Abstract
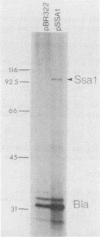
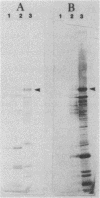
A serotype-specific antigen of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 encoded on the recombinant plasmid pSSA1 is characterized. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the insert DNA in pSSA1 identified the gene ssaI, which codes for a protein of approximately 100 kDa. In vivo labeling of pSSA1-encoded protein in Escherichia coli maxicells showed the expression of a 100-kDa protein from the insert DNA on the recombinant plasmid. Northern blot and primer extension analyses were used to identify the mRNA transcript in P. haemolytica A1 and the putative promoter of ssaI. The antigen (designated Ssa1) could be localized to the outer membrane of P. haemolytica A1 and E. coli clones carrying pSSA1. A rabbit serum against Ssa1 was produced by using whole cells of E. coli expressing Ssa1 on the surface as the immunogen, demonstrating that Ssa1 is immunogenic in rabbits. The results from colony immunoblot analysis with calf serum from animals that were resistant to P. haemolytica A1-induced pneumonia suggest indirectly that Ssa1 is also immunogenic in the animals.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdullah K. M., Lo R. Y., Mellors A. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the Pasteurella haemolytica A1 glycoprotease gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5597–5603. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5597-5603.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIBERSTEIN E. L., GILLS M., KNIGHT H. Serological types of Pasteurella hemolytica. Cornell Vet. 1960 Jul;50:283–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confer A. W., Panciera R. J., Corstvet R. E., Rummage J. A., Fulton R. W. Bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis: effect of culture age of Pasteurella haemolytica used as a live vaccine. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Dec;45(12):2543–2545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon J. A., Shewen P. E., Lo R. Y. Efficacy of recombinant leukotoxin in protection against pneumonic challenge with live Pasteurella haemolytica A1. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):587–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.587-591.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneer H. G., Potter A. A. Iron-repressible outer-membrane proteins of Pasteurella haemolytica. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Feb;135(Pt 2):435–443. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-2-435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H., Smith P. C. Prevalence of Pasteurella haemolytica in transported calves. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Jun;44(6):981–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H., Tabatabai L. B. Neuraminidase activity of Pasteurella haemolytica isolates. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1119–1122. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1119-1122.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H., Wessman G. E. Rapid plate agglutination procedure for serotyping Pasteurella haemolytica. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):142–145. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.142-145.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J., Laird S., Gilmour N. J. A new serotype (biotype T) of Pasteurella haemolytica. Res Vet Sci. 1982 Jan;32(1):127–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Rayos C., Lo R. Y., Shewen P. E., Beveridge T. J. Cloning of a serotype-specific antigen from Pasteurella haemolytica A1. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):505–510. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.505-510.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagblom P., Segal E., Billyard E., So M. Intragenic recombination leads to pilus antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):156–158. doi: 10.1038/315156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Carey A. M. Outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: heat- 2-mercaptoethanol-modifiable proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):902–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.902-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaehler K. L., Markam R. J., Muscoplat C. C., Johnson D. W. Evidence of cytocidal effects of Pasteurella haemolytica on bovine peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Oct;41(10):1690–1693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Cameron L. A. A simple immunological detection method for the direct screening of genes from clone banks. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;64(1):73–76. doi: 10.1139/o86-012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Shewen P. E., Strathdee C. A., Greer C. N. Cloning and expression of the leukotoxin gene of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):667–671. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.667-671.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo R. Y., Strathdee C. A., Shewen P. E. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin genes of Pasteurella haemolytica A1. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1987–1996. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1987-1996.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Meek A. H., Davis D. G., Thomson R. G., Johnson J. A., Lopez A., Stephens L., Curtis R. A., Prescott J. F., Rosendal S. Factors associated with mortality in feedlot cattle: the Bruce County Beef Cattle Project. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Jan;44(1):1–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. A., Simons K. R., Confer A. W., Panciera R. J., Clinkenbeard K. D. Pasteurella haemolytica antigens associated with resistance to pneumonic pasteurellosis. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):711–716. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.711-716.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otulakowski G. L., Shewen P. E., Udoh A. E., Mellors A., Wilkie B. N. Proteolysis of sialoglycoprotein by Pasteurella haemolytica cytotoxic culture supernatant. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):64–70. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.64-70.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Cytotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica acting on bovine leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.91-94.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Vaccination of calves with leukotoxic culture supernatant from Pasteurella haemolytica. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Jan;52(1):30–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squire P. G., Smiley D. W., Croskell R. B. Identification and extraction of Pasteurella haemolytica membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):667–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.667-673.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and characterization of genes encoding the secretion function of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin determinant. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):916–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.916-928.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Regulation of expression of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin determinant. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):5955–5962. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.5955-5962.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. J., McDougall J., Wittmann-Liebold B. Extended N-terminal sequencing of proteins of archaebacterial ribosomes blotted from two-dimensional gels onto glass fiber and poly(vinylidene difluoride) membrane. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6867–6876. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessman G. E., Hilker G. Characterization of Pasteurella hemolytica isolated from the respiratory tract of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1968 Jul;32(3):498–504. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D. A review of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, shipping fever pneumonia and viral-bacterial synergism in respiratory disease of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):225–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]