Abstract
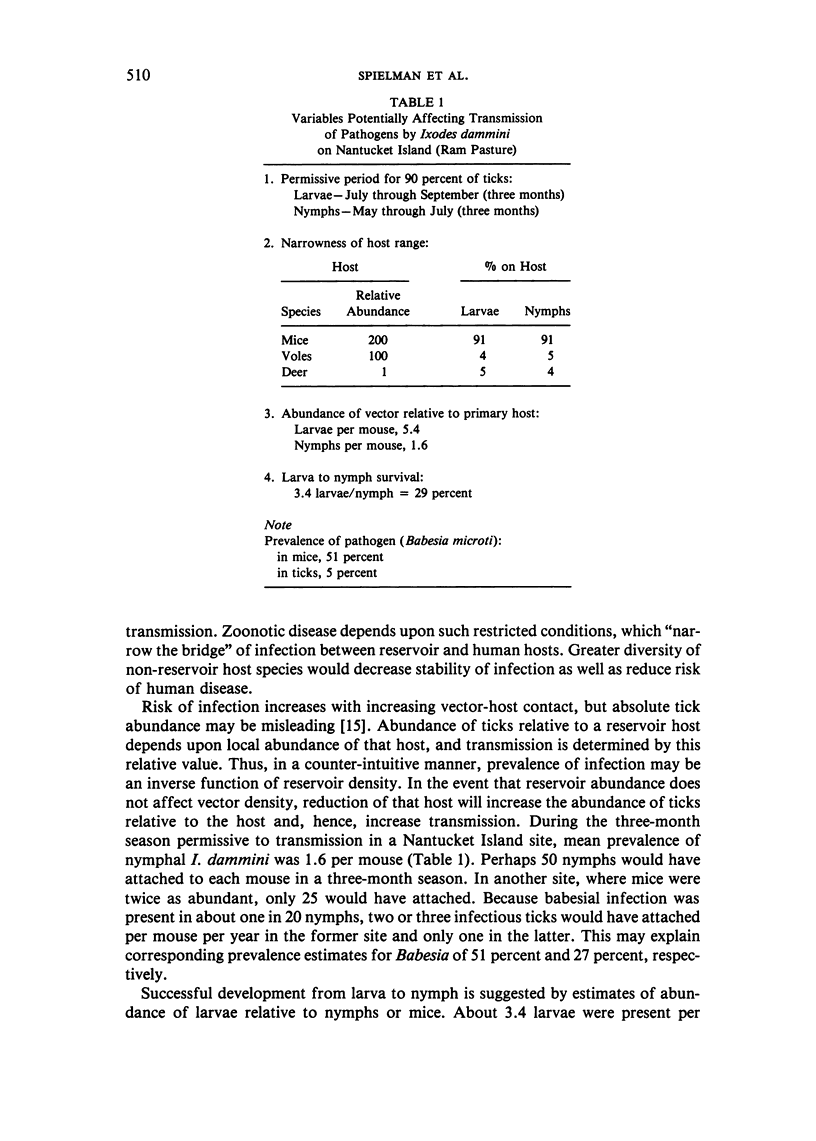
Ixodes dammini, the vector of Lyme disease and babesiosis, is distributed in various locations in the northeastern quadrant of the United States and nearby Canada. The life cycle of this tick, which includes larval, nymphal, and adult stages, spans at least two years. The tick over-winters between larval and nymphal feeding. Horizontal transmission of pathogens is facilitated by a feeding pattern in which both the larval and nymphal stages feed on the white-footed mouse, Peromyscus leucopus, and by a seasonal pattern of activity in which nymphs precede larvae. The species range appears to have expanded from a single island location, and has invaded new sites since the 1940s, some as recently as 1980. This increased abundance appears to be related to the increased abundance of deer, the preferred host of the adult stage. I. muris predominated in coastal Massachusetts before I. dammini became abundant, but is probably now extinct. I. scapularis, which is present in the southern U.S., is a poor vector of mouse parasites because about 90 percent of these immature ticks feed on lizards. To the extent that horizontal transmission occurs, we suggest that mice serve as the principal reservoir for the Lyme spirochete as well as Babesia microti.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A. Vertebrate host relationships and distribution of ixodid ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Connecticut, USA. J Med Entomol. 1980 Jul 31;17(4):314–323. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/17.4.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur D. R., Snow K. R. Ixodes pacificus Cooley and Kohls, 1943: its life-histor and occurrence. Parasitology. 1968 Nov;58(4):893–906. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000069663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dammin G. J., Spielman A., Benach J. L., Piesman J. The rising incidence of clinical Babesia microti infection. Hum Pathol. 1981 May;12(5):398–400. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine P. E. Vectors and vertical transmission: an epidemiologic perspective. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975;266:173–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb35099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARRETT-JONES C. THE HUMAN BLOOD INDEX OF MALARIA VECTORS IN RELATION TO EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;30:241–261. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrousse F., King A. G., Wolbach S. B. THE OVERWINTERING IN MASSACHUSETTS OF IXODIPHAGUS CAUCURTEI. Science. 1928 Mar 30;67(1735):351–353. doi: 10.1126/science.67.1735.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD G. The analysis of equilibrium in malaria. Trop Dis Bull. 1952 Sep;49(9):813–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Spielman A., Etkind P., Ruebush T. K., 2nd, Juranek D. D. Role of deer in the epizootiology of Babesia microti in Massachusetts, USA. J Med Entomol. 1979 Sep 4;15(5-6):537–540. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/15.5-6.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman A., Clifford C. M., Piesman J., Corwin M. D. Human babesiosis on Nantucket Island, USA: description of the vector, Ixodes (Ixodes) dammini, n. sp. (Acarina: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1979 Mar 23;15(3):218–234. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/15.3.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman A., Etkind P., Piesman J., Ruebush T. K., 2nd, Juranek D. D., Jacobs M. S. Reservoir hosts of human babesiosis on Nantucket Island. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 May;30(3):560–565. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman A. Human babesiosis on Nantucket Island: transmission by nymphal Ixodes ticks. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 Nov;25(6):784–787. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Broderick T. F., Malawista S. E. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis: epidemiologic evidence for a tick vector. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Oct;108(4):312–321. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E. Cases of Lyme disease in the United States: locations correlated with distribution of Ixodes dammini. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):730–733. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


