Abstract
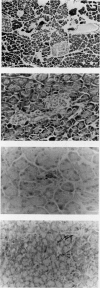
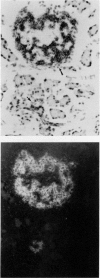
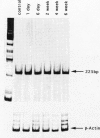
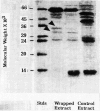
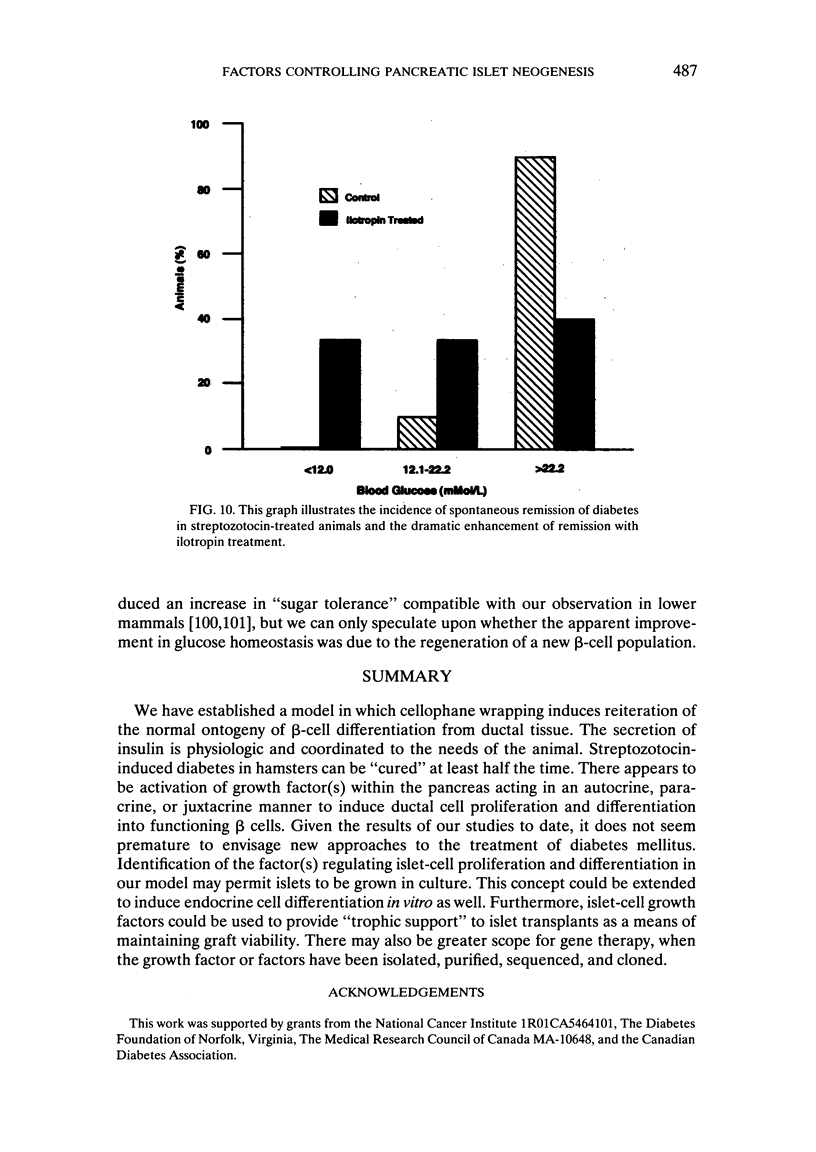
We have established a model in which cellophane wrapping induces reiteration of the normal ontogeny of beta-cell differentiation from ductal tissue. The secretion of insulin is physiologic and coordinated to the needs of the animal. Streptozotocin-induced diabetes in hamsters can be "cured" at least half the time. There appears to be activation of growth factor(s) within the pancreas, acting in an autocrine, paracrine, or juxtacrine manner to induce ductal cell proliferation and differentiation into functioning beta cells. Given the results of our studies to date, it does not seem premature to envisage new approaches to the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Identification of the factor(s) regulating islet-cell proliferation and differentiation in our model may permit islets to be grown in culture. This concept could be extended to induce endocrine cell differentiation in vitro as well. Furthermore, islet-cell growth factors could be used to provide "trophic support" to islet transplants as a means of maintaining graft viability. There may also be greater scope for gene therapy when the growth factor(s) have been isolated, purified, sequenced, and cloned.
Full text
PDF





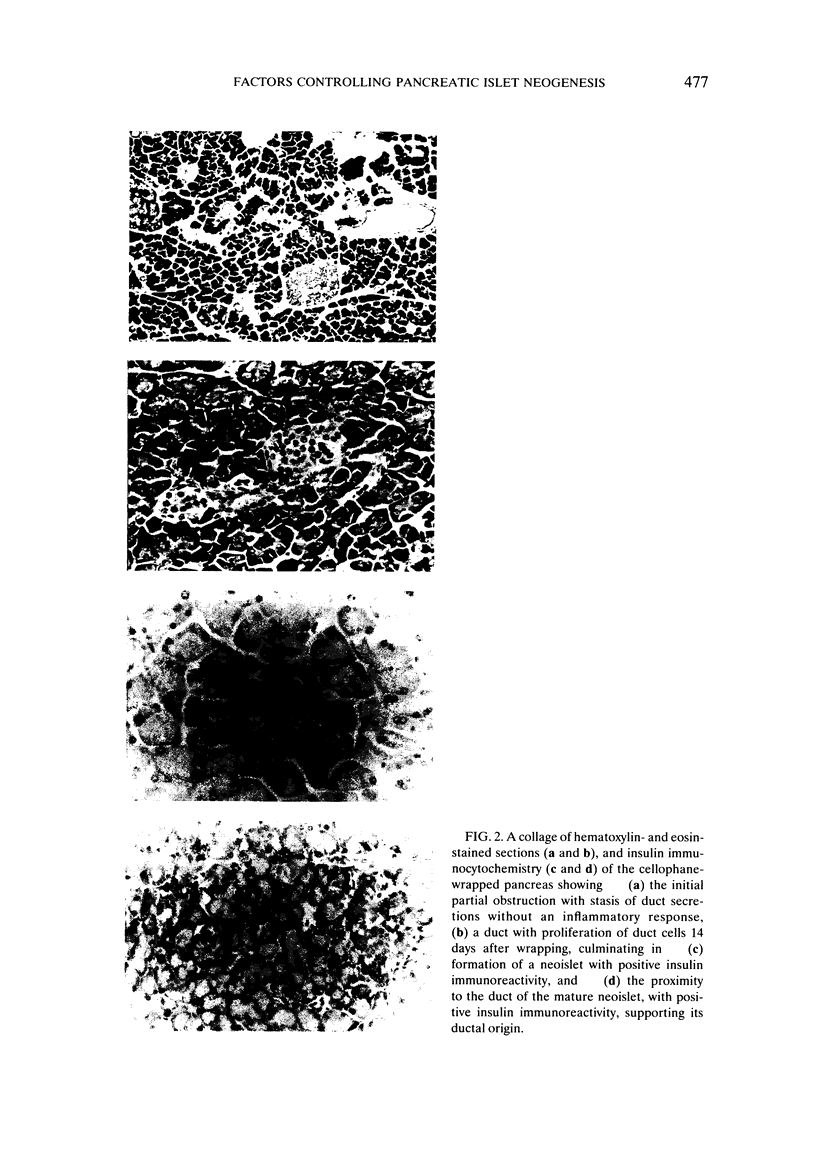
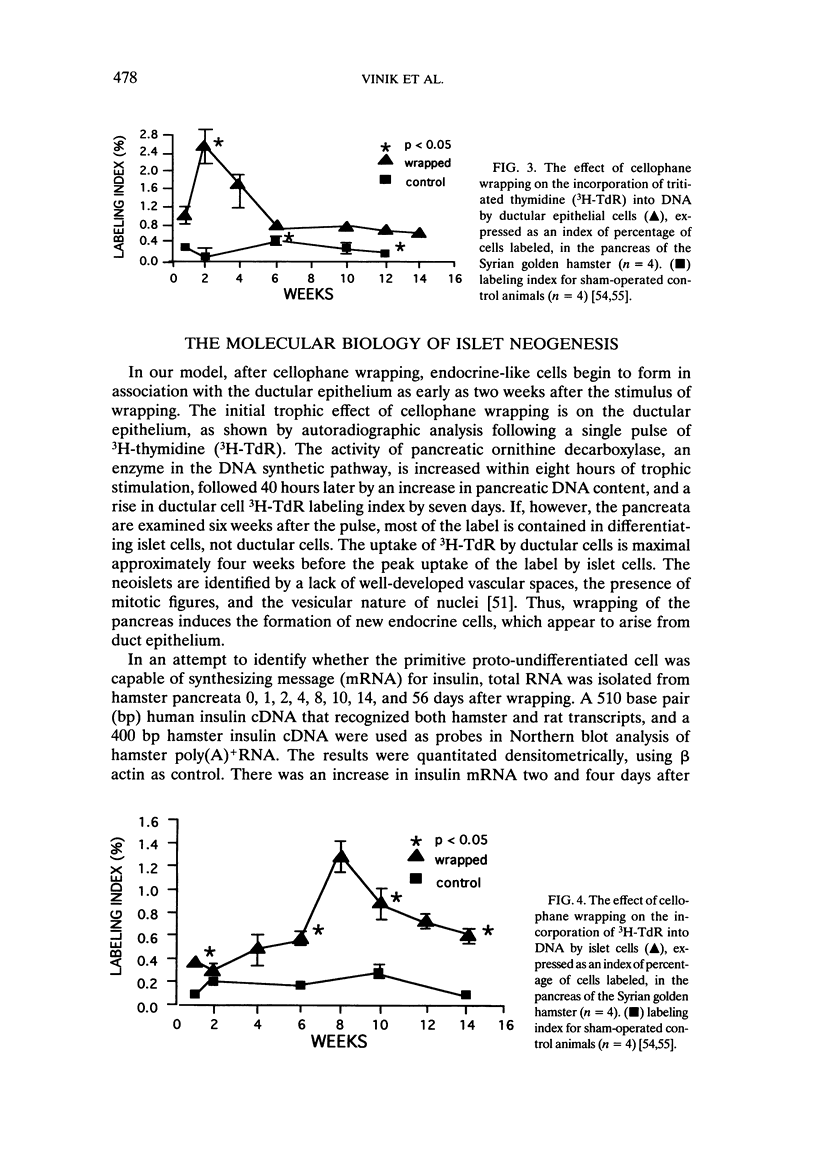

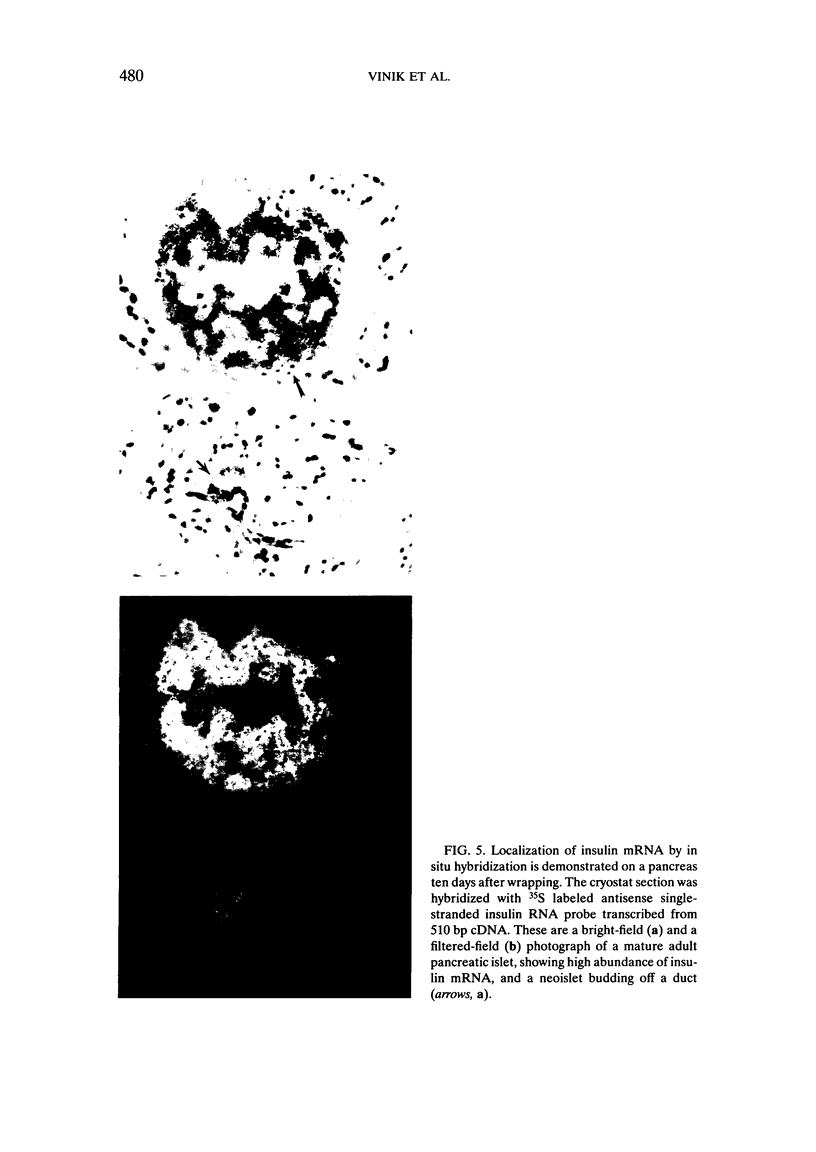

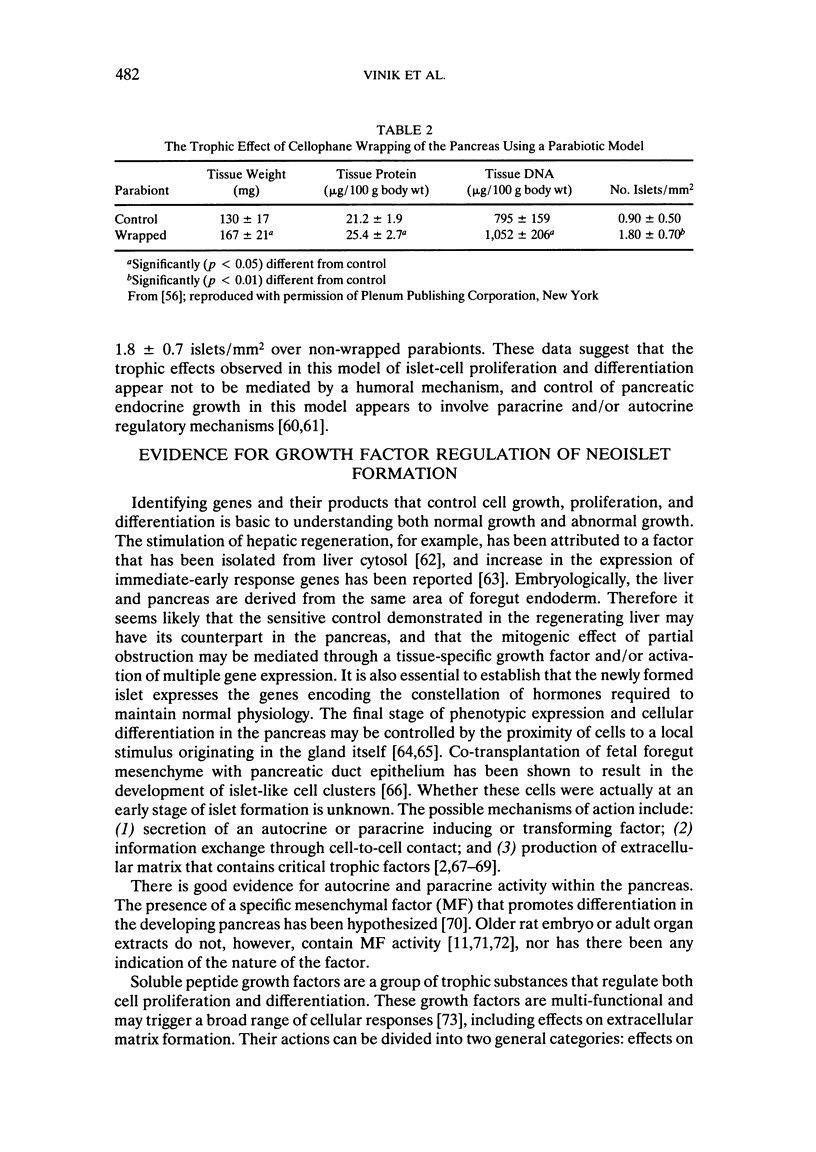






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. A., Mergia A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Friedman J., Hjerrild K. A., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.2425435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew A. An experimental investigation into the possible neural crest origin of pancreatic APUD (islet) cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1976 Jun;35(3):577–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENCOSME S. A. Cytology of islet cells in alloxan diabetic rabbits. Am J Pathol. 1955 Nov-Dec;31(6):1149–1163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton C. M., Hall P. A., Hughes C. M., Gullick W. J., Lemoine N. R. Transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor in human pancreatic cancer. J Pathol. 1991 Feb;163(2):111–116. doi: 10.1002/path.1711630206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billestrup N., Martin J. M. Growth hormone binding to specific receptors stimulates growth and function of cloned insulin-producing rat insulinoma RIN-5AH cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Mar;116(3):1175–1181. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-3-1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner-Weir S., Orci L. New perspectives on the microvasculature of the islets of Langerhans in the rat. Diabetes. 1982 Oct;31(10):883–889. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.10.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquist L., Edström C. Ultrastructure of pancreatic acinar and islet parenchyma in rats at various intervals after duct ligation. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1970;349(1):69–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00548522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockenbrough J. S., Weir G. C., Bonner-Weir S. Discordance of exocrine and endocrine growth after 90% pancreatectomy in rats. Diabetes. 1988 Feb;37(2):232–236. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson J. M., Tuch B. E., Baxter R. C. Production of insulin-like growth factor-II by human fetal pancreas in culture. J Endocrinol. 1989 May;121(2):367–373. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1210367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantenys D., Portha B., Dutrillaux M. C., Hollande E., Rozé C., Picon L. Histogenesis of the endocrine pancreas in newborn rats after destruction by streptozotocin. An immunocytochemical study. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;35(2):109–122. doi: 10.1007/BF02889153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catala J., Bonnafous R., Dutrillaux M. C., Hollande E. Dissociation of Langerhans islets in the rabbit after pancreatic duct ligation. Immunocytochemical and ultrastructural studies. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1987;52(6):539–551. doi: 10.1007/BF02889992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. Diffusion in embryogenesis. Nature. 1970 Jan 31;225(5231):420–422. doi: 10.1038/225420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek R. W., Freinkel N., Lewis N. J., Hellerström C., Johnson R. C. Morphologic study of cultured pancreatic fetal islets during maturation of the insulin stimulus-secretion mechanism. Diabetes. 1980 Jan;29(1):15–21. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek R. W., Lawrence I. E., Jr, Hill R. S., Johnson R. C. Induction of islet cytodifferentiation by fetal mesenchyme in adult pancreatic ductal epithelium. Diabetes. 1991 Aug;40(8):1041–1048. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.8.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek R. W., Lawrence I. E., Jr Morphologic evidence of interactions between adult ductal epithelium of pancreas and fetal foregut mesenchyme. Diabetes. 1988 Jul;37(7):891–900. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.7.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek R. W., Lawrence I. E., Jr Morphologic evidence of interactions between adult ductal epithelium of pancreas and fetal foregut mesenchyme. Diabetes. 1988 Jul;37(7):891–900. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.7.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström C., Falkmer S. Qualitative and quantitative morphology of rat pancreatic islet tissue five weeks after ligation of the pancreatic ducts. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1967;72(5):376–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Shimizu K., Bowring M. A., Wells S. Expression of receptors for tetanus toxin and monoclonal antibody A2B5 by pancreatic islet cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fell P. E., Grobstein C. The influence of extra-epithelial factors on the growth of embryonic mouse pancreatic epithelium. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Oct;53(1):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90381-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLOSOW N., GROBSTEIN C. Epitheliomesenchymal interaction in pancreatic morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1962 Apr;4:242–255. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(62)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittes G. K., Rutter W. J. Onset of cell-specific gene expression in the developing mouse pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1128–1132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goustin A. S., Leof E. B., Shipley G. D., Moses H. L. Growth factors and cancer. Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1015–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerström C. The life story of the pancreatic B cell. Diabetologia. 1984 Jun;26(6):393–400. doi: 10.1007/BF00262208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Frazer A., Swenne I., Wirdnam P. K., Milner R. D. Somatomedin-C in human fetal pancreas. Cellular localization and release during organ culture. Diabetes. 1987 Apr;36(4):465–471. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.4.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Hogg J. Expression of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and their binding proteins (IGF BPs) during pancreatic development in rat, and modulation of IGF actions on rat islet DNA synthesis by IGF BPs. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;321:113–122. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3448-8_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. Cyclical changes in the islets of Langerhans in the rat pancreas. J Anat. 1947 Jan;81(Pt 1):82–92.2. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhappan C., Stahle C., Harkins R. N., Fausto N., Smith G. H., Merlino G. T. TGF alpha overexpression in transgenic mice induces liver neoplasia and abnormal development of the mammary gland and pancreas. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1137–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90076-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. M., Teillet M. A. The migration of neural crest cells to the wall of the digestive tract in avian embryo. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1973 Aug;30(1):31–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Rochford R., Todaro G. J., Villarreal L. P. Developmental expression of rat transforming growth factor-alpha mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3644–3646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker D. S., Pettengill O. S., Davis B. H., Schaeffer B. K., Zurlo J., Hong H. L., Kuhlmann E. T. Characterization of preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions in the rat pancreas. Am J Pathol. 1991 Feb;138(2):333–340. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels J. E., Bauer G. E., Dixit P. K. On the origin of induced pancreatic islet tumors: a radioautographic study. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1987 Feb;184(2):218–224. doi: 10.3181/00379727-184-42471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. D., Ashworth M. A., Barson A. J. Insulin release from human foetal pancreas in response to glucose, leucine and arginine. J Endocrinol. 1972 Mar;52(3):497–505. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0520497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyaura C., Chen L., Appel M., Alam T., Inman L., Hughes S. D., Milburn J. L., Unger R. H., Newgard C. B. Expression of reg/PSP, a pancreatic exocrine gene: relationship to changes in islet beta-cell mass. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Feb;5(2):226–234. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-2-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohn K. L., Laz T. M., Melby A. E., Taub R. Immediate-early gene expression differs between regenerating liver, insulin-stimulated H-35 cells, and mitogen-stimulated Balb/c 3T3 cells. Liver-specific induction patterns of gene 33, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, and the jun, fos, and egr families. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21914–21921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Mouron P., Amherdt M., Orci L. Collagen matrix promotes reorganization of pancreatic endocrine cell monolayers into islet-like organoids. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):935–939. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohoshi T., Kanda M., Klöppel G. On the histogenesis of experimental pancreatic endocrine tumors. An immunocytochemical and electron microscopical study. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1984 Mar;34(2):271–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1984.tb07555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Malaisse-Lagae F., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Weisswange A., Dobbs R., Perrelet A., Unger R. Cell contacts in human islets of Langerhans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Nov;41(5):841–844. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-5-841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Unger R. H. Functional subdivision of islets of Langerhans and possible role of D cells. Lancet. 1975 Dec 20;2(7947):1243–1244. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otonkoski T., Andersson S., Knip M., Simell O. Maturation of insulin response to glucose during human fetal and neonatal development. Studies with perifusion of pancreatic isletlike cell clusters. Diabetes. 1988 Mar;37(3):286–291. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.3.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patent G. J., Alfert M. Histological changes in the pancreatic islets of alloxan-treated mice, with comments on beta-cell regeneration. Acta Anat (Basel) 1967;66(4):504–519. doi: 10.1159/000142962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G. Common cytochemical and ultrastructural characteristics of cells producing polypeptide hormones (the APUD series) and their relevance to thyroid and ultimobranchial C cells and calcitonin. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 May 14;170(1018):71–80. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pictet R. L., Rall L. B., Phelps P., Rutter W. J. The neural crest and the origin of the insulin-producing and other gastrointestinal hormone-producing cells. Science. 1976 Jan 16;191(4223):191–192. doi: 10.1126/science.1108195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
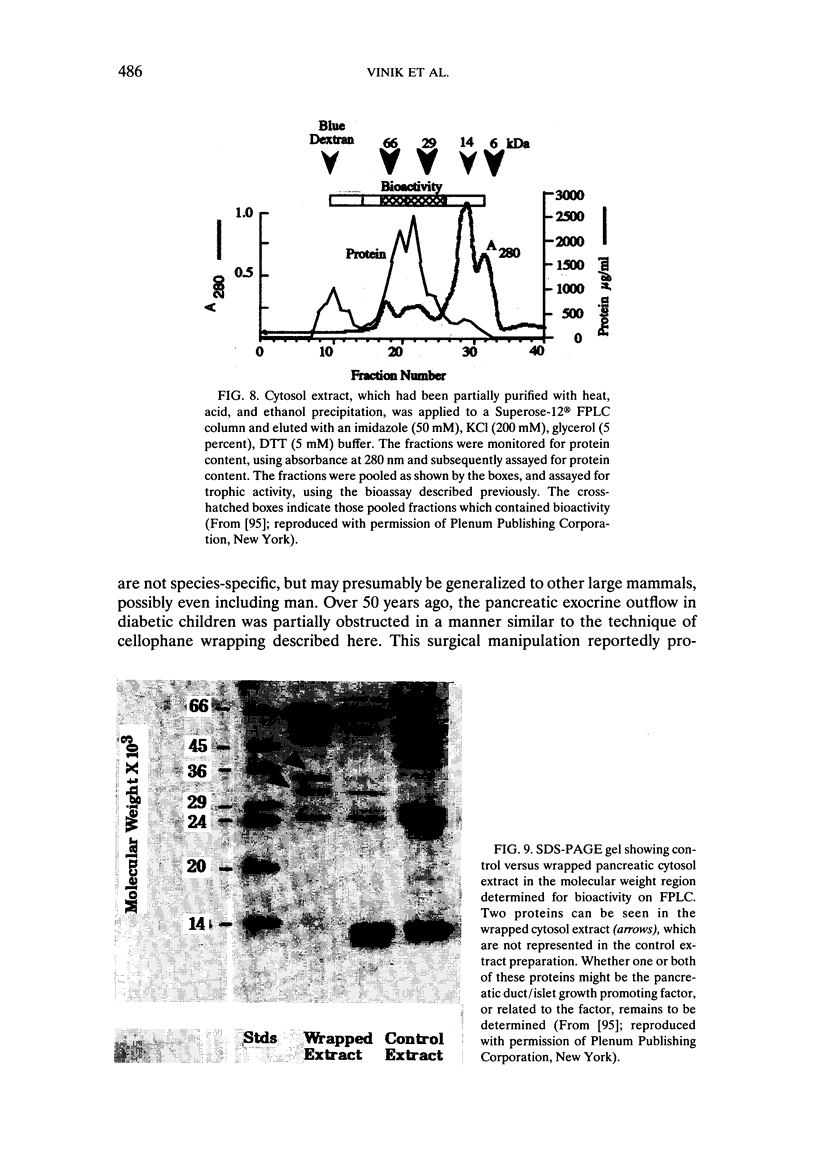
- Pittenger G. L., Vinik A. I., Rosenberg L. The partial isolation and characterization of ilotropin, a novel islet-specific growth factor. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;321:123–132. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3448-8_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popiela H., Tomita T., Hegre O., Moore W. Islet neoformation in tissue culture. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Nov;48(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90161-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pour P. Islet cells as a component of pancreatic ductal neoplasms. I. Experimental study: ductular cells, including islet cell precursors, as primary progenitor cells of tumors. Am J Pathol. 1978 Feb;90(2):295–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch A., Quigley C., Rechler M. M. Growth hormone stimulates islet B-cell replication in neonatal rat pancreatic monolayer cultures. Diabetes. 1983 Apr;32(4):307–312. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.4.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch A., Quigley C., Russell T., Patel Y., Mintz D. H. Insulin and multiplication stimulating activity (an insulin-like growth factor) stimulate islet (beta-cell replication in neonatal rat pancreatic monolayer cultures. Diabetes. 1982 Feb;31(2):160–164. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahier J., Fält K., Müntefering H., Becker K., Gepts W., Falkmer S. The basic structural lesion of persistent neonatal hypoglycaemia with hyperinsulinism: deficiency of pancreatic D cells or hyperactivity of B cells? Diabetologia. 1984 Apr;26(4):282–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00283651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzio R. A., Rutter W. J. Effects of a partially purified factor from chick embryos on macromolecular synthesis of embryonic pancreatic epithelia. Dev Biol. 1973 Feb;30(2):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
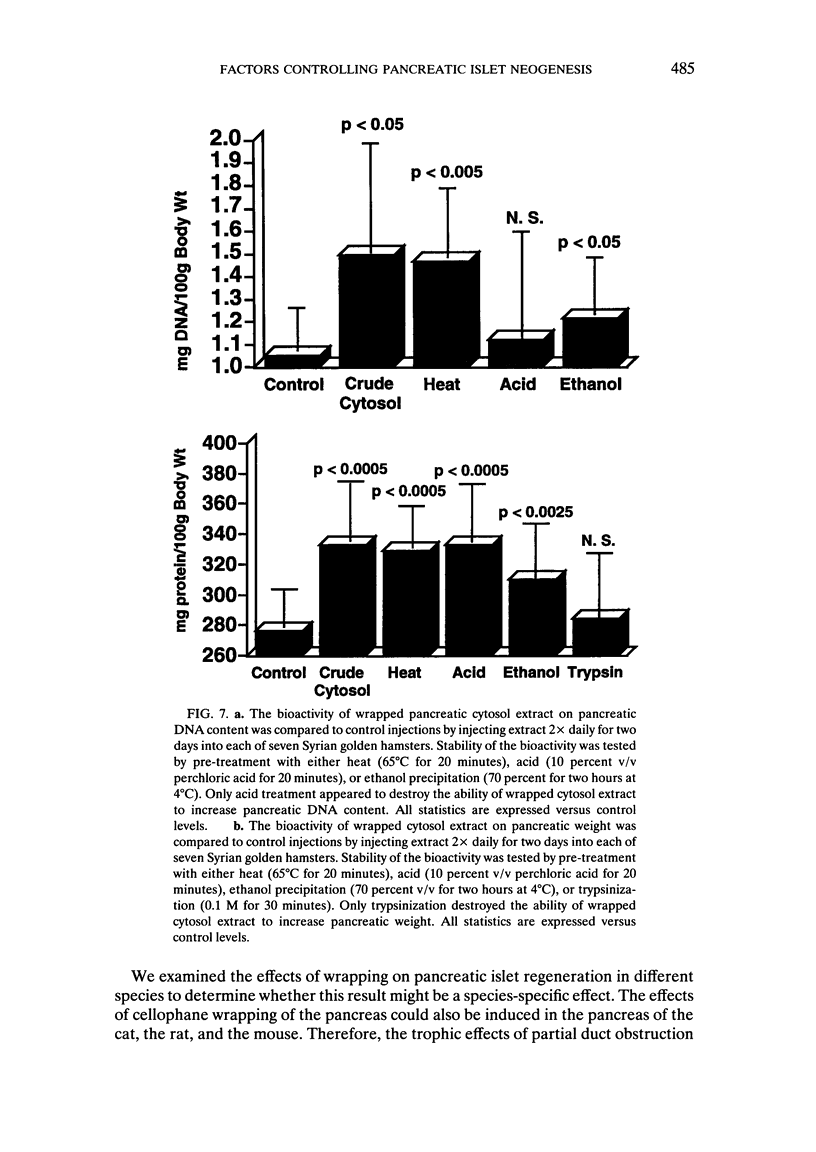
- Rosenberg L., Brown R. A., Duguid W. P. A new approach to the induction of duct epithelial hyperplasia and nesidioblastosis by cellophane wrapping of the hamster pancreas. J Surg Res. 1983 Jul;35(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(83)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Duguid W. P., Brown R. A., Vinik A. I. Induction of nesidioblastosis will reverse diabetes in Syrian golden hamster. Diabetes. 1988 Mar;37(3):334–341. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.3.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Duguid W. P., Vinik A. I. The effect of cellophane wrapping of the pancreas in the Syrian golden hamster: autoradiographic observations. Pancreas. 1989;4(1):31–37. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198902000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Duguid W. P., Vinik A. I. The pancreas of Syrian golden hamsters. Age-related autoradiographic observations. Int J Pancreatol. 1989 Apr;4(3):273–280. doi: 10.1007/BF02938463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Vinik A. I. Induction of endocrine cell differentiation: a new approach to management of diabetes. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Jul;114(1):75–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Vinik A. I. Trophic stimulation of the ductular-islet cell axis: a new approach to the treatment of diabetes. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;321:95–109. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3448-8_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter W. J. The development of the endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Monogr Pathol. 1980;21:30–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samols E., Bonner-Weir S., Weir G. C. Intra-islet insulin-glucagon-somatostatin relationships. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Feb;15(1):33–58. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(86)80041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samols E., Stagner J. I. Intra-islet regulation. Am J Med. 1988 Nov 28;85(5A):31–35. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Winkler M. E., Derynck R. Transforming growth factor-alpha: a more potent angiogenic mediator than epidermal growth factor. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1250–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.2422759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz L. C., Makowka L., Falk J. A., Falk R. The characterization and partial purification of hepatocyte proliferation factor. Ann Surg. 1985 Sep;202(3):296–302. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198509000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. E., Rosen K. M., Villa-Komaroff L., Weir G. C., Bonner-Weir S. Enhanced insulin-like growth factor I gene expression in regenerating rat pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6152–6156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner B. S., Cohen H. I., Faubion J. Development of the embryonic mammalian pancreas: the relationship between morphogenesis and cytodifferentiation. Dev Biol. 1977 Dec;61(2):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Peptide growth factors are multifunctional. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):217–219. doi: 10.1038/332217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenne I. Glucose-stimulated DNA replication of the pancreatic islets during the development of the rat fetus. Effects of nutrients, growth hormone, and triiodothyronine. Diabetes. 1985 Aug;34(8):803–807. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.8.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenne I., Heldin C. H., Hill D. J., Hellerström C. Effects of platelet-derived growth factor and somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I on the deoxyribonucleic acid replication of fetal rat islets of Langerhans in tissue culture. Endocrinology. 1988 Jan;122(1):214–218. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-1-214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasawa S., Yamamoto H., Terazono K., Okamoto H. Novel gene activated in rat insulinomas. Diabetes. 1986 Oct;35(10):1178–1180. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.10.1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G. Cellular and molecular analysis of pancreatic islet cell lineage and differentiation. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1991;47:259–297. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571147-0.50012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Transformation of catecholaminergic precursors into glucagon (A) cells in mouse embryonic pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5225–5229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G., Lee J., Reis D. J. Differentiation of prospective mouse pancreatic islet cells during development in vitro and during regeneration. Dev Biol. 1987 Apr;120(2):425–433. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terazono K., Uchiyama Y., Ide M., Watanabe T., Yonekura H., Yamamoto H., Okamoto H. Expression of reg protein in rat regenerating islets and its co-localization with insulin in the beta cell secretory granules. Diabetologia. 1990 Apr;33(4):250–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00404804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terazono K., Yamamoto H., Takasawa S., Shiga K., Yonemura Y., Tochino Y., Okamoto H. A novel gene activated in regenerating islets. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2111–2114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Rios-Candelore M., Giménez-Gallego G., DiSalvo J., Bennett C., Rodkey J., Fitzpatrick S. Pure brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor is a potent angiogenic vascular endothelial cell mitogen with sequence homology to interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6409–6413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. J., Doran J. F., Jackson P., Dhillon A. P., Rode J. PGP 9.5--a new marker for vertebrate neurons and neuroendocrine cells. Brain Res. 1983 Nov 14;278(1-2):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood L. E., D'Ercole A. J., Clemmons D. R., Van Wyk J. J. Paracrine functions of somatomedins. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Feb;15(1):59–77. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(86)80042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker P. G., Taylor K. W. Direct effects of rat growth hormone in rat islets of langerhans in tissues culture. Diabetologia. 1980 Apr;18(4):323–328. doi: 10.1007/BF00251014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W., Kuhn C., Moll R., Gould V. E. Synaptophysin: a marker protein for neuroendocrine cells and neoplasms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3500–3504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]