Abstract
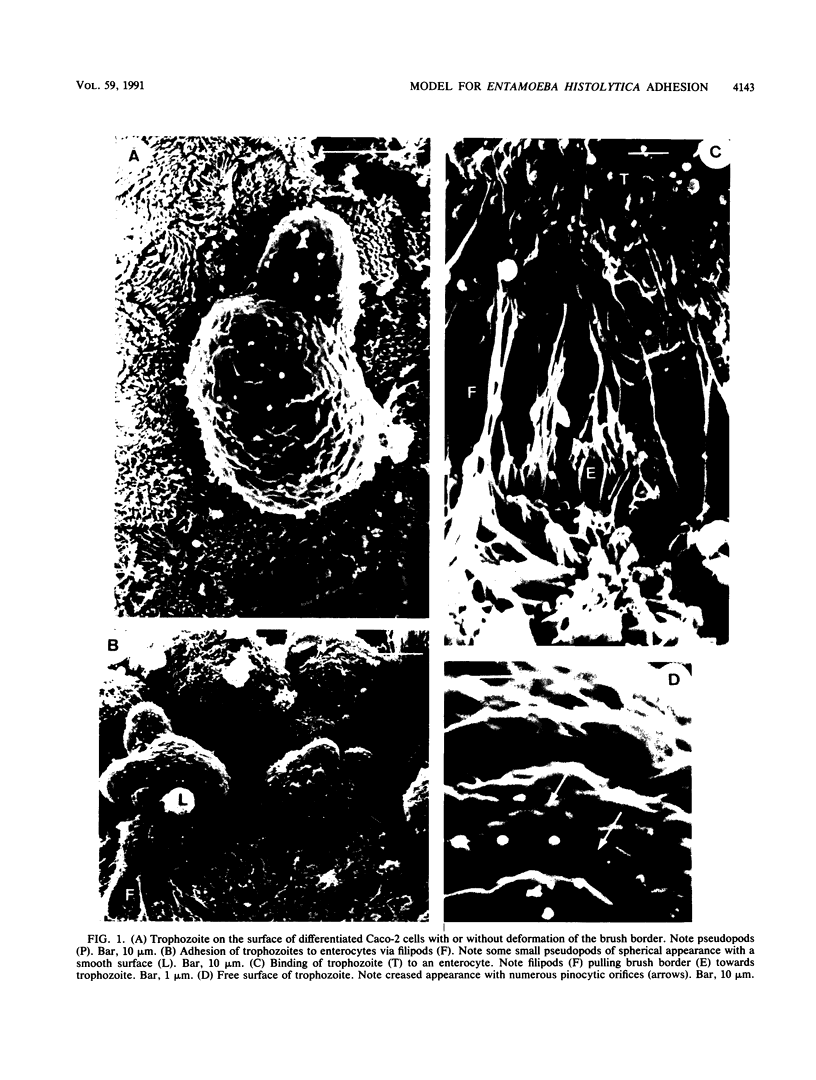
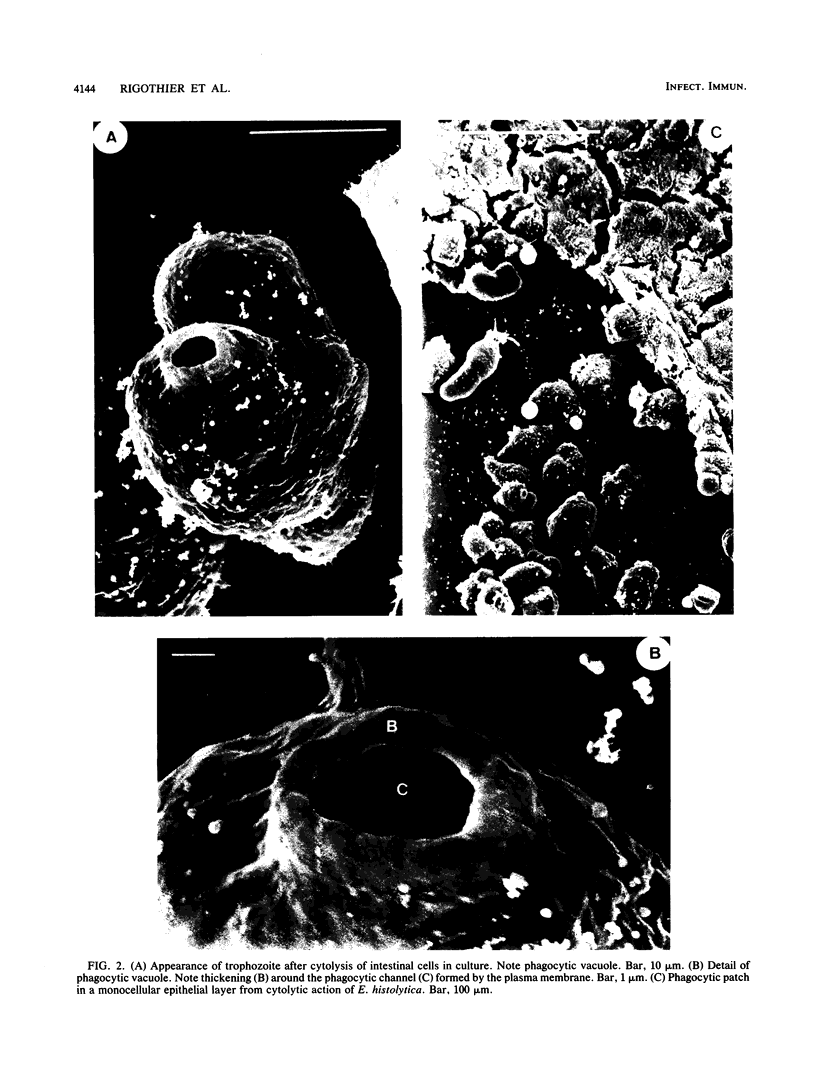
The human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2, which is widely used to study the adhesion and cytotoxicity of enterobacteria, was used to investigate the adhesion of the trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica. We observed a high percentage of adhesion of amoebae to Caco-2 cells. Scanning electron microscopy showed that amoebial membrane structures were involved in adhesion and the cytolytic action. These differentiated cells should prove to be a useful model system for investigation of the pathogenic action of amoebae.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bos H. J., van den Eijk A. A. Serum-inhibited toxicity of Entamoeba histolytica. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1980;11(1 Suppl):135–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cano-Mancera R., López-Revilla R. Inhibition of the adhesion of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites to human erythrocytes by carbohydrates. Parasitol Res. 1987;74(1):18–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00534926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darfeuille-Michaud A., Aubel D., Chauviere G., Rich C., Bourges M., Servin A., Joly B. Adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2 in culture. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):893–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.893-902.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanigan T. P., Aji T., Marshall R., Soave R., Aikawa M., Kaetzel C. Asexual development of Cryptosporidium parvum within a differentiated human enterocyte cell line. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):234–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.234-239.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogh J., Fogh J. M., Orfeo T. One hundred and twenty-seven cultured human tumor cell lines producing tumors in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jul;59(1):221–226. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.1.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Rivera G., Sánchez T., Orozco E., Guarneros G. Aislamiento de clonas de E. histolytica deficientes en adhesión a eritrocitos humanos. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1982;13 (Suppl 3):129–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Diamond L. S. Clonal growth of Entamoeba histolytica and other species of Entamoeba in agar. J Protozool. 1978 Nov;25(4):539–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb04182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitler C., Calef E., Rosenberg I. Cytopathogenicity of Entamoeba histolytica. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Nov 13;307(1131):73–85. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Robles A., Martínez-Palomo A. Morfología de trofozoítos de Entamoeba histolytica en substratos naturales. Estudio mediante microscopia electrónica de barrido. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1982;13 (Suppl 3):145–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Robles A., Martínez-Palomo A. Scanning electron microscopy of attached trophozoites of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Protozool. 1983 Nov;30(4):692–700. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1983.tb05345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobiler D., Mirelman D. Adhesion of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites to monolayers of human cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Dec;144(6):539–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.6.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitch G. J., Dickey A. D., Udezulu I. A., Bailey G. B. Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites in the lumen and mucus blanket of rat colons studied in vivo. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):68–73. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.68-73.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lushbaugh W. B., Pittman F. E. Microscopic observations on the filopodia of Entamoeba histolytica. J Protozool. 1979 May;26(2):186–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1979.tb02759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Palomo A., González-Robles A., Chávez B., Orozco E., Fernández-Castelo S., Cervantes A. Structural bases of the cytolytic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. J Protozool. 1985 Feb;32(1):166–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco M. E., Fernández Castelo S., Martínez Palomo A. Detección del daño celular temprano producido por Entamoeba histolytica sobre epitelios. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1982;13 (Suppl 3):169–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco M. E., Martínez Palomo A., González Robles A., Guarneros G., Galindo J. M. Las interacciones entre lectina y receptor median la adherencia de E. histolytica a células epiteliales. Relación de la adhesión con la virulencia de las cepas. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1982;13 (Suppl 3):159–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi P., Tall B. D., Russell R. G., Detolla L. J., Morris J. G., Jr Development of an in vitro model for study of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae virulence using Caco-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3415–3424. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3415-3424.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman F. E., el-Hashimi W. K., Pittman J. C. Studies of human amebiasis. II. Light and electron-microscopic observations of colonic mucosa and exudate in acute amebic colitis. Gastroenterology. 1973 Oct;65(4):588–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Croft B. Y., Guerrant R. L. Cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):377–390. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Guerrant R. L. Role of adherence in cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. Study with mammalian tissue culture cells and human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., John J. E., Johnston L. I., Innes D. J., Guerrant R. L. Adherence of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites to rat and human colonic mucosa. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):292–297. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.292-297.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. L., Sargeaunt P. G., Braude A. I. Resistance to lysis by human serum of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(2):248–253. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez M. A., Hernández F., Santos L., Valdez A., Orozco E. Entamoeba histolytica: molecules involved in the target cell-parasite relationship. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Nov;37(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales-Encina J. L., Meza I., López-De-León A., Talamás-Rohana P., Rojkind M. Isolation of a 220-kilodalton protein with lectin properties from a virulent strain of Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):790–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepulveda B. Progress in amebiasis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1982;77:153–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]