Abstract
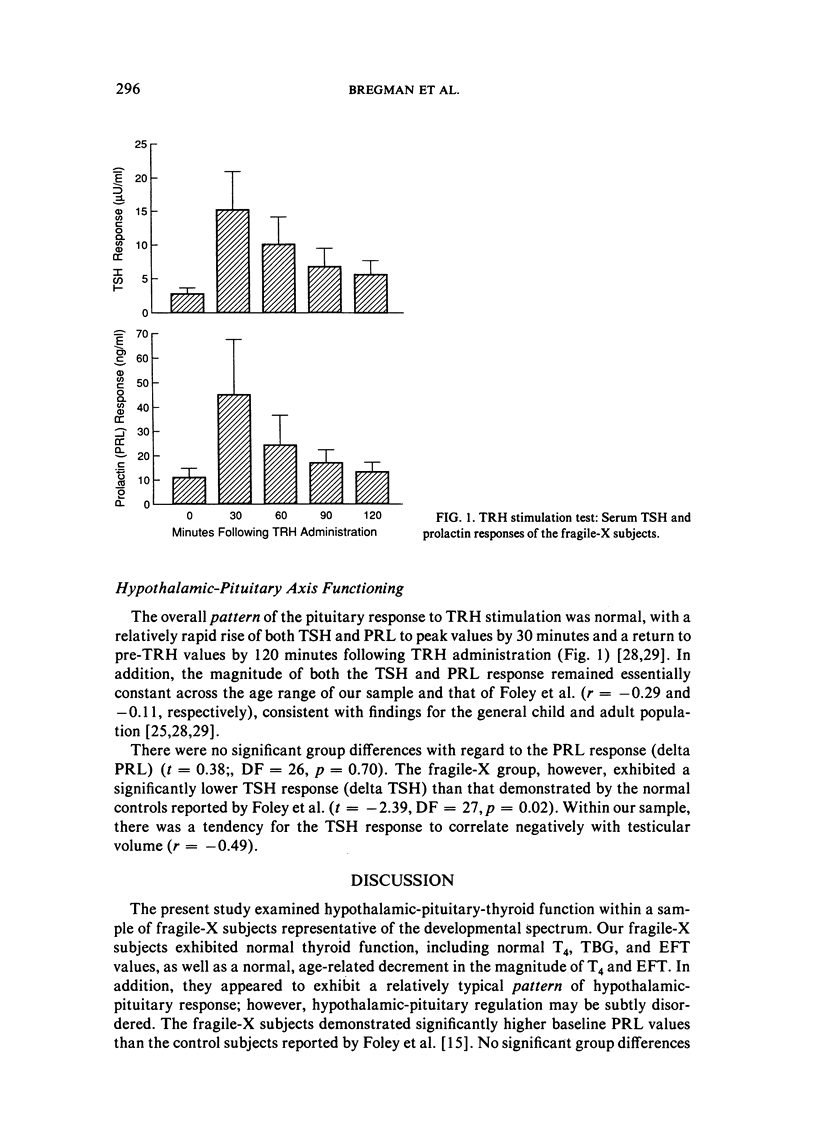
Twelve males with fragile-X syndrome between the ages of three and 28 years underwent assessment of thyroid function. All 12 subjects demonstrated normal baseline values for thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), thyroxine, thyroid binding globulin (TBG), and estimated free thyroxine (EFT). Relative to a control group reported in the literature, however, the fragile-X subjects exhibited a blunted TSH response to thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH). This finding suggests the presence of subtle dysfunction within the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. Elevated baseline prolactin levels were also observed among the fragile-X subjects. These results support previous reports of hypothalamic-pituitary abnormalities among fragile-X syndrome males.
Full text
PDF
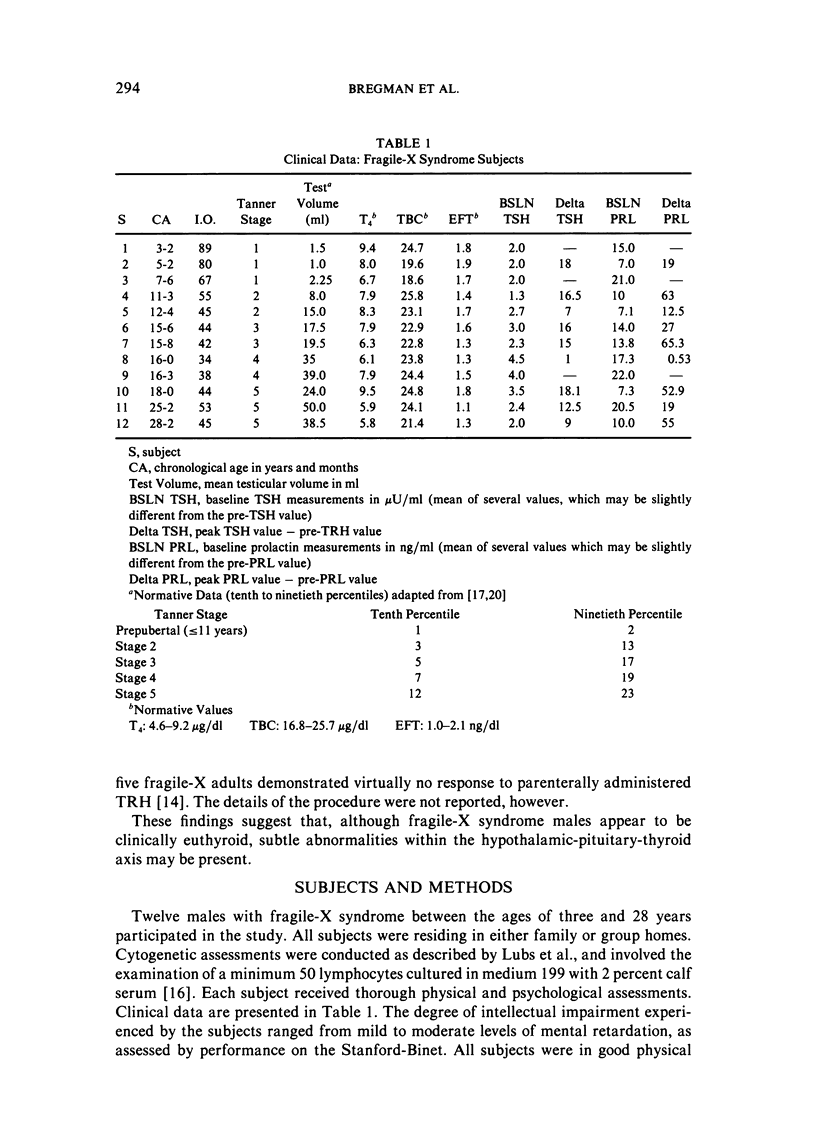




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. S., Bowers C. Y., Kastin A. J., Schalch D. S., Schally A. V., Snyder P. J., Utiger R. D., Wilber J. F., Wise A. J. Synthetic thyrotropin-releasing hormone. A potent stimulator of thyrotropin secretion in man. N Engl J Med. 1971 Dec 2;285(23):1279–1283. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197112022852302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnetz B. B., Lahnborg G., Eneroth P. Age-related differences in the pituitary prolactin response to thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Life Sci. 1986 Jul 14;39(2):135–139. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90447-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes N. D., Hayles A. B., Ryan R. J. Sexual maturation in juvenile hypothyroidism. Mayo Clin Proc. 1973 Dec;48(12):849–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregman J. D., Dykens E., Watson M., Ort S. I., Leckman J. F. Fragile-X syndrome: variability of phenotypic expression. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1987 Jul;26(4):463–471. doi: 10.1097/00004583-198707000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantú J. M., Scaglia H. E., Medina M., González-Diddi M., Morato T., Moreno M. E., Pérez-Palacios G. Inherited congenital normofunctional testicular hyperplasia and mental deficiency. Hum Genet. 1976 Jul 7;33(1):23–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00447283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. A radioimmunoassay for measurement of 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine (reverse T3). J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):583–592. doi: 10.1172/JCI107795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKS R. C., STEMPFEL R. S., Jr JUVENILE HYPOTHYROIDISM AND PRECOCIOUS TESTICULAR MATURATION. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1963 Aug;23:805–810. doi: 10.1210/jcem-23-8-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A. Advances in the laboratory diagnosis of thyroid disease. I. J Pediatr. 1973 Jan;82(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley T. P., Jr, Jacobs L. S., Hoffman W., Daughaday W. H., Blizzard R. M. Human prolactin and thyrotropin concentrations in the serums of normal and hypopituitary children before and after the administration of synthetic thyrotropin-releasing hormone. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2143–2150. doi: 10.1172/JCI107021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayek A., Maloof F., Crawford J. D. Thyrotropin behavior in thyroid disorders of childhood. Pediatr Res. 1973 Jan;7(1):28–38. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197301000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood N. J., Lockhart L. H., Bryan G. T. Acquired hypothyroidism with muscular hypertrophy and precocious testicular enlargement. J Pediatr. 1974 Aug;85(2):233–236. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z., Karp M., Dolberg L. Juvenile hypothyroidism with testicular enlargement. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1970 May;59(3):317–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1970.tb09010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubs H. A., Watson M., Breg R., Lujan E. Restudy of the original marker X family. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):133–144. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott A., Walters R., Howell R. T., Gardner A. Fragile X chromosome: clinical and cytogenetic studies on cases from seven families. J Med Genet. 1983 Jun;20(3):169–178. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.3.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meryash D. L., Cronk C. E., Sachs B., Gerald P. S. An anthropometric study of males with the fragile-X syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):159–174. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K. B., Tommerup N., Dyggve H. V., Schou C. Macroorchidism and fragile X in mentally retarded males. Clinical, cytogenetic, and some hormonal investigations in mentally retarded males, including two with the fragile site at Xq28, fra(X)(q28). Hum Genet. 1982;61(2):113–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00274199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare J. P., O'Brien I. A., Arendt J., Astley P., Ratcliffe W., Andrews H., Walters R., Corrall R. J. Does melatonin deficiency cause the enlarged genitalia of the fragile-X syndrome? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1986 Mar;24(3):327–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1986.tb03274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell W. D., Wilber J. F., Paul W. E. Radioimmunoassay of thyrotropin in human serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Sep;25(9):1179–1188. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-9-1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prader A. Testicular size: assessment and clinical importance. Triangle. 1966;7(6):240–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pueschel S. M., Hays R. M., Mendoza T. Familial X-linked mental retardation syndrome associated with minor congenital anomalies, macro-orchidism, and fragile X-chromosome. Am J Ment Defic. 1983 Jan;87(4):372–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renier W. O., Smeets D. F., Scheres J. M., Hustinx T. W., Hulsmans C. F., Ophey C. P., Bomers A. J., Gabreëls F. J. The Martin-Bell syndrome: a psychological, logopaedic and cytogenetic study of two affected brothers. J Ment Defic Res. 1983 Mar;27(Pt 1):51–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1983.tb00163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvalcaba R. H., Myhre S. A., Roosen-Runge E. C., Beckwith J. B. X-linked mental deficiency megalotestes syndrome. JAMA. 1977 Oct 10;238(15):1646–1650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligson H., Seligson D. Measurement of serum thyroxine-binding capacity. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Oct 2;89(1):47–58. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligson H., Seligson D. Measurement of thyroxine by competitive protein binding. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Apr;38(1):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha Y. N., Selby F. W., Lewis U. J., VanderLaan W. P. A homologous radioimmunoassay for human prolactin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Mar;36(3):509–516. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-3-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachmann M., Prader A., Kind H. P., Häfliger H., Budliger H. Testicular volume during adolescence. Cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1974 Apr;29(1):61–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


