Abstract
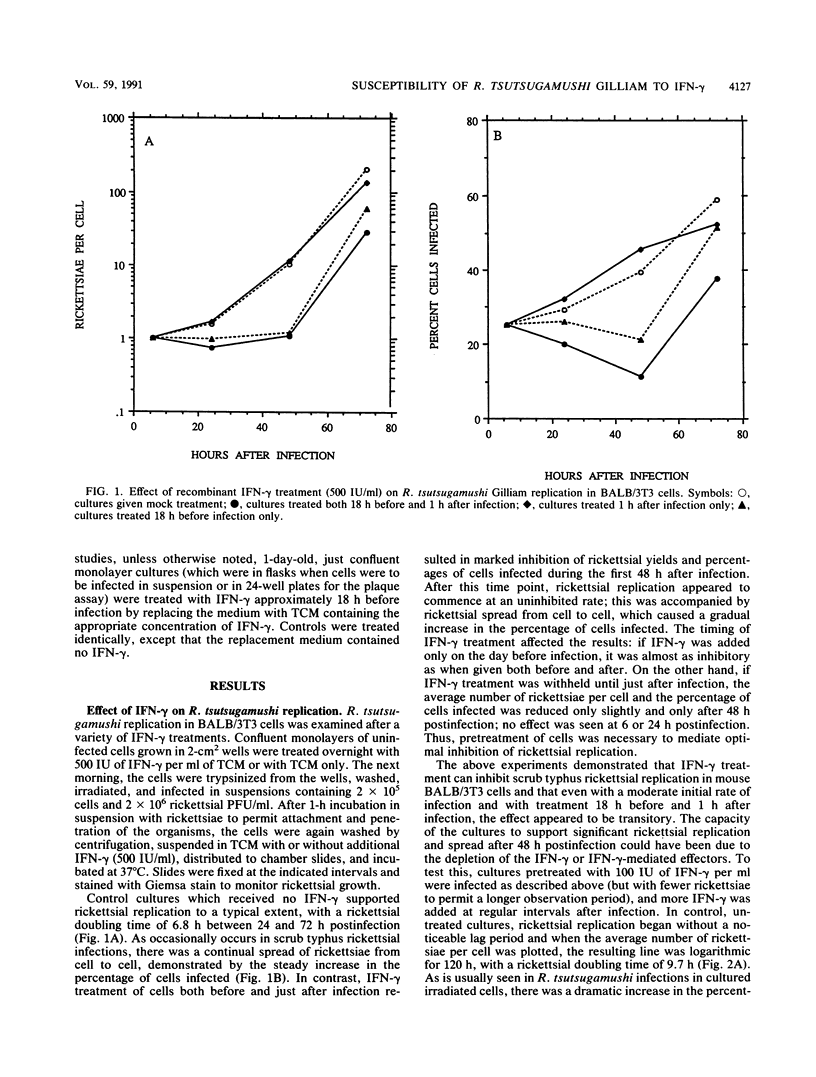
Recombinant rodent gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) inhibited the infection of cultured BALB/3T3 mouse fibroblasts by Rickettsia tsutsugamushi Gilliam, apparently mainly by clearance of intracellular rickettsiae. No significant effect on rickettsial entry into the cells was noted; IFN-gamma was toxic to infected cells, as measured by the capacity of treated, infected cells to attach to the surfaces of culture vessels. In a small proportion of IFN-gamma-treated cells, rickettsial replication appeared to persist at normal levels. A fraction (28%) of rickettsiae clonally isolated from cultures treated with IFN-gamma was resistant to IFN-gamma-mediated inhibition, but four serial passages of these resistant clones in the absence of additional IFN-gamma resulted in the loss of resistance. In several respects, therefore, the IFN-gamma-mediated inhibition of scrub typhus rickettsiae in cultured fibroblasts was similar to that reported for Rickettsia prowazekii.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano K., Tamura A., Ohashi N., Urakami H., Kaya S., Fukushi K. Deficiency of peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide components in Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2290–2292. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2290-2292.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. Comparative susceptibility to mouse interferons of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi strains with different virulence in mice and of Rickettsia rickettsii. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4134–4141. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4134-4141.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. Factors influencing Rickettsia tsutsugamushi infection of cultured cells. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 May;36(3):621–630. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. Improved plaque assay for Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 May;36(3):631–638. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Eisemann C. S. Role of T-lymphocytes in production of antibody to antigens of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi and other Rickettsia species. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):666–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.666-674.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Turco J., Winkler H. H., Spitalny G. L. Neutralization of lymphokine-mediated antirickettsial activity of fibroblasts and macrophages with monoclonal antibody specific for murine interferon gamma. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):355–359. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.355-359.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazar J., Krautwurst P. A., Gordon F. B. Effect of Interferon and Interferon Inducers on Infections with a Nonviral Intracellular Microorganism, Rickettsia akari. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):819–824. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.819-824.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazár J. Interferon-like inhibitor in mouse sera induced by rickettsiae. Acta Virol. 1966 May;10(3):277–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Kawamura S., Oyama T. Immunological studies of experimental tsutsugamushi disease in congenitally athymic (nude) mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 May;34(3):568–577. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama K., Kawamura S., Yasukawa M., Kobayashi Y. Establishment and characterization of a T-cell line specific for Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2490–2495. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2490-2495.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama K., Yasukawa M., Kobayashi Y. Effect of rickettsial antigen-specific T cell line on the interaction of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi with macrophages. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(4):435–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono S., Kohase M., Sakata H., Shimizu Y., Hikita M. Production of interferon in primary chick embryonic cells infected with Rickettsia mooseri. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1553–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopmans-Gargantiel A. I., Wisseman C. L., Jr Differential requirements for enriched atmospheric carbon dioxide content for intracellular growth in cell culture among selected members of the genus Rickettsia. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1277–1280. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1277-1280.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Jerrells T. R., Spitalny G. L., Walker D. H. Gamma interferon as a crucial host defense against Rickettsia conorii in vivo. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1252–1255. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1252-1255.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan J. G., Rice R. M., Jerrells T. R. Development of antigen-specific cell-mediated immune responses after infection of cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) with Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):739–749. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manor E., Sarov I. Inhibition of Rickettsia conorii growth by recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha: enhancement of inhibition by gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1886–1890. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1886-1890.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Groves M. G. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infections: early host defense mechanisms in experimental scrub typhus. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1239–1250. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1239-1250.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Leonard E. J., Meltzer M. S. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infections: characterization of lymphokines that induce rickettsiacidal activity in macrophages. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):204–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Meltzer M. S. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infection: macrophage activation in vitro for killing of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2544–2549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Meltzer M. S. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infection: strains of mice susceptible to the lethal effects of Rickettsia akari show defective macrophage Rickettsicidal activity in vitro. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1096–1101. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1096-1101.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: role of normal and activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):744–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.744-750.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer B. A., Hetrick F. M., Jerrells T. R. Gamma interferon production in response to homologous and heterologous strain antigens in mice chronically infected with Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):237–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.237-244.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patarca R., Freeman G. J., Singh R. P., Wei F. Y., Durfee T., Blattner F., Regnier D. C., Kozak C. A., Mock B. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Structural and functional studies of the early T lymphocyte activation 1 (Eta-1) gene. Definition of a novel T cell-dependent response associated with genetic resistance to bacterial infection. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):145–161. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R. Interferon gamma blocks the growth of Toxoplasma gondii in human fibroblasts by inducing the host cells to degrade tryptophan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):908–912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Wisseman C. L., Jr Comparative ultrastructural study on the cell envelopes of Rickettsia prowazekii, Rickettsia rickettsii, and Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1020–1023. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1020-1023.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Keysary A., Winkler H. H. Interferon-gamma- and rickettsia-induced killing of macrophage-like cells is inhibited by anti-rickettsial antibodies and does not require the respiratory burst. J Interferon Res. 1989 Oct;9(5):615–629. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Cloned mouse interferon-gamma inhibits the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2159–2164. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Effect of mouse lymphokines and cloned mouse interferon-gamma on the interaction of Rickettsia prowazekii with mouse macrophage-like RAW264.7 cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):303–308. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.303-308.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Gamma-interferon-induced inhibition of the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in fibroblasts cannot be explained by the degradation of tryptophan or other amino acids. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):38–46. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.38-46.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Inhibition of the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in cultured fibroblasts by lymphokines. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):974–986. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Interferon-alpha/beta and Rickettsia prowazekii: induction and sensitivity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:168–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Isolation of Rickettsia prowazekii with reduced sensitivity to gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1765–1772. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1765-1772.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Selection of alpha/beta interferon- and gamma interferon-resistant rickettsiae by passage of Rickettsia prowazekii in L929 cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3279–3285. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3279-3285.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. Interferonlike factors from antigen- and mitogen-stimulated human leukocytes with antirickettsial and cytolytic actions on Rickettsia prowazekii. Infected human endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1780–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


