Abstract
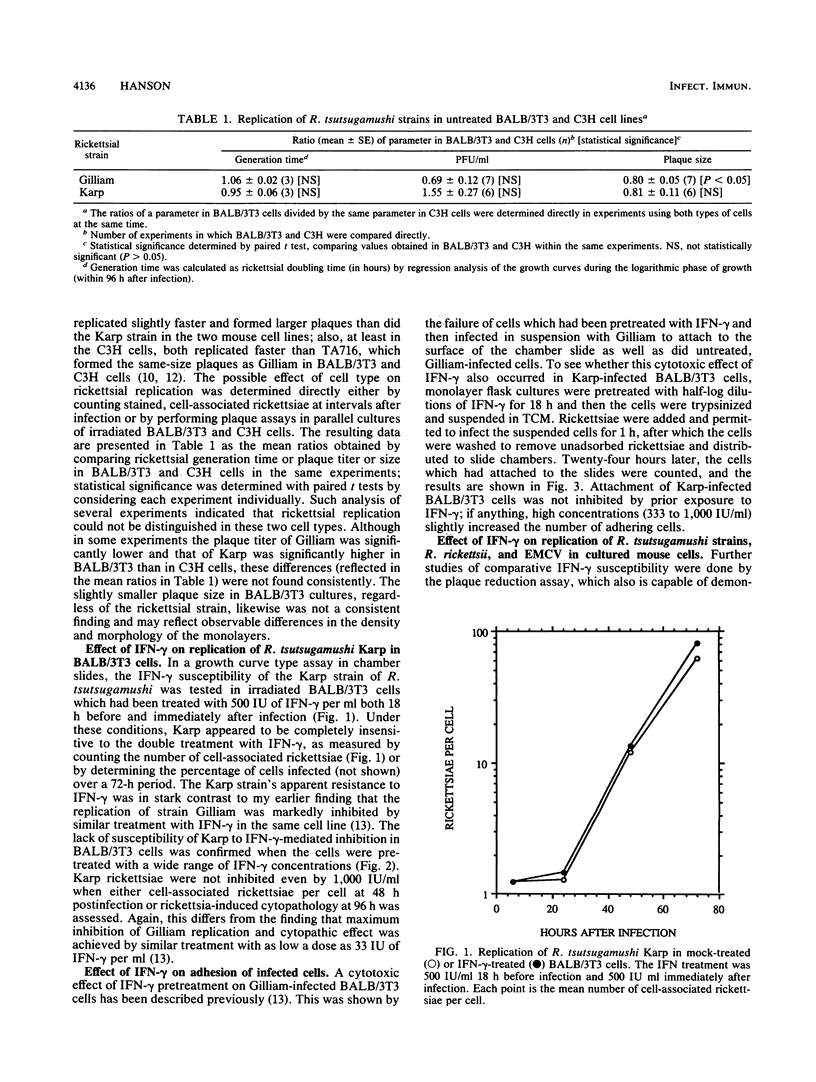
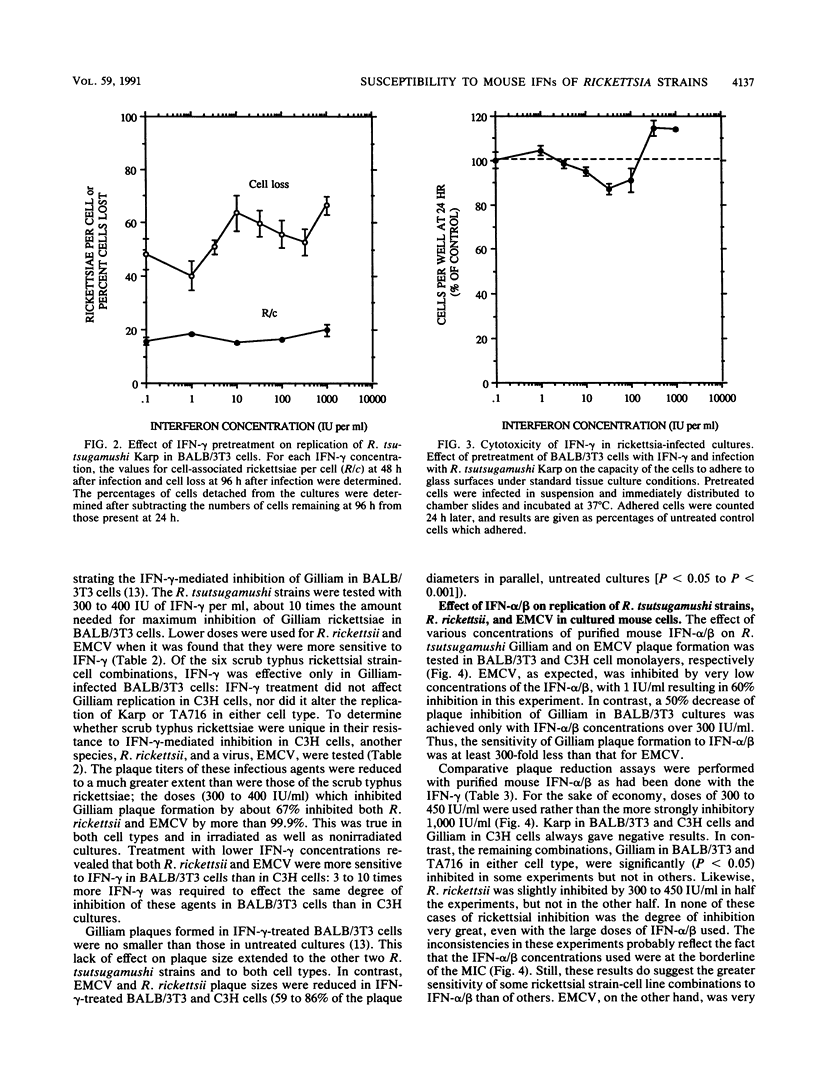
Three strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi (Karp, Gilliam, and TA716, representing three virulence types in mice) were examined for their sensitivity to the inhibitory effects of recombinant gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and purified IFN-alpha/beta in two cultured mouse fibroblast cell lines. The susceptibilities of another species, Rickettsia rickettsii, and of encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) were also tested for comparative purposes. IFN-gamma inhibited rickettsial replication in only one of the six combinations of R. tsutsugamushi strains and mouse cells (strain Gilliam and the BALB/c mouse-derived cell line). In contrast, R. rickettsii and EMCV replication were markedly inhibited in both cell types, but to a greater extent in the BALB/c line than in the C3H cells. IFN-alpha/beta (300 to 450 U/ml) was uniformly ineffective in three of the combinations of R. tsutsugamushi strains and mouse cells (Gilliam in C3H cells and Karp in both C3H and BALB/c cells); in the remaining sets, IFN-alpha/beta-mediated inhibition of rickettsial replication was variable and in no case was it very pronounced. The tests with R. rickettsii in both cell types also indicated slight, variable sensitivity to IFN-alpha/beta. EMCV, on the other hand, was very susceptible to IFN-alpha/beta, confirming the potency of the preparation used; as with IFN-gamma, virus replication was inhibited to a greater degree in the BALB/c cell line than in the C3H cultures. These results are discussed in terms of their relationship to the virulence properties of the R. tsutsugamushi strains in BALB/c and C3H mice and to the known IFN-sensitivities of the more widely studied Rickettsia prowazekii.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bang F. B. Genetics of resistance of animals to viruses: I. Introduction and studies in mice. Adv Virus Res. 1978;23:269–348. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60102-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. G., Kelly D. J. Characterization of factors determining Rickettsia tsutsugamushi pathogenicity for mice. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1476–1482. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1476-1482.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. G., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: genetics of natural resistance to infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):583–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.583-588.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. G., Rosenstreich D. L., Taylor B. A., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: mapping the gene that controls natural resistance in mice. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1395–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gröschel D., Koprowski H. Development of a virus-resistant inbred mouse strain for the study of innate resistance to Arbo B viruses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;17(3):379–391. doi: 10.1007/BF01241192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. Factors influencing Rickettsia tsutsugamushi infection of cultured cells. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 May;36(3):621–630. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. Improved plaque assay for Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 May;36(3):631–638. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. Susceptibility of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi Gilliam to gamma interferon in cultured mouse cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4125–4133. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4125-4133.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: inflammatory response of congenic C3H mice differing at the Ric gene. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1014–1022. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1014-1022.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Osterman J. V. Role of macrophages in innate and acquired host resistance to experimental scrub typhus infection of inbred mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1066–1073. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1066-1073.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Turco J., Winkler H. H., Spitalny G. L. Neutralization of lymphokine-mediated antirickettsial activity of fibroblasts and macrophages with monoclonal antibody specific for murine interferon gamma. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):355–359. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.355-359.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazar J., Krautwurst P. A., Gordon F. B. Effect of Interferon and Interferon Inducers on Infections with a Nonviral Intracellular Microorganism, Rickettsia akari. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):819–824. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.819-824.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazár J. Interferon-like inhibitor in mouse sera induced by rickettsiae. Acta Virol. 1966 May;10(3):277–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Kawamura S., Oyama T. Immunological studies of experimental tsutsugamushi disease in congenitally athymic (nude) mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 May;34(3):568–577. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama K., Kawamura S., Yasukawa M., Kobayashi Y. Establishment and characterization of a T-cell line specific for Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2490–2495. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2490-2495.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama K., Yasukawa M., Kobayashi Y. Effect of rickettsial antigen-specific T cell line on the interaction of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi with macrophages. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(4):435–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokorin I. N., Kyet C. D., Kekcheeva N. G., Miskarova E. D. Cytological investigation of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi infection of mice with different allotypic susceptibility to the agent. Acta Virol. 1976 Apr;20(2):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Groves M. G. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infections: early host defense mechanisms in experimental scrub typhus. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1239–1250. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1239-1250.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Leonard E. J., Meltzer M. S. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infections: characterization of lymphokines that induce rickettsiacidal activity in macrophages. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):204–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Meltzer M. S. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infection: macrophage activation in vitro for killing of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2544–2549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: role of normal and activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):744–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.744-750.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patarca R., Freeman G. J., Singh R. P., Wei F. Y., Durfee T., Blattner F., Regnier D. C., Kozak C. A., Mock B. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Structural and functional studies of the early T lymphocyte activation 1 (Eta-1) gene. Definition of a novel T cell-dependent response associated with genetic resistance to bacterial infection. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):145–161. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patarca R., Wei F. Y., Singh P., Morasso M. I., Cantor H. Dysregulated expression of the T cell cytokine Eta-1 in CD4-8- lymphocytes during the development of murine autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1177–1183. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. M., Huxsoll D. L. Protection against scrub typhus infection engendered by the passive transfer of immune sera. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1975 Dec;6(4):477–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Catanzaro P. J., Phillips S. M., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: role of cellular immunity in heterologous protection. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):39–46. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.39-46.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Wisseman C. L., Jr Serologic classification of scrub typhus isolates from Pakistan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1975 Jan;24(1):145–153. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1975.24.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R. P., Patarca R., Schwartz J., Singh P., Cantor H. Definition of a specific interaction between the early T lymphocyte activation 1 (Eta-1) protein and murine macrophages in vitro and its effect upon macrophages in vivo. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):1931–1942. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Comparison of properties of virulent, avirulent, and interferon-resistant Rickettsia prowazekii strains. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1647–1655. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1647-1655.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Effect of mouse lymphokines and cloned mouse interferon-gamma on the interaction of Rickettsia prowazekii with mouse macrophage-like RAW264.7 cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):303–308. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.303-308.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Inhibition of the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in cultured fibroblasts by lymphokines. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):974–986. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Interferon-alpha/beta and Rickettsia prowazekii: induction and sensitivity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:168–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Selection of alpha/beta interferon- and gamma interferon-resistant rickettsiae by passage of Rickettsia prowazekii in L929 cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3279–3285. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3279-3285.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


