Abstract
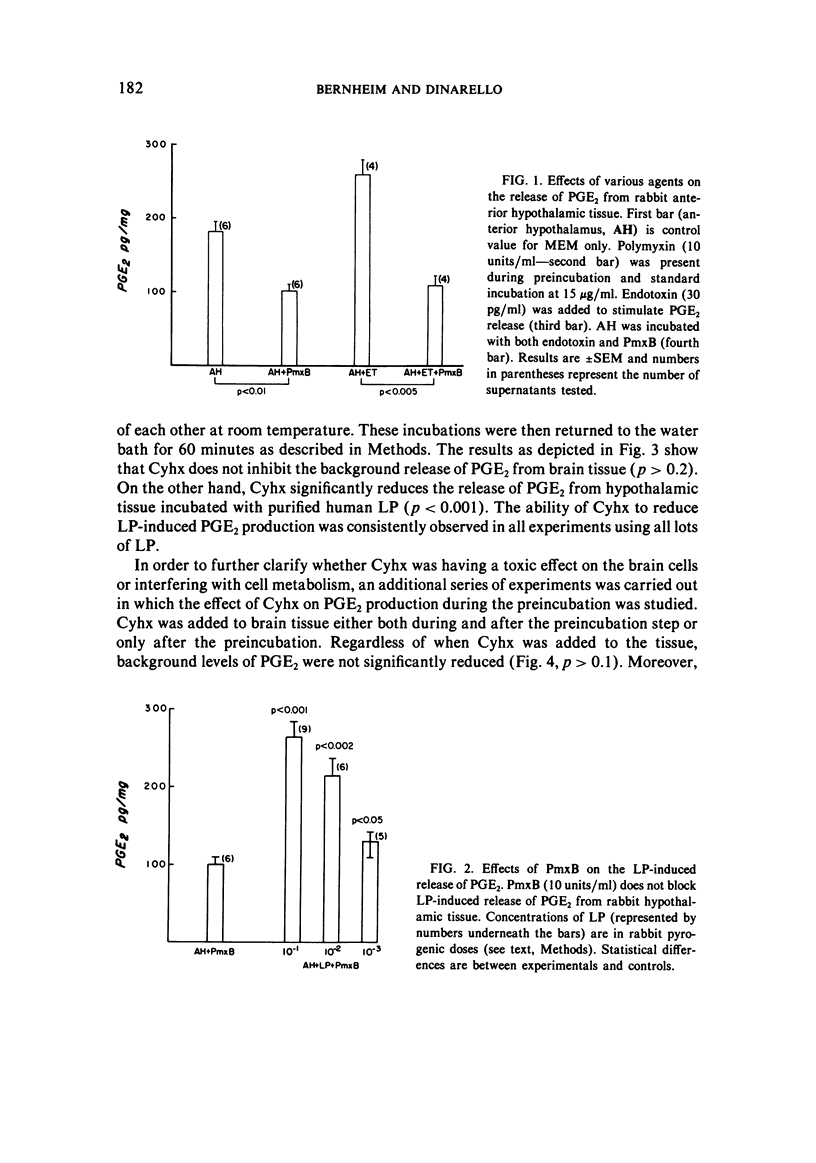
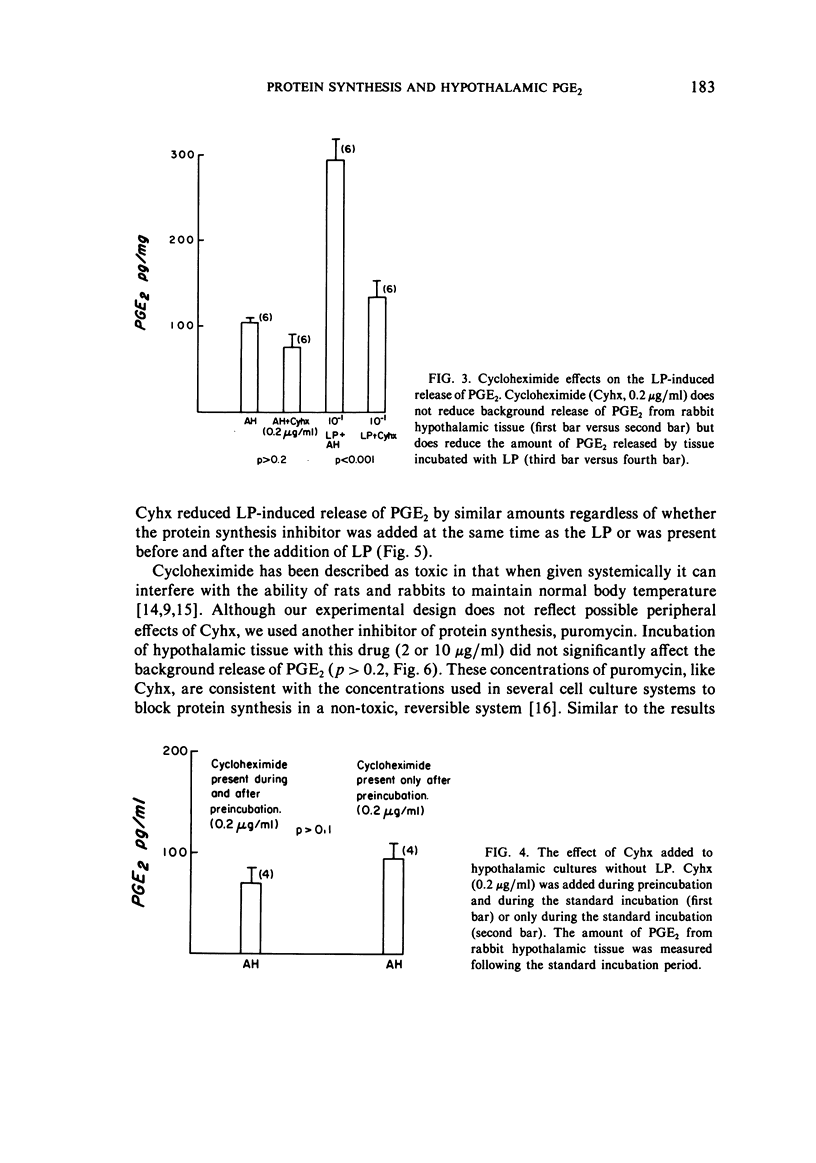
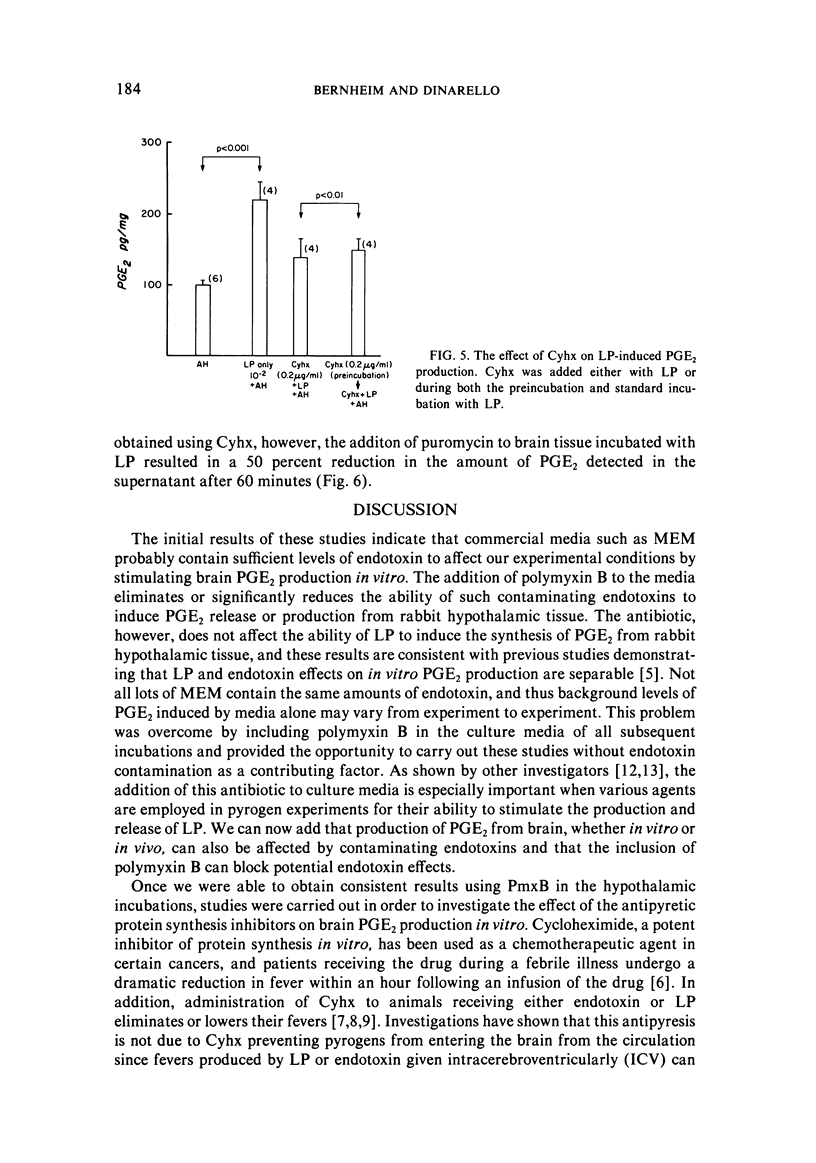
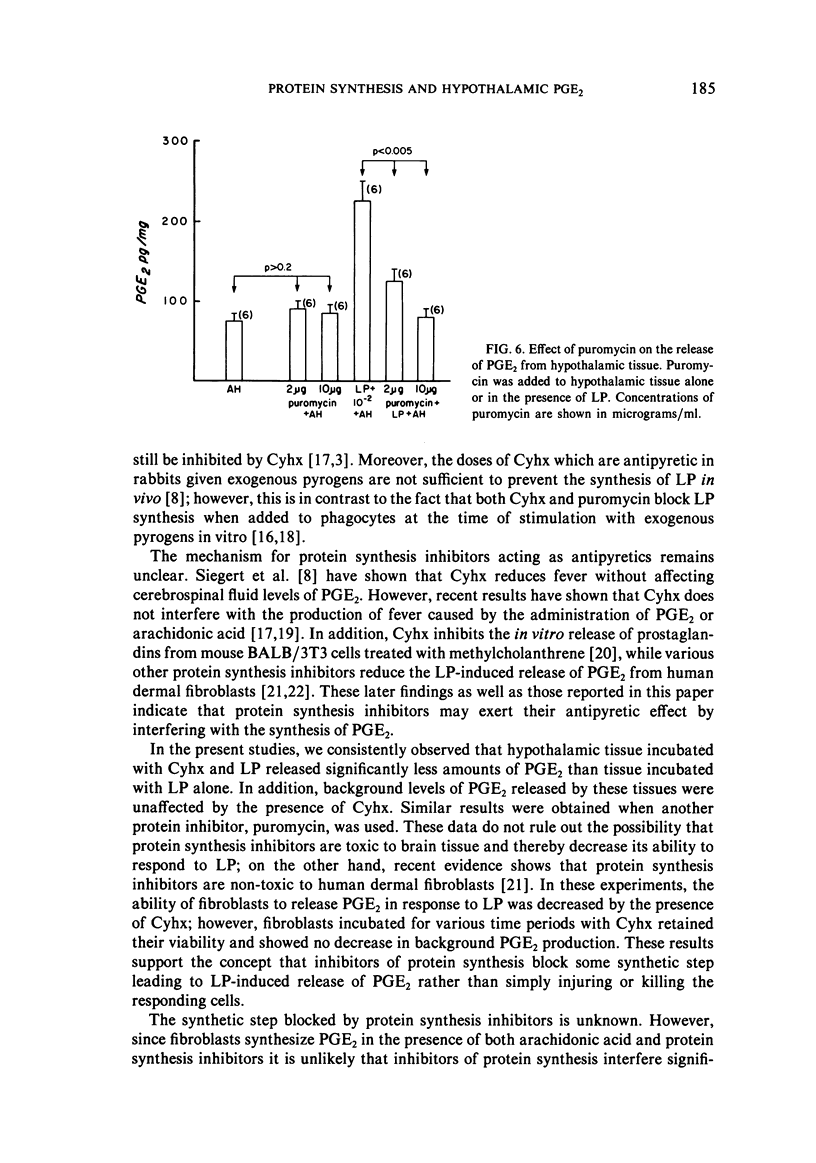
In order to study the antipyretic effect of inhibitors of protein synthesis, hypothalamic tissue was incubated in vitro under controlled conditions and the amount of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) measured in the supernatant medium. Rabbit anterior hypothalamic tissue was incubated with purified human leukocytic pyrogen (LP) and after 60 minutes the supernatant fluid was assayed for PGE2 by radioimmunoassay. Control tissue incubated with Eagle's medium (MEM) released elevated levels of PGE2; however, the addition of polymyxin B (PmxB), a cationic antibiotic which blocks the activities of bacterial endotoxins, significantly reduced PGE2. In addition, endotoxin added to MEM induced from the brain tissue PGE2 production which could be reduced by the addition of PmxB. Thus, commercial culture media such as MEM may contain sufficient amounts of endotoxin to stimulate brain PGE2 production in vitro. Purified human LP incubated with hypothalamic tissue in the presence of PmxB induced PGE2 production in a dose-dependent fashion. This release could be reduced (p less than 0.001) by the presence of either cycloheximide or puromycin during incubation with LP. The addition of these inhibitors to unstimulated hypothalamic tissue incubations did not reduce background levels of PGE2. It is concluded that the antipyretic effect of protein synthesis inhibitors results in a specific decrease in LP-induced levels of PGE2.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barney C. C., Katovich M. J., Fregly M. J. Effect of cycloheximide on temperature regulation in rats. Brain Res Bull. 1979 May-Jun;4(3):355–358. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(79)80013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheim H. A., Gilbert T. M., Stitt J. T. Prostaglandin E levels in third ventricular cerebrospinal fluid of rabbits during fever and changes in body temperature. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:69–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodel P. Studies on the mechanism of endogenous pyrogen production. I. Investigation of new protein synthesis in stimulated human blood leucocytes. Yale J Biol Med. 1970 Dec;43(3):145–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Bishai I., Dinarello C. A., Fitzpatrick F. A. Prostaglandin E2 and thromboxane B2 in cerebrospinal fluid of afebrile and febrile cat. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):R785–R793. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1983.244.6.R785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranston W. I., Dawson N. J., Hellon R. F., Townsend Y. Contrasting actions of cycloheximide on fever caused by arachidonic acid and by pyrogen [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Dec;285:35P–35P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranston W. I., Hellon R. F., Townsend Y. Suppression of fever in rabbits by a protein synthesis inhibitor, anisomycin. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:337–344. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Bendtzen K., Wolff S. M. Studies on the active site of human leukocytic pyrogen. Inflammation. 1982 Mar;6(1):63–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00910720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Bernheim H. A. Ability of human leukocytic pyrogen to stimulate brain prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):702–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb12544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Renfer L., Wolff S. M. Human leukocytic pyrogen: purification and development of a radioimmunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4624–4627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff G. W., Atkins E. The inhibitory effect of polymyxin B on endotoxin-induced endogenous pyrogen production. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Aug 13;52(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund J. J., Root R. K., Wolff S. M. Studies on the origin of human leukocytic pyrogen. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):727–743. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pong S. S., Hong S. L., Levine L. Prostaglandin production by methylcholanthrene-transformed mouse BALB/3T3. Requirement for protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1408–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruwe W. D., Myers R. D. Fever produced by intrahypothalamic pyrogen: effect of protein synthesis inhibition by anisomycin. Brain Res Bull. 1979 Nov-Dec;4(6):741–745. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(79)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegert R., Philipp-Dormston W. K., Radsak K., Menzel H. Mechanism of fever induction in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1130–1137. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1130-1137.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt J. T. Prosaglandin E1 fever induced in rabbits. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):163–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley P. J., Needleman P. Mechanism of enhanced fibroblast arachidonic acid metabolism by mononuclear cell factor. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2249–2253. doi: 10.1172/JCI111651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG C. W., ROBINSON P. F., SACKTOR B. INHIBITION OF THE SYNTHESIS OF PROTEIN IN INTACT ANIMALS BY ACETOXYCYCLOHEXIMIDE AND A METABOLIC DERANGEMENT CONCOMITANT WITH THIS BLOCKADE. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Aug;12:855–865. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C. W., Dowling M. D., Jr Antipyretic effect of cycloheximide, and inhibitor of protein synthesis, in patients with Hodgkin's disease or other malignant neoplasms. Cancer Res. 1975 May;35(5):1218–1224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Miert A. S., van Duin C. T. Further studies on the antipyretic action of polymyxin B in pyrogen-induced fever. Arzneimittelforschung. 1978;28(12):2246–2251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


