Abstract
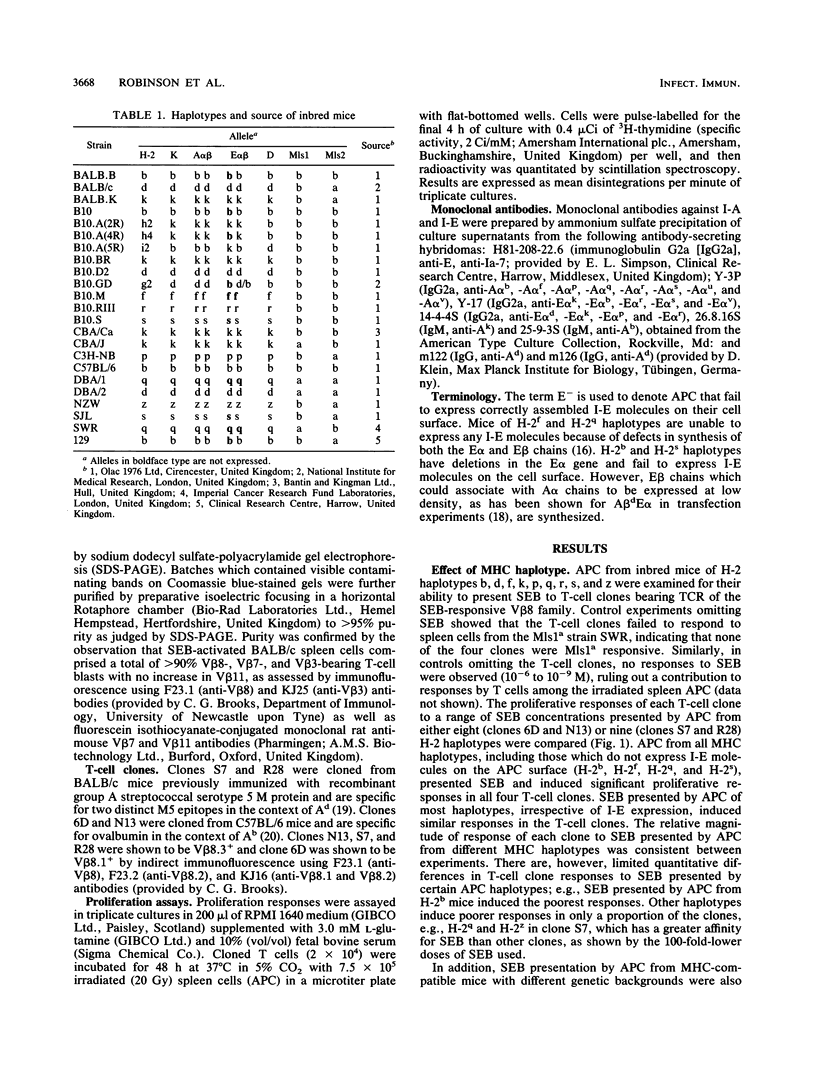
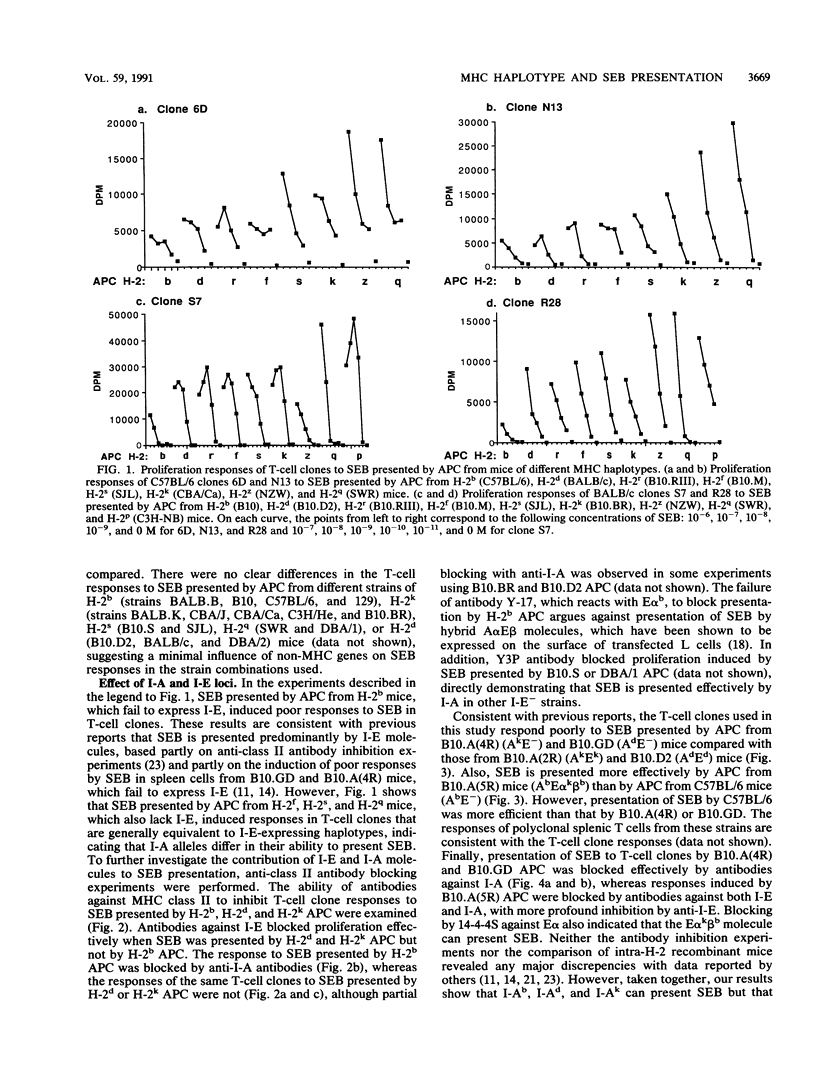
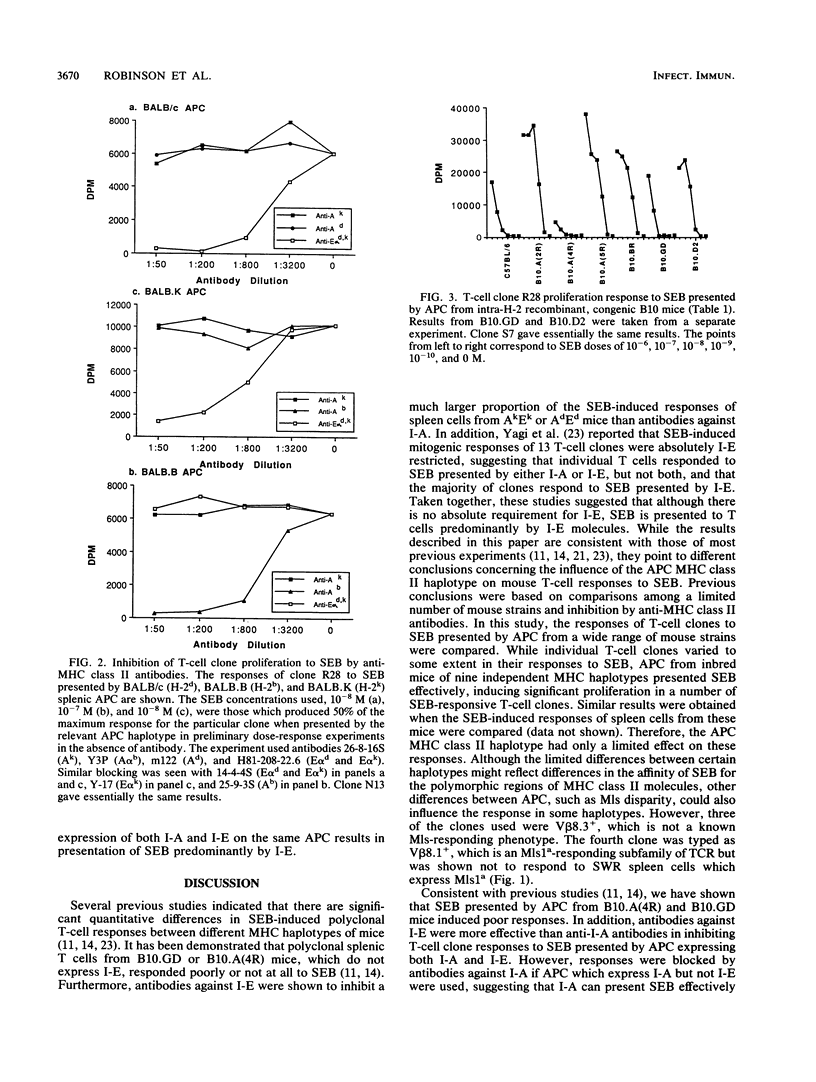
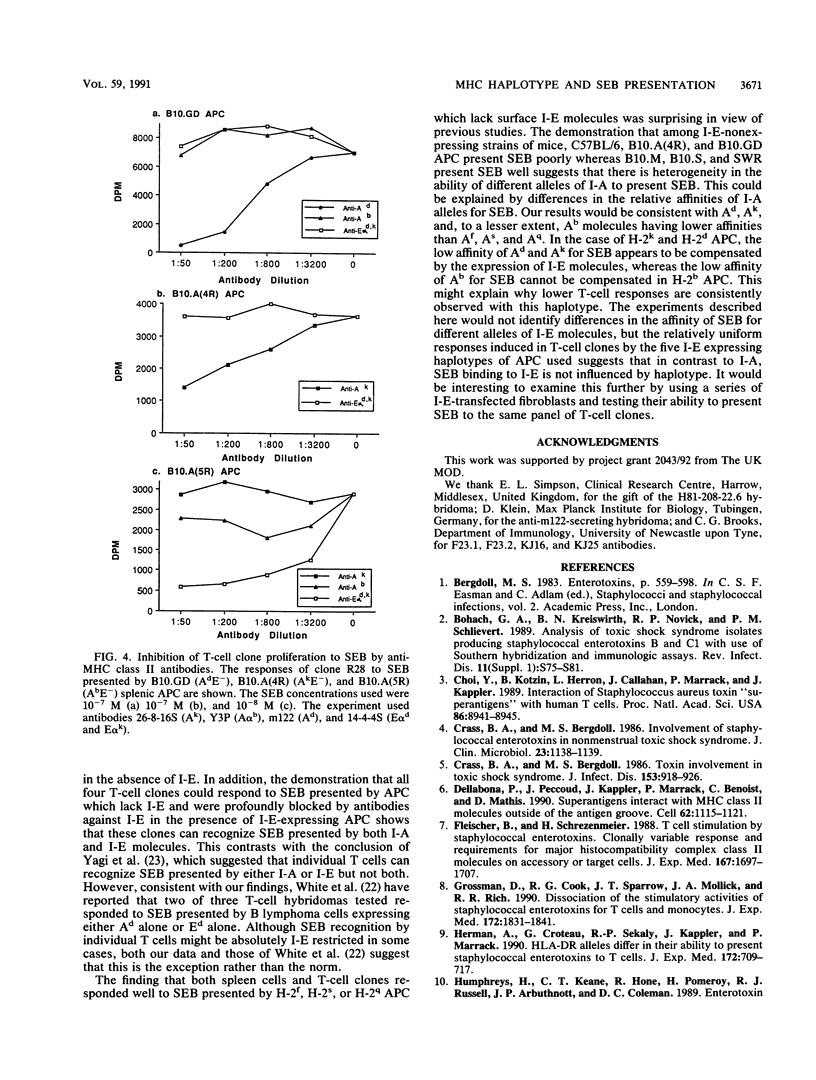
The abilities of antigen-presenting cells (APC) from nine independent major histocompatibility complex haplotypes and a number of intra-H-2 recombinant congenic strains of mice to present staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) and induce proliferation in murine T-cell receptor V beta 8+ T-cell clones were compared. SEB presented by APC of all haplotypes tested induced significant responses in each of the T-cell clones. The magnitude of response was similar for most haplotypes, but there were limited quantitative differences between certain haplotypes. SEB presented by APC from H-2b mice as well as the intra-H-2 recombinant strains B10.GD and B10.A(4R), which do not express cell surface I-E (designated I-E-), induced the poorest T-cell responses. However, APC from AfE-, AsE-, and AqE- mice were as potent in SEB presentation as APC expressing both I-A and I-E. Antibodies against I-E were more effective than anti-I-A antibodies at inhibiting responses to SEB presented by APC expressing both I-A and I-E, whereas responses induced by APC expressing I-A but not I-E were blocked by antibodies against I-A. Thus, our results show that I-A can present SEB efficiently but that expression of both I-A and I-E on the same APC results in presentation of SEB predominantly by I-E. In addition, experiments using four distinct I-E- strains of mice indicate that I-A alleles differ in their ability to present SEB.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohach G. A., Kreiswirth B. N., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M. Analysis of toxic shock syndrome isolates producing staphylococcal enterotoxins B and C1 with use of southern hybridization and immunologic assays. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11 (Suppl 1):S75–S82. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_1.s75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. W., Kotzin B., Herron L., Callahan J., Marrack P., Kappler J. Interaction of Staphylococcus aureus toxin "superantigens" with human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8941–8945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crass B. A., Bergdoll M. S. Involvement of staphylococcal enterotoxins in nonmenstrual toxic shock syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1138–1139. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1138-1139.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crass B. A., Bergdoll M. S. Toxin involvement in toxic shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):918–926. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellabona P., Peccoud J., Kappler J., Marrack P., Benoist C., Mathis D. Superantigens interact with MHC class II molecules outside of the antigen groove. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1115–1121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90388-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Schrezenmeier H. T cell stimulation by staphylococcal enterotoxins. Clonally variable response and requirement for major histocompatibility complex class II molecules on accessory or target cells. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1697–1707. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman D., Cook R. G., Sparrow J. T., Mollick J. A., Rich R. R. Dissociation of the stimulatory activities of staphylococcal enterotoxins for T cells and monocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1831–1841. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A., Croteau G., Sekaly R. P., Kappler J., Marrack P. HLA-DR alleles differ in their ability to present staphylococcal enterotoxins to T cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):709–717. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Yagi J., Conrad P. J., Katz M. E., Jones B., Vroegop S., Buxser S. T-cell responses to Mls and to bacterial proteins that mimic its behavior. Immunol Rev. 1989 Feb;107:61–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J., Kotzin B., Herron L., Gelfand E. W., Bigler R. D., Boylston A., Carrel S., Posnett D. N., Choi Y., Marrack P. V beta-specific stimulation of human T cells by staphylococcal toxins. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):811–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2524876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Blackman M., Kushnir E., Kappler J. The toxicity of staphylococcal enterotoxin B in mice is mediated by T cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):455–464. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):705–711. doi: 10.1126/science.2185544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M., McDevitt H. O. Several mechanisms can account for defective E alpha gene expression in different mouse haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):273–277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizkallah M. F., Tolaymat A., Martinez J. S., Schlievert P. M., Ayoub E. M. Toxic shock syndrome caused by a strain of Staphylococcus aureus that produces enterotoxin C but not toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. Am J Dis Child. 1989 Jul;143(7):848–849. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1989.02150190098031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant A. J., Braunstein N. S., Germain R. N. Predominant role of amino-terminal sequences in dictating efficiency of class II major histocompatibility complex alpha beta dimer expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8065–8069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vroegop S. M., Buxser S. E. Cell surface molecules involved in early events in T-cell mitogenic stimulation by staphylococcal enterotoxins. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1816–1824. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1816-1824.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Herman A., Pullen A. M., Kubo R., Kappler J. W., Marrack P. The V beta-specific superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: stimulation of mature T cells and clonal deletion in neonatal mice. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90980-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi J., Baron J., Buxser S., Janeway C. A., Jr Bacterial proteins that mediate the association of a defined subset of T cell receptor:CD4 complexes with class II MHC. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):892–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


