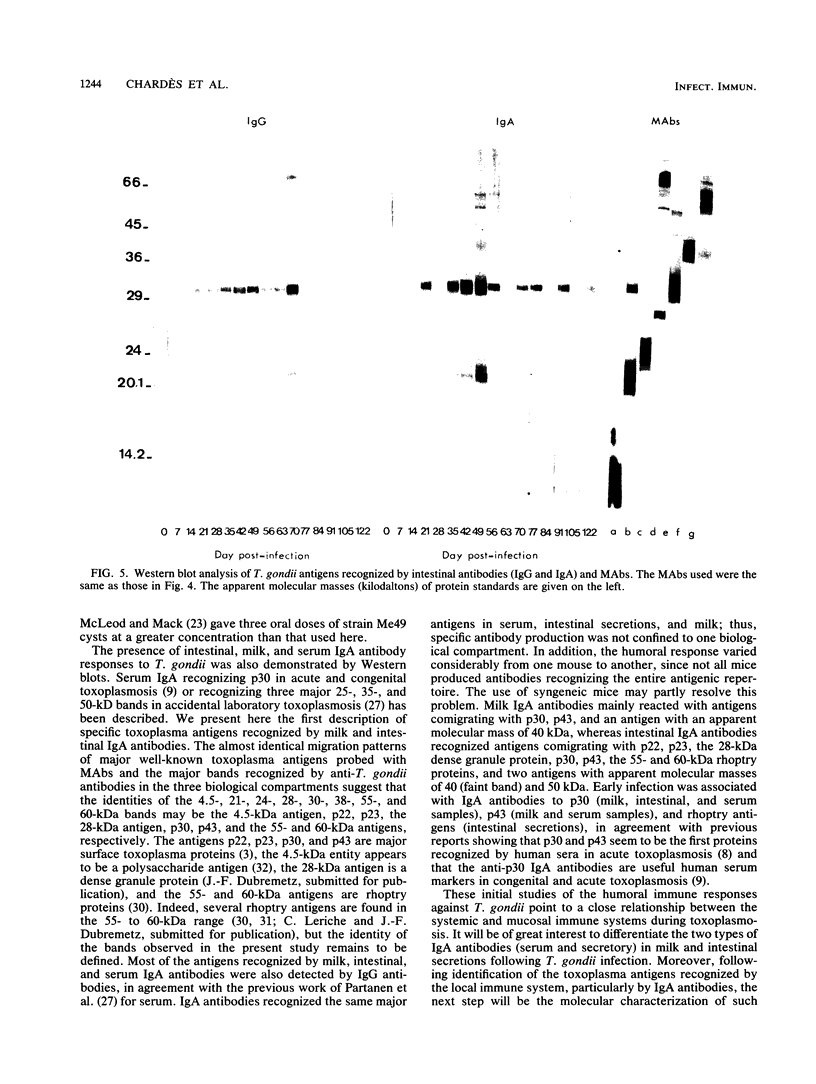
Toxoplasma gondii-specific antibody responses in serum, intestinal secretions, and milk were identified with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay following a single oral infection of mice with strain 76K cysts of T. gondii. Immunoglobulin A (IgA) production began during week 2 of infection in serum and milk and during week 3 of infection in intestinal secretions and persisted in all three throughout the experiment (17 weeks). IgG but not IgM antibodies were detected in intestinal secretions later in the infection. Serum and milk IgG and IgM production began at the same time after infection as did the IgA response. In Western blotting (immunoblotting), intestinal IgA antibodies were shown to react with antigens comigrating with the T. gondii proteins p22, p23, p30, and p43, the 28-kilodalton antigen, and the 55- and 60-kilodalton rhoptry proteins, as recognized by specific monoclonal antibodies. Milk IgA antibodies reacted with antigens comigrating with p30 and p43. Most of the antigens recognized by IgA antibodies were also detected by IgG antibodies. IgA antibodies from all three biological samples detected the same major T. gondii antigens; thus, there was apparently no specific antibody production unique to one locality.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bessen D., Fischetti V. A. Passive acquired mucosal immunity to group A streptococci by secretory immunoglobulin A. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1945–1950. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couvreur G., Sadak A., Fortier B., Dubremetz J. F. Surface antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology. 1988 Aug;97(Pt 1):1–10. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000066695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz J. R., Carlsson B. V., Hofvander Y., Holme D. T., Hanson L. A. Studies of human milk. II. Concentration of antibodies against Salmonella and Shigella in milk of women from different populations and the daily intake by their breast-fed infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1985 May;74(3):338–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1985.tb10980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz J. R., Gil L., Cano F., Caceres P., Pareja G. Breast milk anti-Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin IgA antibodies protect against toxin-induced infantile diarrhea. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1988 Sep;77(5):658–662. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1988.tb10726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. J., Porter P. A mechanism for secretory IgA-mediated inhibition of the cell penetration and intracellular development of Eimeria tenella. Immunology. 1979 Mar;36(3):471–477. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decoster A., Darcy F., Capron A. Recognition of Toxoplasma gondii excreted and secreted antigens by human sera from acquired and congenital toxoplasmosis: identification of markers of acute and chronic infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Sep;73(3):376–382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decoster A., Darcy F., Caron A., Capron A. IgA antibodies against P30 as markers of congenital and acute toxoplasmosis. Lancet. 1988 Nov 12;2(8620):1104–1107. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90523-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmonts G., Couvreur J., Alison F., Baudelot J., Gerbeaux J., Lelong M. Etude épidémiologique sur la toxoplasmose: de l'influence de la cuisson des viandes de boucherie sur la fréquence de l'infection humaine. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1965 Nov;10(9):952–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W., Lefkowitz J. A lavage technique allowing repeated measurement of IgA antibody in mouse intestinal secretions. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Feb 24;67(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Dubey J. P., Miller N. L. Toxoplasma gondii: fecal forms separated from eggs of the nematode Toxocara cati. Science. 1969 Apr 25;164(3878):432–433. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3878.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K. Pathophysiology of toxoplasmosis. Parasitol Today. 1988 Oct;4(10):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(88)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. I., Svennerholm A. M., Stoll B. J., Khan M. R., Hossain K. M., Huq M. I., Holmgren J. Protection against cholera in breast-fed children by antibodies in breast milk. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jun 9;308(23):1389–1392. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198306093082304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan B. S., Uni S., Aikawa M., Mahmoud A. A. Effector mechanism of host resistance in murine giardiasis: specific IgG and IgA cell-mediated toxicity. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1975–1981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., McDonald R. A., Scott P. J., Rosner A. M., Strubel E. Effect of antigen form on local immunoglobulin A memory response of intestinal secretions to Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):123–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.123-128.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laugier M., Quilici M. Intérêt expérimental d'une souche de Toxoplasme peu pathogène pour la souris. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp. 1970 Jul-Aug;45(4):389–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautenslager J. P. Toxoplasmosis as a significant disease in man and animals with special reference to preventive measures by the farm community. Can Vet J. 1987 May;28(5):261–264. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Fichoux Y., Marty P., Chan H. Les IgA sériques spécifiques dans le diagnostic de la toxoplasmose. Ann Pediatr (Paris) 1987 May;34(5):375–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascart-Lemone F., Carlsson B., Jalil F., Hahn-Zoric M., Duchateau J., Hanson L. A. Polymeric and monomeric IgA response in serum and milk after parenteral cholera and oral typhoid vaccination. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Oct;28(4):443–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod R., Frenkel J. K., Estes R. G., Mack D. G., Eisenhauer P. B., Gibori G. Subcutaneous and intestinal vaccination with tachyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii and acquisition of immunity to peroral and congenital toxoplasma challenge. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1632–1637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod R., Mack D. G. Secretory IgA specific for Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2640–2643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. Use of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for detection of monoclonal antibodies: experience with antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nashar T. O., Stokes C. R., Cripps P. J., Bourne F. J. The humoral immune response of mice to intra-mammary immunization with ovalbumin. Immunology. 1988 Oct;65(2):319–321. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen P., Turunen H. J., Paasivuo R. T., Leinikki P. O. Immunoblot analysis of Toxoplasma gondii antigens by human immunoglobulins G, M, and A antibodies at different stages of infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):133–135. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.133-135.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr, Sacci J. B., Jr, Craig J. P., Germanier R., Fürer E. Procholeragenoid: a safe and effective antigen for oral immunization against experimental cholera. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1112–1118. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1112-1118.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinon J. M., Thoannes H., Pouletty P. H., Poirriez J., Damiens J., Pelletier P. Detection of IgA specific for toxoplasmosis in serum and cerebrospinal fluid using a non-enzymatic IgA-capture assay. Diagn Immunol. 1986;4(5):223–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadak A., Taghy Z., Fortier B., Dubremetz J. F. Characterization of a family of rhoptry proteins of Toxoplasma gondii. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jun;29(2-3):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. D., Mullenax J., Araujo F. G., Erlich H. A., Remington J. S. Western Blot analysis of the antigens of Toxoplasma gondii recognized by human IgM and IgG antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):977–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Mata L., Urrutia J. J., Garciá B., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Secretory antibody directed against rotavirus in human milk--measurement by means of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Pediatr. 1978 Dec;93(6):916–921. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]