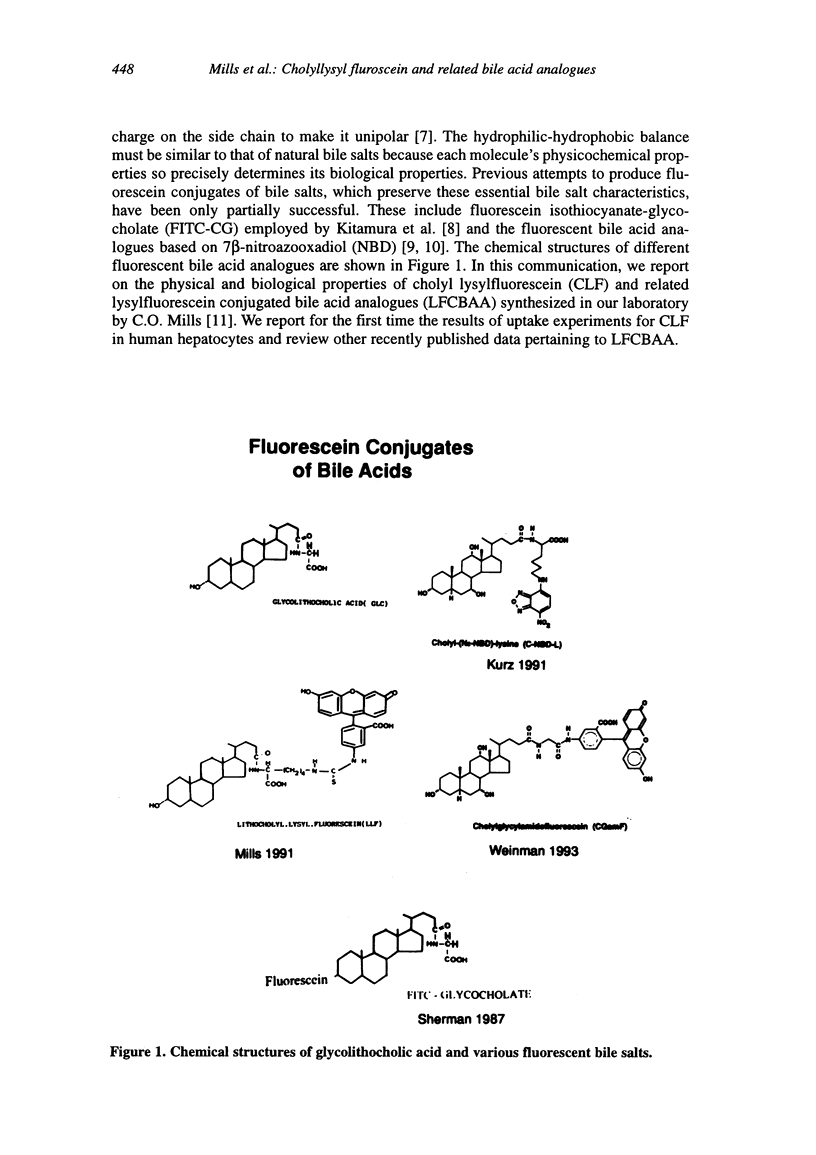
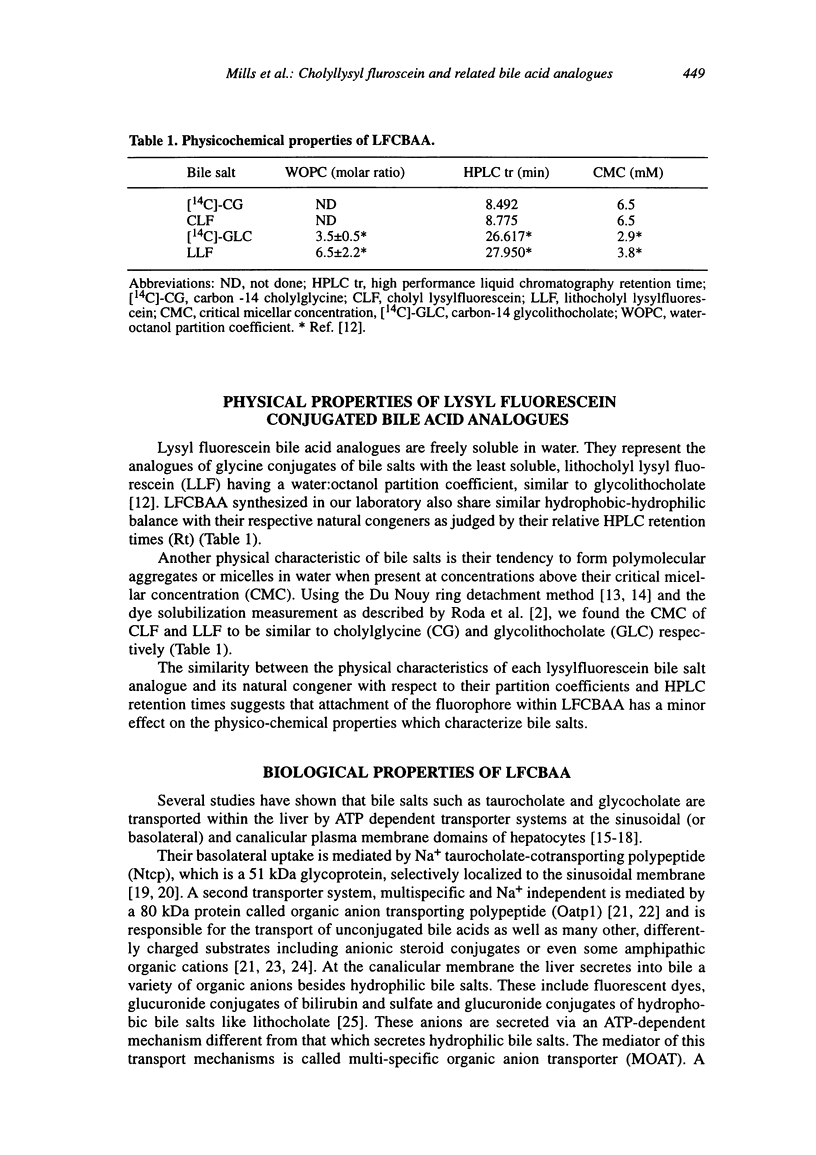
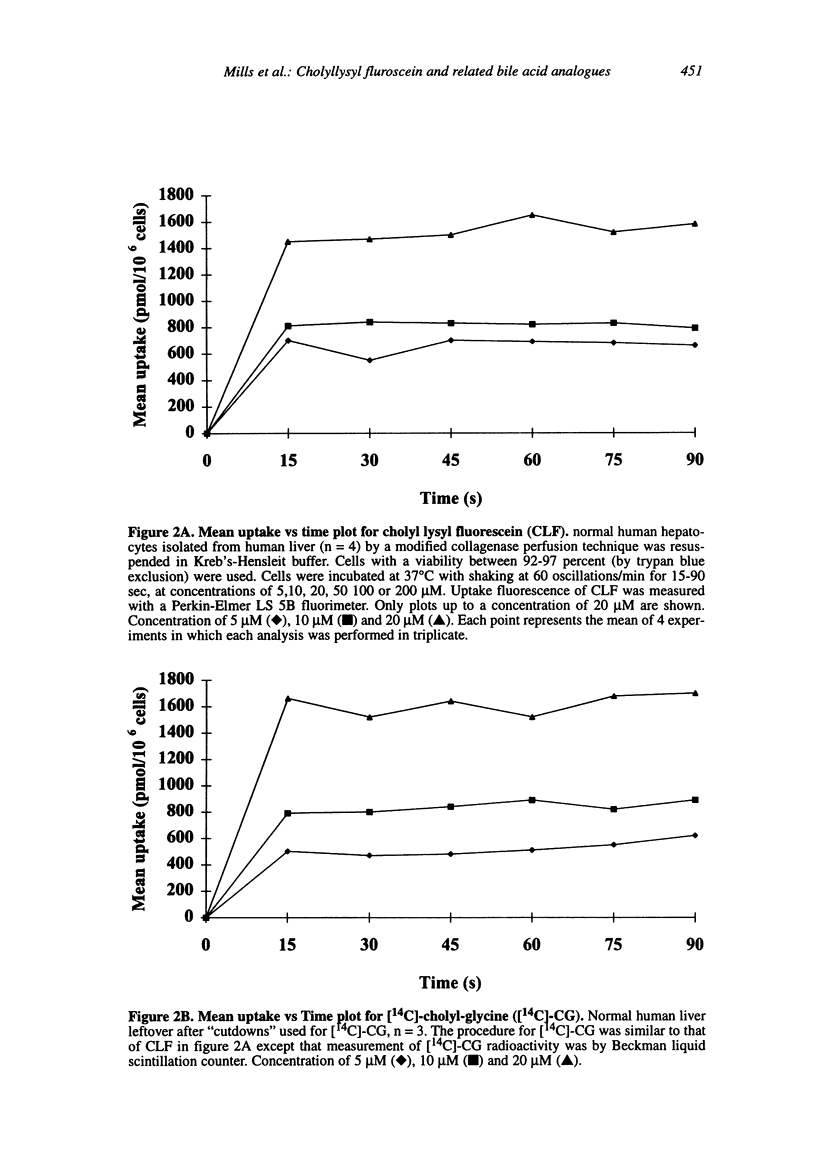
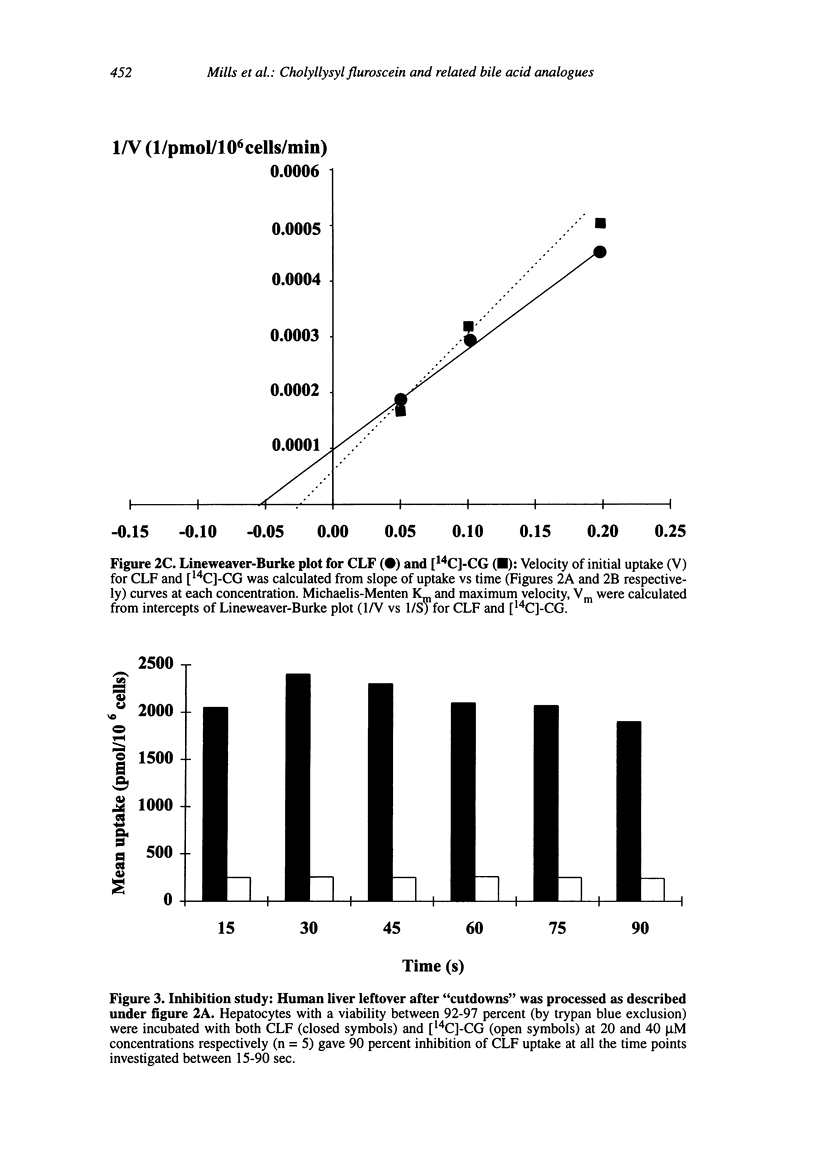
Abstract
There have been attempts to couple bile acids to fluorescein to permit their visualization during studies of physiology and pathophysiology. Although conjugation has been achieved by many, the product differed in many respects from the parent bile acid congener. We describe lysylfluorescein conjugated bile acid analogues (LFCBAA) synthesized in our laboratory as model divalent "unipolar" molecules. We have determined LFCBAA properties including their water:octanol partition coefficient, HPLC retention time and critical micellar concentration and compared them with their parent bile acid congeners. Cholyl lysylfluorescein (CLF) and lithocholyl lysylfluoroscein (LLF) have properties similar to cholylglycine (CG) and glycolithocholate (GLC), respectively. In human and rat hepatocytes uptake of CLF follows Michaelis-Menten kinetics with K(m) and Vmax similar to CG. Biliary excretion rates of CLF and LLF closely resemble those of CG and GLC in both normal and mutant TR- rats which lack the multiorganic anion transporter (MOAT), strongly supporting the notion that CLF and LLF are substrates for the canalicular bile salt transporter (cBST). The close similarity of hepatocyte uptake and biliary secretion of these LFCBAA and their parent bile acid congeners makes them potentially useful probes for the intracellular visualization of bile salt movement and deposition in various models of bile formation and secretion.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi Y., Kobayashi H., Kurumi Y., Shouji M., Kitano M., Yamamoto T. ATP-dependent taurocholate transport by rat liver canalicular membrane vesicles. Hepatology. 1991 Oct;14(4 Pt 1):655–659. doi: 10.1016/0270-9139(91)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ananthanarayanan M., Ng O. C., Boyer J. L., Suchy F. J. Characterization of cloned rat liver Na(+)-bile acid cotransporter using peptide and fusion protein antibodies. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 1):G637–G643. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.267.4.G637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter D. J., Rahman K., Bushell A. J., Mills C. O., Elias E., Billington D. Biliary lipid output by isolated perfused rat livers in response to cholyl-lysylfluorescein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Jun 6;1256(3):374–380. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(95)00050-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boelsterli U. A., Zimmerli B., Meier P. J. Identification and characterization of a basolateral dicarboxylate/cholate antiport system in rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1995 May;268(5 Pt 1):G797–G805. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.268.5.G797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossuyt X., Müller M., Hagenbuch B., Meier P. J. Polyspecific drug and steroid clearance by an organic anion transporter of mammalian liver. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996 Mar;276(3):891–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Graf J., Meier P. J. Hepatic transport systems regulating pHi, cell volume, and bile secretion. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:415–438. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broelsch C. E., Emond J. C., Whitington P. F., Thistlethwaite J. R., Baker A. L., Lichtor J. L. Application of reduced-size liver transplants as split grafts, auxiliary orthotopic grafts, and living related segmental transplants. Ann Surg. 1990 Sep;212(3):368–377. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199009000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R., Wilton J. C., Stone V., Chipman J. K. Hepatobiliary function and toxicity in vitro using isolated hepatocyte couplets. Gen Pharmacol. 1995 Nov;26(7):1445–1453. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(95)00071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowen A. E., Korman M. G., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Plasma disappearance of radioactivity after intravenous injection of labeled bile acids in man. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jun;68(6):1567–1573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Seaidy A. Z., Mills C. O., Elias E., Crawford J. M. Lack of evidence for vesicle trafficking of fluorescent bile salts in rat hepatocyte couplets. Am J Physiol. 1997 Feb;272(2 Pt 1):G298–G309. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1997.272.2.G298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelking L. R., Barnes S., Dasher C. A., Naftel D. C., Hirschowitz B. I. Radiolabelled bile acid clearance in control subjects and patients with liver disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Dec;57(6):499–508. doi: 10.1042/cs0570499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbuch B., Stieger B., Foguet M., Lübbert H., Meier P. J. Functional expression cloning and characterization of the hepatocyte Na+/bile acid cotransport system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10629–10633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison W. G., Heasley V. L., Shellhamer D. F. Specificity of the hepatocyte Na(+)-dependent taurocholate transporter: influence of side chain length and charge. Hepatology. 1991 Jan;13(1):68–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman D. M. Quantitative estimation of the hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance of mixed bile salt solutions. J Lipid Res. 1989 May;30(5):719–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Small D. M. Detergent properties of bile salts: correlation with physiological function. Annu Rev Med. 1967;18:333–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.18.020167.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak W., Waldram R., Murray-Lyon I. M., Schuster E., Williams R. Kinetics of [14C]cholic acid in fulminant hepatic failure: a prognostic test. Gastroenterology. 1976 Nov;71(5):809–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin E., Hagenbuch B., Stieger B., Wolkoff A. W., Meier P. J. Expression cloning of a rat liver Na(+)-independent organic anion transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):133–137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Serial quantitative image analysis and confocal microscopy of hepatic uptake, intracellular distribution and biliary secretion of a fluorescent bile acid analog in rat hepatocyte doublets. Hepatology. 1990 Dec;12(6):1358–1364. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Jansen P., Hardenbrook C., Kamimoto Y., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Defective ATP-dependent bile canalicular transport of organic anions in mutant (TR-) rats with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3557–3561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers F., Enserink M., Havinga R., van der Steen A. B., Hardonk M. J., Fevery J., Vonk R. J. Separate transport systems for biliary secretion of sulfated and unsulfated bile acids in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1593–1599. doi: 10.1172/JCI113493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullak-Ublick G. A., Hagenbuch B., Stieger B., Wolkoff A. W., Meier P. J. Functional characterization of the basolateral rat liver organic anion transporting polypeptide. Hepatology. 1994 Aug;20(2):411–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maglova L. M., Jackson A. M., Meng X. J., Carruth M. W., Schteingart C. D., Ton-Nu H. T., Hofmann A. F., Weinman S. A. Transport characteristics of three fluorescent conjugated bile acid analogs in isolated rat hepatocytes and couplets. Hepatology. 1995 Aug;22(2):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milkiewicz P., Baiocchi L., Mills C. O., Ahmed M., Khalaf H., Keogh A., Baker J., Elias E. Plasma clearance of cholyl-lysyl-fluorescein: a pilot study in humans. J Hepatol. 1997 Dec;27(6):1106–1109. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills C. O., Milkiewicz P., Molloy D. P., Baxter D. J., Elias E. Synthesis, physical and biological properties of lithocholyl-lysyl-fluorescein: a fluorescent monohydroxy bile salt analogue with cholestatic properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997 Oct 20;1336(3):485–496. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(97)00063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills C. O., Rahman K., Coleman R., Elias E. Cholyl-lysylfluorescein: synthesis, biliary excretion in vivo and during single-pass perfusion of isolated perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 6;1115(2):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90024-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Ishikawa T., Berger U., Klünemann C., Lucka L., Schreyer A., Kannicht C., Reutter W., Kurz G., Keppler D. ATP-dependent transport of taurocholate across the hepatocyte canalicular membrane mediated by a 110-kDa glycoprotein binding ATP and bile salt. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18920–18926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida T., Hardenbrook C., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. ATP-dependent organic anion transport system in normal and TR- rat liver canalicular membranes. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):G629–G635. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.4.G629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg K., Johansson A., Camner P., Johard U., Eklund A. Phagolysosomal pH in alveolar macrophages from smokers and non-smokers. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1994 Mar;13(3):175–179. doi: 10.1177/096032719401300307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oddi A., Mills C. O., Custureri F., Di Nicola V., Elias E., Di Matteo G. Intraoperative biliary tree imaging with cholyl-lysyl-fluorescein: an experimental study in the rabbit. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1996 Jun;6(3):198–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oude Elferink R. P., Ottenhoff R., Radominska A., Hofmann A. F., Kuipers F., Jansen P. L. Inhibition of glutathione-conjugate secretion from isolated hepatocytes by dipolar bile acids and other organic anions. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):281–286. doi: 10.1042/bj2740281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulusma C. C., Bosma P. J., Zaman G. J., Bakker C. T., Otter M., Scheffer G. L., Scheper R. J., Borst P., Oude Elferink R. P. Congenital jaundice in rats with a mutation in a multidrug resistance-associated protein gene. Science. 1996 Feb 23;271(5252):1126–1128. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5252.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roda A., Hofmann A. F., Mysels K. J. The influence of bile salt structure on self-association in aqueous solutions. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6362–6370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roda A., Minutello A., Angellotti M. A., Fini A. Bile acid structure-activity relationship: evaluation of bile acid lipophilicity using 1-octanol/water partition coefficient and reverse phase HPLC. J Lipid Res. 1990 Aug;31(8):1433–1443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Román I. D., Coleman R. Disruption of canalicular function in isolated rat hepatocyte couplets caused by cyclosporin A. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Dec 16;48(12):2181–2188. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90352-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi X., Bai S., Ford A. C., Burk R. D., Jacquemin E., Hagenbuch B., Meier P. J., Wolkoff A. W. Stable inducible expression of a functional rat liver organic anion transport protein in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 27;270(43):25591–25595. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.43.25591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger B., O'Neill B., Meier P. J. ATP-dependent bile-salt transport in canalicular rat liver plasma-membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1992 May 15;284(Pt 1):67–74. doi: 10.1042/bj2840067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone V., Johnson G. D., Wilton J. C., Coleman R., Chipman J. K. Effect of oxidative stress and disruption of Ca2+ homeostasis on hepatocyte canalicular function in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Feb 11;47(4):625–632. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thjodleifsson B., Barnes S., Chitranukroh A., Billing B. H., Sherlock S. Assessment of the plasma disappearance of cholyl'l14C-glycine as a test of hepatocellular disease. Gut. 1977 Sep;18(9):697–702. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.9.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman S. A., Graf J., Veith C., Boyer J. L. Electroneutral uptake and electrogenic secretion of a fluorescent bile salt by rat hepatocyte couplets. Am J Physiol. 1993 Feb;264(2 Pt 1):G220–G230. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.264.2.G220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton J. C., Chipman J. K., Lawson C. J., Strain A. J., Coleman R. Periportal- and perivenous-enriched hepatocyte couplets: differences in canalicular activity and in response to oxidative stress. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 15;292(Pt 3):773–779. doi: 10.1042/bj2920773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton J. C., Coleman R., Lankester D. J., Chipman J. K. Stability and optimization of canalicular function in hepatocyte couplets. Cell Biochem Funct. 1993 Sep;11(3):179–185. doi: 10.1002/cbf.290110305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton J. C., Matthews G. M., Burgoyne R. D., Mills C. O., Chipman J. K., Coleman R. Fluorescent choleretic and cholestatic bile salts take different paths across the hepatocyte: transcytosis of glycolithocholate leads to an extensive redistribution of annexin II. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):401–410. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters H., Kuipers F., Slooff M. J., Vonk R. J. Adenosine triphosphate-dependent taurocholate transport in human liver plasma membranes. J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2321–2326. doi: 10.1172/JCI116120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimniak P., Awasthi Y. C. ATP-dependent transport systems for organic anions. Hepatology. 1993 Feb;17(2):330–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimniak P. Dubin-Johnson and Rotor syndromes: molecular basis and pathogenesis. Semin Liver Dis. 1993 Aug;13(3):248–260. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1007353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


