Abstract
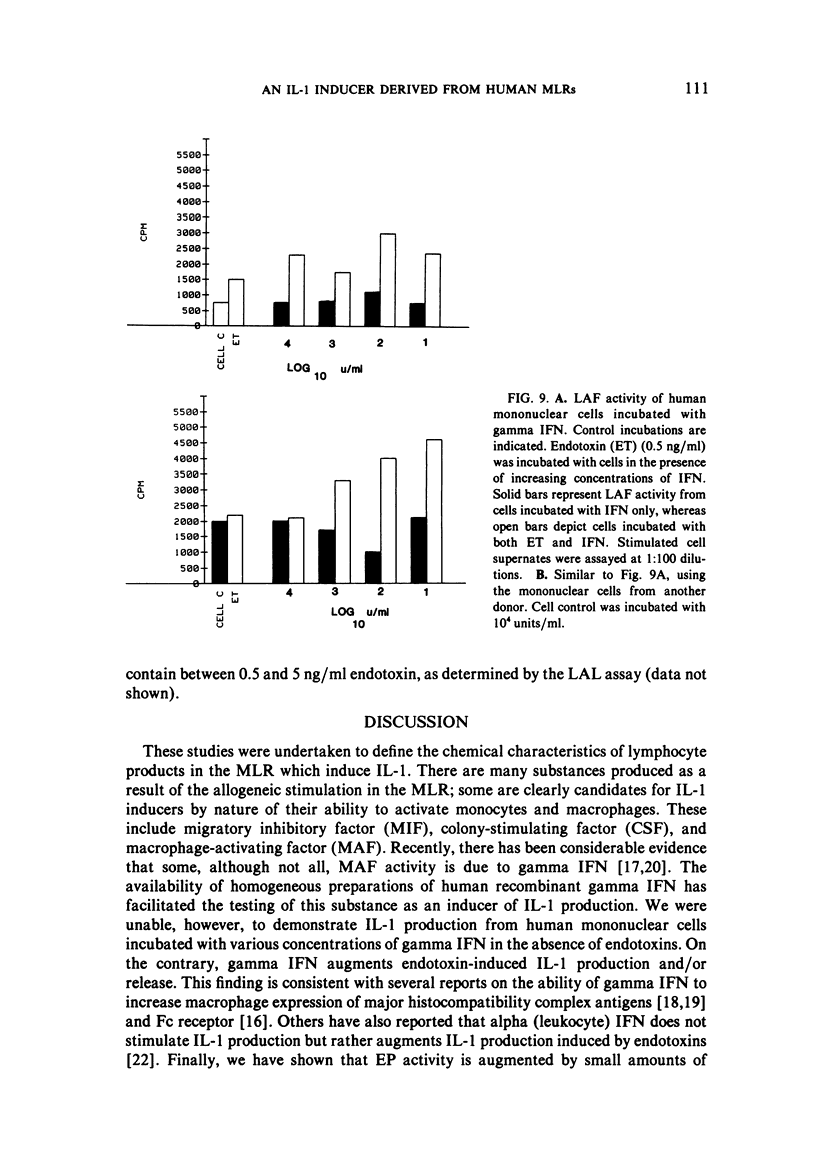
Lymphocyte products released during the human mixed reaction were studied for their ability to stimulate human monocytes to produce endogenous pyrogen and lymphocyte activating factor. These two biological activities are considered properties of the same molecule, called interleukin-1 (IL-1). In these experiments, physical characteristics such as molecular weight, isoelectric point, and binding to concanavalin A (Con A) sepharose were studied under conditions which excluded bacterial endotoxins. Gel filtration revealed molecular weights of approximately 60 and 25 kD with IL-1-inducing activity. Isoelectric points ranged from 5.9 to 6.3. The IL-1-inducing properties of mixed leukocyte reaction supernates did not bind to Con A sepharose. Recombinant human gamma interferon did not induce IL-1 production under various conditions but rather augmented IL-1 induced by endotoxin. In contrast, the mixed leukocyte reaction results in production of lymphokines which directly stimulate IL-1 production in the absence of endotoxins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Virelizier J. L. Interferons as macrophage-activating factors. II. Enhanced secretion of interleukin 1 by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Jun;13(6):437–440. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins E., Feldman J. D., Francis L., Hursh E. Studies on the mechanism of fever accompanying delayed hypersensitivity. The role of the sensitized lymphocyte. J Exp Med. 1972 May 1;135(5):1113–1132. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.5.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins E. Fever: the old and the new. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):339–348. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins E., Francis L., Bernheim H. A. Pathogenesis of fever in delayed hypersensitivity: role of monocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):813–820. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.813-820.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins E., Francis L. Pathogenesis of fever in delayed hypersensitivity: factors influencing release of pyrogen-inducing lymphokines. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):806–812. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.806-812.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Recombinant interferon-gamma increases HLA-DR synthesis and expression. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1492–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheim H. A., Block L. H., Atkins E. Fever: pathogenesis, pathophysiology, and purpose. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):261–270. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheim H. A., Block L. H., Francis L., Atkins E. Release of endogenous pyrogen-activating factor from concanavalin A-stimulated human lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1811–1816. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao P., Francis L., Atkins E. The release of an endogenous pyrogen from guinea pig leukocytes in vitro: a new model for investigating the role of lymphocytes in fevers induced by antigen in hosts with delayed hypersensitivity. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1288–1298. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Bernheim H. A., Duff G. W., Le H. V., Nagabhushan T. L., Hamilton N. C., Coceani F. Mechanisms of fever induced by recombinant human interferon. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):906–913. doi: 10.1172/JCI111508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
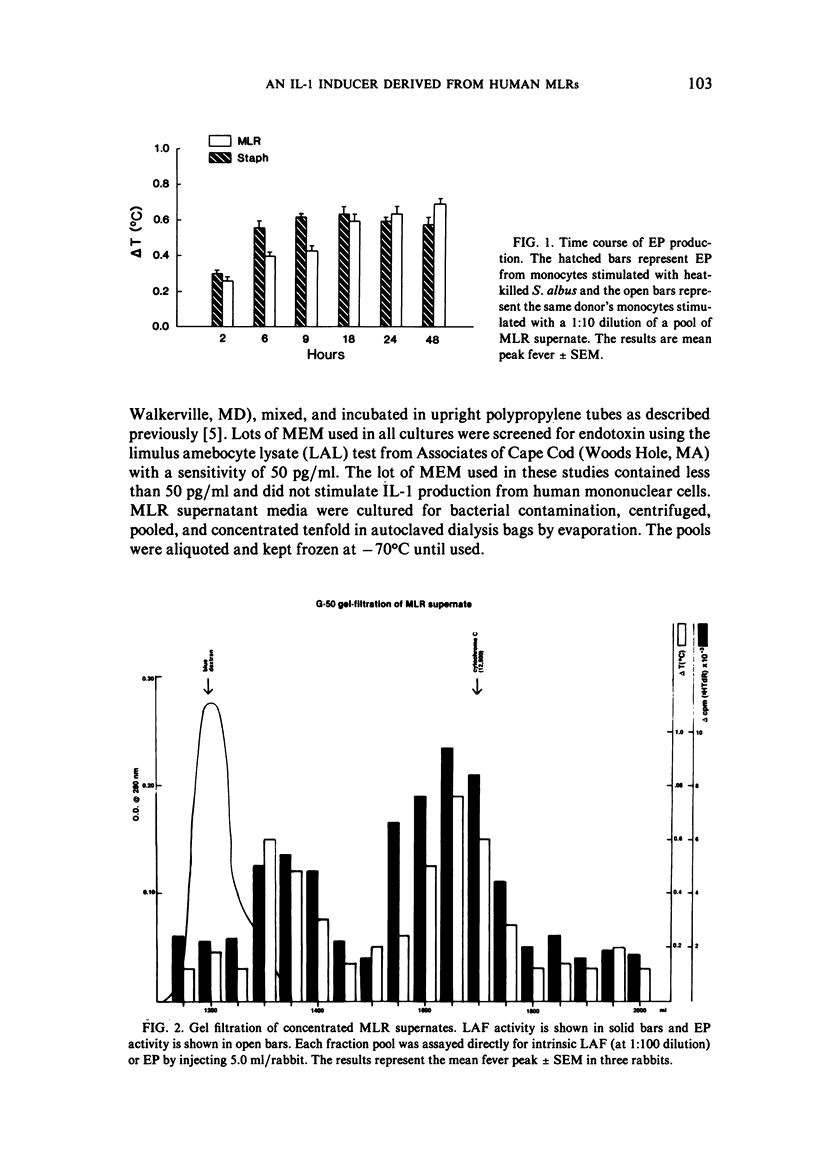
- Dinarello C. A. Demonstration of a human pyrogen-inducing factor during mixed leukocyte reactions. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1215–1224. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Wolff S. M. Molecular basis of fever in humans. Am J Med. 1982 May;72(5):799–819. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff G. W., Atkins E. The detection of endotoxin by in vitro production of endogenous pyrogen: comparison with limulus amebocyte lysate gelation. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Aug 13;52(3):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff G. W., Atkins E. The inhibitory effect of polymyxin B on endotoxin-induced endogenous pyrogen production. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Aug 13;52(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fertsch D., Vogel S. N. Recombinant interferons increase macrophage Fc receptor capacity. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2436–2439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley V. E., Fiers W., Strom T. B. Cloned human interferon-gamma, but not interferon-beta or -alpha, induces expression of HLA-DR determinants by fetal monocytes and myeloid leukemic cell lines. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Prensky W., Yip Y. K., Chang Z., Hoffman T., Stevenson H. C., Balazs I., Sadlik J. R., Vilcek J. Activation of human monocyte cytotoxicity by natural and recombinant immune interferon. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2821–2826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. N., Oppenheim J. J., Farrar J. J., Carter C. S., Jr, Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Production of lymphocyte-activating factor (Interleukin 1) by macrophages activated with colony-stimulating factors. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1302–1305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold H. G., Mednis A. D. Two migration inhibitory factors with different chromatographic behavior and isoelectric points. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2015–2019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Bendtzen K., Greineder D. Mediators of immunity: lymphokines and monokines. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:55–136. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwasser L. J., Dinarello C. A. Ability of human leukocytic pyrogen to enhance phytohemagglutinin induced murine thymocyte proliferation. Cell Immunol. 1981 Sep 1;63(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz R. M., Kleinschmidt W. J. Functional identity between murine gamma interferon and macrophage activating factor. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):239–240. doi: 10.1038/305239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


