Abstract
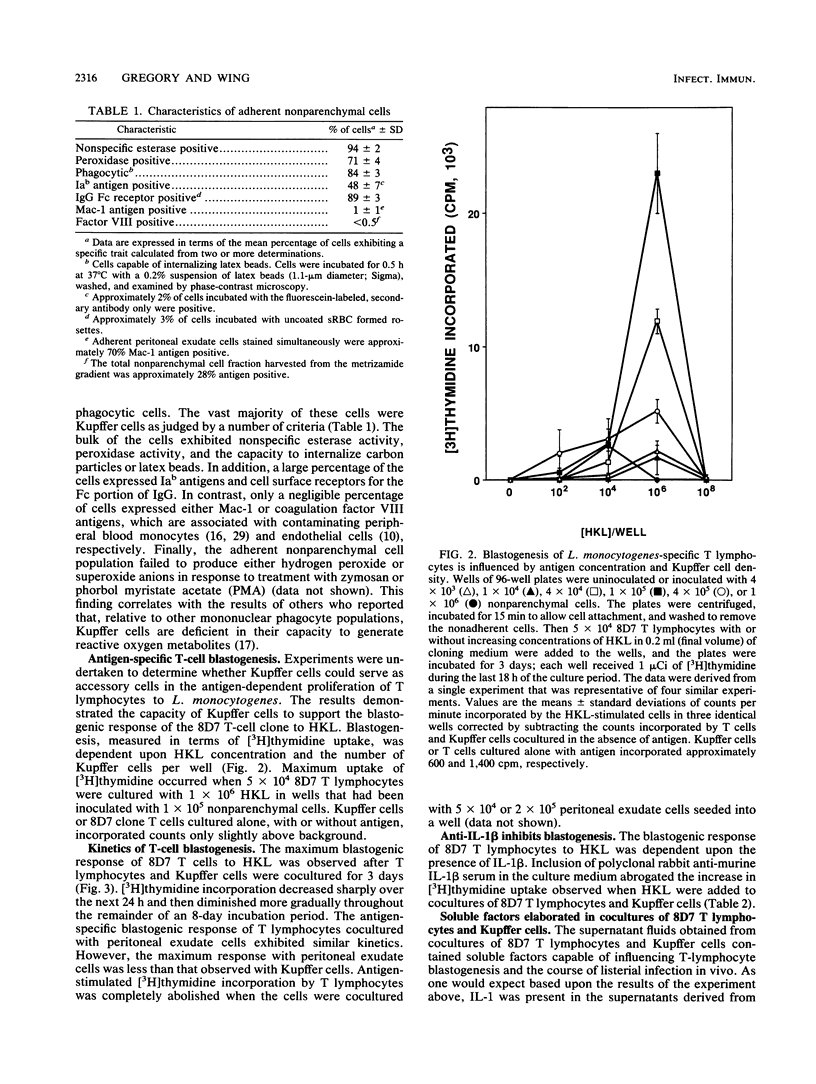
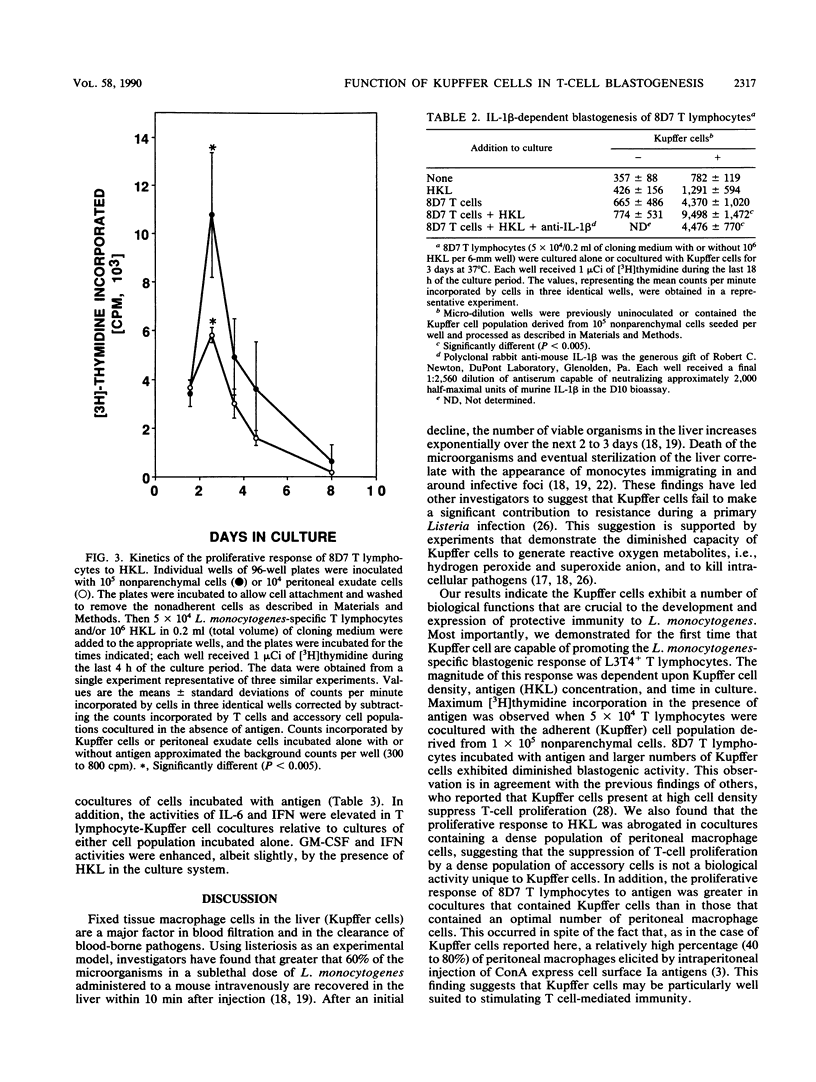
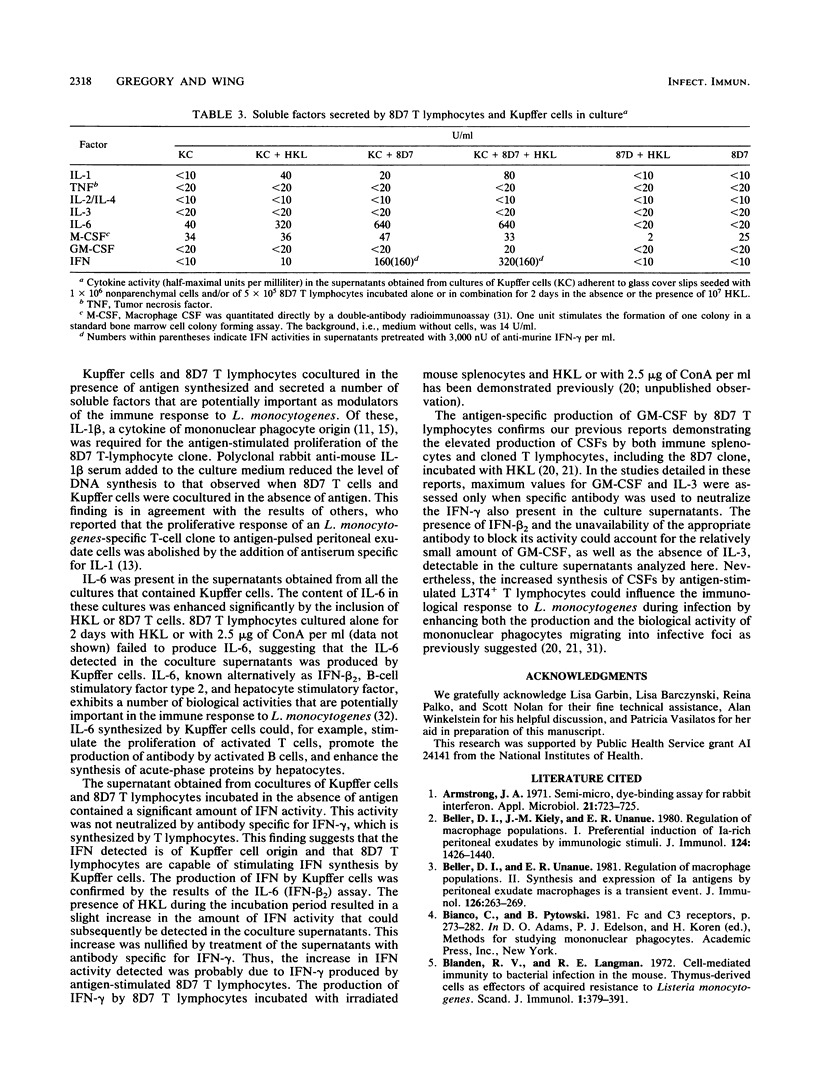
The function of Kupffer cells in the development of protective immunity to infection by Listeria monocytogenes is controversial. To determine their role in antilisterial host defenses, Kupffer cells were separated from other nonparenchymal cells of the liver by centrifugation on a metrizamide gradient followed by adherence to glass or plastic. The resultant highly enriched Kupffer cell population supported the antigen-specific blastogenic response [( 3H]thymidine incorporation) of cloned L3T4+ T lymphocytes to L. monocytogenes in vitro. Blastogenesis was dependent upon the duration of the incubation period, the concentration of the antigen, and the number of Kupffer cells in culture. Maximum reactivity was greater than that observed when the same T-cell population was incubated with adherent peritoneal exudate cells and antigen under optimal conditions. The addition of antibodies specific for murine interleukin-1 beta to cocultures of Kupffer cells and T lymphocytes eliminated the antigen-stimulated incorporation of [3H]thymidine, indicating a requirement for interleukin-1. Analysis of the culture supernatants demonstrated that, in addition to interleukin-1, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, interleukin-6, and gamma interferon were elaborated in cocultures containing cloned T lymphocytes, Kupffer cells, and antigen. These results suggest that Kupffer cells may serve a critical role in the development of immunity to infection by L. monocytogenes in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A. Semi-micro, dye-binding assay for rabbit interferon. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):723–725. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.723-725.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Kiely J. M., Unanue E. R. Regulation of macrophage populations. I. Preferential induction of Ia-rich peritoneal exudates by immunologic stimuli. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1426–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beller D. I., Unanue E. R. Regulation of macrophage populations. II. Synthesis and expression of Ia antigens by peritoneal exudate macrophages is a transient event. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):263–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Langman R. E. Cell-mediated immunity to bacterial infection in the mouse. Thymus-derived cells as effectors of acquired resistance to Listeria monocytogenes. Scand J Immunol. 1972;1(4):379–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1972.tb03304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boegel F., Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Evaluation of radioimmunoassay and in vitro colony assay techniques for determination of colony-stimulating factor and inhibitory activity in murine serum and tissue. Blood. 1981 Dec;58(6):1141–1147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle M., Boeije L., Aarden L. A. Functional discrimination between interleukin 6 and interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1535–1540. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide S., Steinman R. M. Induction of murine interleukin 1: stimuli and responsive primary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3802–3806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Beller D. I., Mizel S. B., Unanue E. R. Identification of a membrane-associated interleukin 1 in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane F. C., Unanue E. R. Requirement of thymus (T) lymphocytes for resistance to listeriosis. J Exp Med. 1972 May 1;135(5):1104–1112. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.5.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Kunkel S. L. The role of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 in the immunoinflammatory response. Pharm Res. 1988 Mar;5(3):129–139. doi: 10.1023/a:1015904721223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Crocker P., Gordon S. Macrophage plasma membrane and secretory properties in murine malaria. Effects of Plasmodium yoelii blood-stage infection on macrophages in liver, spleen, and blood. J Exp Med. 1986 Jan 1;163(1):54–74. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepay D. A., Nathan C. F., Steinman R. M., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Murine Kupffer cells. Mononuclear phagocytes deficient in the generation of reactive oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1079–1096. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepay D. A., Steinman R. M., Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Liver macrophages in murine listeriosis. Cell-mediated immunity is correlated with an influx of macrophages capable of generating reactive oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1503–1512. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee D. M., Wing E. J. Antigen-specific production of colony-stimulating factors by Listeria monocytogenes-immune, L3T4-positive cells. J Infect Dis. 1988 May;157(5):941–949. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.5.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee D. M., Wing E. J. Cloned L3T4+ T lymphocytes protect mice against Listeria monocytogenes by secreting IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3203–3207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee D. M., Wing E. J. Secretion of colony-stimulating factors by T cell clones. Role in adoptive protection against Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2336–2341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magilavy D. B., Rothstein J. L. Spontaneous production of tumor necrosis factor alpha by Kupffer cells of MRL/lpr mice. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):789–794. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Cellular mediators of anti-Listeria immunity as an enlarged population of short lived, replicating T cells. Kinetics of their production. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):342–355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The relative importance of blood monocytes and fixed macrophages to the expression of cell-mediated immunity to infection. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):521–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Klingenstein R. J., Richman J. A., Strober W., Berzofsky J. A. The murine Kupffer cell. I. Characterization of the cell serving accessory function in antigen-specific T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2602–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Gordon S., North R. J. Exacerbation of murine listeriosis by a monoclonal antibody specific for the type 3 complement receptor of myelomonocytic cells. Absence of monocytes at infective foci allows Listeria to multiply in nonphagocytic cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):27–37. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver C. T., Hawrylowicz C. M., Unanue E. R. T helper cell subsets require the expression of distinct costimulatory signals by antigen-presenting cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8181–8185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Changes in serum colony-stimulating factor and monocytic progenitor cells during Listeria monocytogenes infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):180–184. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.180-184.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Clark S. C. Multiple actions of interleukin 6 within a cytokine network. Immunol Today. 1988 May;9(5):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



