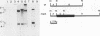Abstract
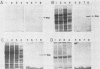
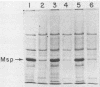
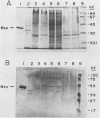
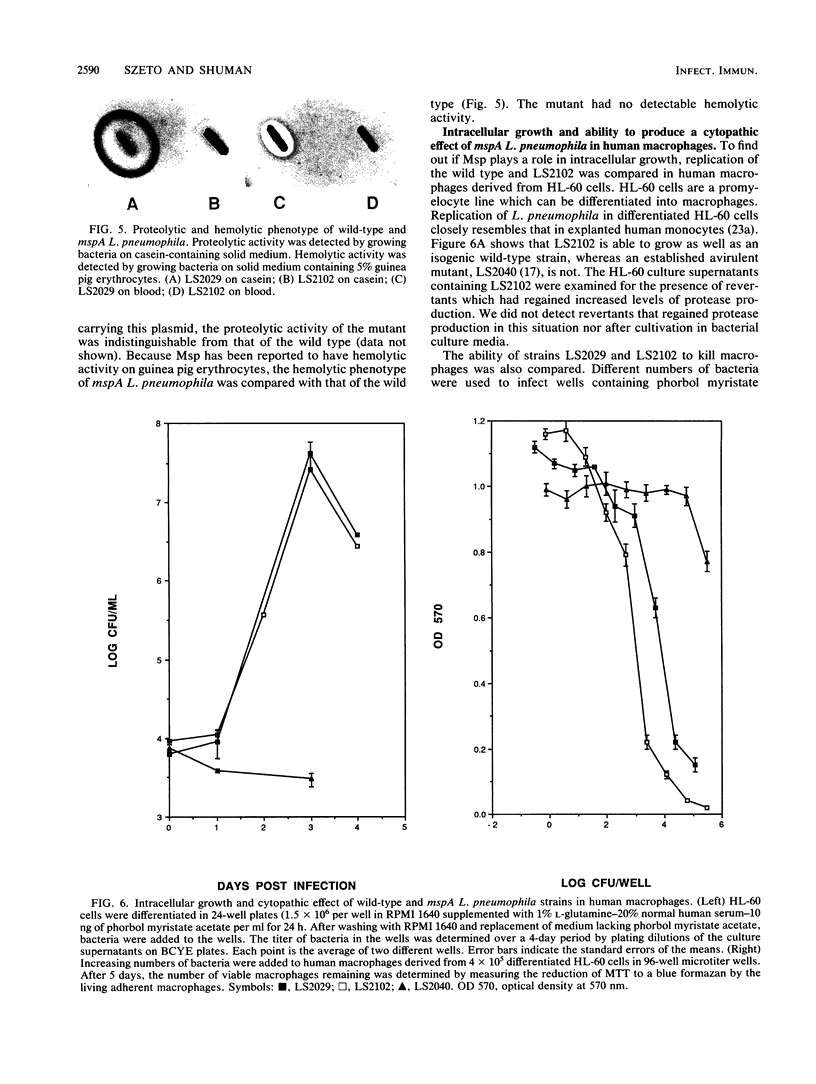
The Legionella pneumophila major secretory protein (Msp) is a Zn2+ metalloprotease whose function in pathogenesis is unknown. The structural gene for the Msp protease, mspA, was isolated from an L. pneumophila genomic library. In Escherichia coli which contain plasmids with the mspA gene, Msp protein and activity are found in the periplasmic space and the cytoplasm. Transposon mutagenesis with Tn9 of an mspA-containing plasmid in E. coli yielded mutants which no longer expressed protease activity and others with increased protease activity. These results suggested that mspA expression might be regulated. Msp was shown to be produced at a much higher level in L. pneumophila grown in rich compared to semidefined media. A Tn9 insertion which abolishes Msp expression was introduced into the L. pneumophila genome. This mspA::Tn9 L. pneumophila strain showed no detectable production of Msp by immunoblot analysis, and it had less than 0.1% of the protease activity found in the wild-type strain. This mutant was fully capable of growing within and killing human macrophages derived from the HL-60 cell line.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand C. M., Skinner A. R., Malic A., Kurtz J. B. Interaction of L. pneumophilia and a free living amoeba (Acanthamoeba palestinensis). J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Oct;91(2):167–178. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood L. L., Stone R. M., Iglewski B. H., Pennington J. E. Evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A and elastase as virulence factors in acute lung infection. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):198–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.198-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blander S. J., Horwitz M. A. Vaccination with the major secretory protein of Legionella pneumophila induces cell-mediated and protective immunity in a guinea pig model of Legionnaires' disease. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):691–705. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breiman R. F., Horwitz M. A. Guinea pigs sublethally infected with aerosolized Legionella pneumophila develop humoral and cell-mediated immune responses and are protected against lethal aerosol challenge. A model for studying host defense against lung infections caused by intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):799–811. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N. P., Eisenstein B. I., Mody C. H., Toews G. B., Engleberg N. C. A Legionella pneumophila gene encoding a species-specific surface protein potentiates initiation of intracellular infection. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1255–1262. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1255-1262.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P. L., Ryter A., Mounier J., Sansonetti P. J. Plasmid-mediated early killing of eucaryotic cells by Shigella flexneri as studied by infection of J774 macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):521–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.521-527.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlan J. W., Baskerville A., Ashworth L. A. Separation of Legionella pneumophila proteases and purification of a protease which produces lesions like those of Legionnaires' disease in guinea pig lung. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jun;132(6):1565–1574. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-6-1565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., McGee Z. A., Mulks M. H., Koomey J. M., Hindman T. L. Attachment to and invasion of human fallopian tube mucosa by an IgA1 protease-deficient mutant of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and its wild-type parent. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):737–744. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Iglewski B. H. Purification and characterization of an extracellular protease of Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):736–743. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.736-743.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. S., Shotts E. B., Jr, Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Martin W. T. Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as an intracellular parasite of the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena pyriformis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):467–471. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.467-471.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Bagdasarian M., Feiss D., Franklin F. C., Deshusses J. Stable cosmid vectors that enable the introduction of cloned fragments into a wide range of gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L., Kreger A. Microscopic characterization of rabbit lung damage produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteases. Infect Immun. 1979 Jan;23(1):150–159. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.1.150-159.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Characterization of avirulent mutant Legionella pneumophila that survive but do not multiply within human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1310–1328. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen M. G., Hoffman P. S. Characterization of a Legionella pneumophila extracellular protease exhibiting hemolytic and cytotoxic activities. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):732–738. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.732-738.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharazmi A., Döring G., Høiby N., Valerius N. H. Interaction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease and elastase with human polymorphonuclear leukocytes in vitro. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):161–165. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.161-165.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharazmi A., Eriksen H. O., Döring G., Goldstein W., Høiby N. Effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteases on human leukocyte phagocytosis and bactericidal activity. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1986 Oct;94(5):175–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1986.tb02108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopilato J., Bortner S., Beckwith J. Mutations in a new chromosomal gene of Escherichia coli K-12, pcnB, reduce plasmid copy number of pBR322 and its derivatives. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):285–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00430440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra A., Horwitz M. A., Shuman H. A. The HL-60 model for the interaction of human macrophages with the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2738–2744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra A., Shuman H. A. Isolation of a Legionella pneumophila restriction mutant with increased ability to act as a recipient in heterospecific matings. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):2238–2240. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.2238-2240.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. A family of serine esterases in lytic granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):679–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90544-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz C. S., Chen J. X., Shuman H. A. Isolation and characterization of auxotrophic mutants of Legionella pneumophila that fail to multiply in human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1449–1455. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1449-1455.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome A. L., Baker R. L., Miller R. D., Arnold R. R. Interactions between Naegleria fowleri and Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):449–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.449-452.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck R. A one-plate assay for macrophage bactericidal activity. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Sep 3;82(1):131–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90232-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. S., Barlam T. Isolation of a DNA fragment containing replication functions from IncP2 megaplasmid pMG2. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):792–794. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.792-794.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn F. D., Tompkins L. S. Analysis of a cloned sequence of Legionella pneumophila encoding a 38 kD metalloprotease possessing haemolytic and cytotoxic activities. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jun;3(6):797–805. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira S. K., Chou J., Richaud F. V., Casadaban M. J. New versatile plasmid vectors for expression of hybrid proteins coded by a cloned gene fused to lacZ gene sequences encoding an enzymatically active carboxy-terminal portion of beta-galactosidase. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J. Broad-host-range vectors for delivery of TnphoA: use in genetic analysis of secreted virulence determinants of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1870–1878. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1870-1878.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Pope D. H., Cherry W. B., Fliermans C. B. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in association with blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):456–459. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.456-459.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twining S. S. Fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled casein assay for proteolytic enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1984 Nov 15;143(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90553-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witholt B., Boekhout M., Brock M., Kingma J., Heerikhuizen H. V., Leij L. D. An efficient and reproducible procedure for the formation of spheroplasts from variously grown Escherichia coli. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jul;74(1):160–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Broadbent D. A. Biochemical characterization of extracellular proteases from Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):875–883. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.875-883.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]