Abstract
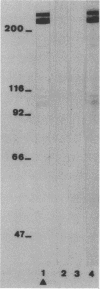
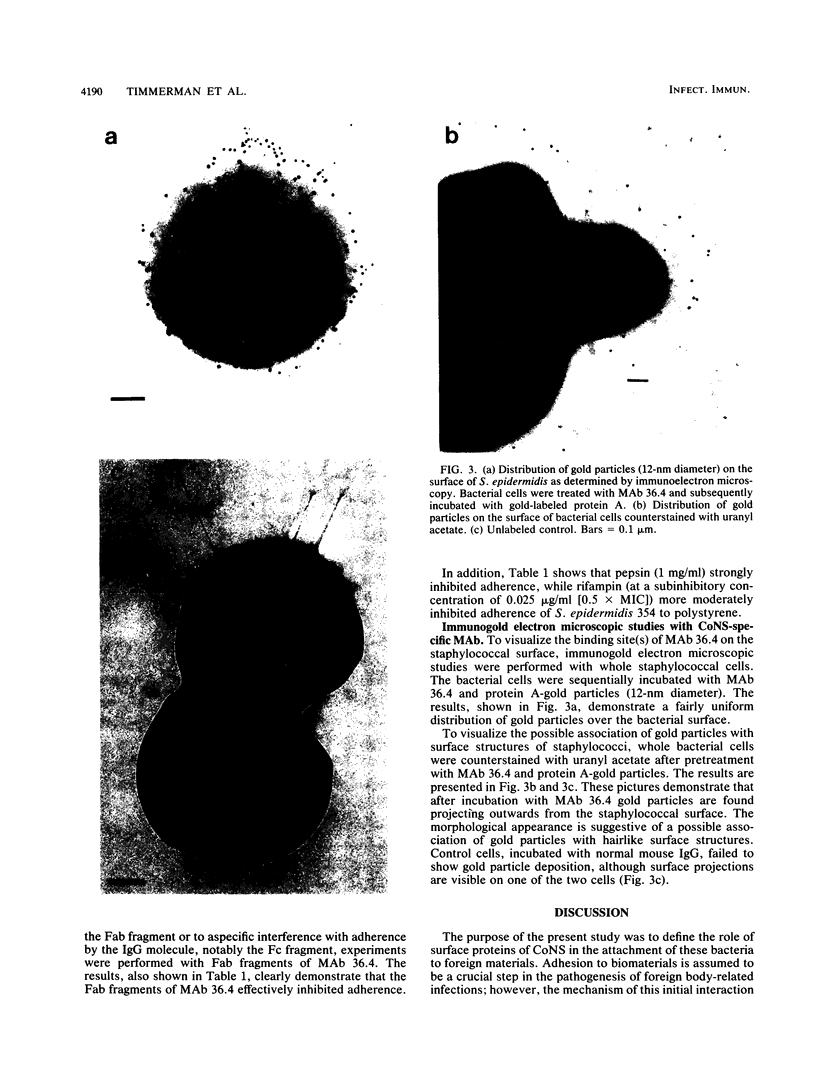
Coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) have evolved into important agents of foreign body-related infections. Adhesion of causative bacteria to biomaterials is considered to be an essential step in these infections. We and others have shown that adhesion of CoNS to biomaterials may be mediated by protease-sensitive surface constituents. In the present study we expanded on these investigations by characterizing a biomaterial adhesin of Staphylococcus epidermidis 354 by using a strain-specific monoclonal antibody (MAb 36.4). MAb 36.4 was strongly and exclusively reactive with strain 354 in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in which whole bacteria were used as antigens. Immunoblotting of cell wall polypeptides of strain 354 revealed strong reactivity with a 200- to 220-kDa band and a weaker reaction in the 100- to 110-kDa range. Preincubation of strain 354 with MAb 36.4 resulted in a 54 to 91% (mean +/- standard deviation, 74% +/- 14%; n = 10) inhibition of adhesion to polystyrene spheres. Fab fragments prepared from MAb 36.4 also inhibited adhesion effectively, indicating specific blocking of an adhesion antigen rather than aspecific inhibition. Immunogold electron microscopy with MAb 36.4 revealed deposition of gold particles on the cell surface and possibly also on fimbrialike surface projections. It is concluded that a surface-located protein antigen of S. epidermidis 354 recognized by MAb 36.4 acts as an adhesin mediating attachment to uncoated foreign material. It is speculated that this type of adhesion to biomaterials may play an important role in the pathogenesis of foreign body-related infections caused by CoNS.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christensen G. D., Parisi J. T., Bisno A. L., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Characterization of clinically significant strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):258–269. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.258-269.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. P., SMITH I. W., DEMPSTER G., EDMUNDS P. N. Non-flagellar filamentous appendages (fimbriae) and haemagglutinating activity in Bacterium coli. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(2):335–348. doi: 10.1002/path.1700700210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport D. S., Massanari R. M., Pfaller M. A., Bale M. J., Streed S. A., Hierholzer W. J., Jr Usefulness of a test for slime production as a marker for clinically significant infections with coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):332–339. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder B. L., Fives-Taylor P. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for adhesion: isolation of an adhesin of Streptococcus sanguis FW213. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):421–427. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.421-427.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. S., Carter P. L., Fielding J. Streptococcus salivarius strains carry either fibrils or fimbriae on the cell surface. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):64–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.64-72.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann M., Vaudaux P. E., Pittet D., Auckenthaler R., Lew P. D., Schumacher-Perdreau F., Peters G., Waldvogel F. A. Fibronectin, fibrinogen, and laminin act as mediators of adherence of clinical staphylococcal isolates to foreign material. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):693–701. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogt A. H., Dankert J., de Vries J. A., Feijen J. Adhesion of coagulase-negative staphylococci to biomaterials. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2959–2968. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak M. A., Gröschel D. H., Mandell G. L., Wenzel R. P. Association of slime with pathogenicity of coagulase-negative staphylococci causing nosocomial septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1025–1029. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1025-1029.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. Fimbrial adhesions of Escherichia coli. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7(3):321–340. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.3.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont R. J., Rosan B., Baker C. T., Nelson G. M. Characterization of an adhesion antigen of Streptococcus sanguis G9B. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2417–2423. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2417-2423.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Bloomquist C. G. Isolation of a protein-containing cell surface component from Streptococcus sanguis which affects its adherence to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.428-434.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwicka A., Uhlenbruck G., Peters G., Seng P. N., Gray E. D., Jeljaszewicz J., Pulverer G. Investigation on extracellular slime substance produced by Staphylococcus epidermidis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1984 Dec;258(2-3):256–267. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(84)80043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki D. G., Cobb L., Garman J. K., Shapiro J. M., Ringer M., Helgerson R. B. An attachable silver-impregnated cuff for prevention of infection with central venous catheters: a prospective randomized multicenter trial. Am J Med. 1988 Sep;85(3):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90579-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., Ganeshkumar N., McBride B. C. Cell surface components of Streptococcus sanguis: relationship to aggregation, adherence, and hydrophobicity. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):255–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.255-262.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., Ganeshkumar N., Song M., McBride B. C. Identification and preliminary characterization of a Streptococcus sanguis fibrillar glycoprotein. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.164-171.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascual A., Fleer A., Westerdaal N. A., Verhoef J. Modulation of adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to Teflon catheters in vitro. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;5(5):518–522. doi: 10.1007/BF02017694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Adherence and growth of coagulase-negative staphylococci on surfaces of intravenous catheters. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):479–482. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Naumann G., Putzke H. P. Detection of different fimbriae-like structures on the surface of Staphylococcus saprophyticus. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Apr;268(2):228–237. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snydman D. R., Gorbea H. F., Pober B. R., Majka J. A., Murray S. A., Perry L. K. Predictive value of surveillance skin cultures in total-parenteral-nutrition-related infection. Lancet. 1982 Dec 18;2(8312):1385–1388. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Stock A. M., Mottonen J. M. Signal transduction in bacteria. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):395–400. doi: 10.1038/344395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo M., Yamashita N., Goldmann D. A., Pier G. B. Isolation and characterization of a capsular polysaccharide adhesin from Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):713–722. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P., Pittet D., Haeberli A., Huggler E., Nydegger U. E., Lew D. P., Waldvogel F. A. Host factors selectively increase staphylococcal adherence on inserted catheters: a role for fibronectin and fibrinogen or fibrin. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):865–875. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P., Suzuki R., Waldvogel F. A., Morgenthaler J. J., Nydegger U. E. Foreign body infection: role of fibronectin as a ligand for the adherence of Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):546–553. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef J., Peterson P. K., Quie P. G. Kinetics of staphylococcal opsonization, attachment, ingestion and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a quantitative assay using [3H]thymidine labeled bacteria. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorhout W. F., Leunissen-Bijvelt J. J., Leunissen J. L., Verkleij A. J. Steric hindrance in immunolabelling. J Microsc. 1986 Mar;141(Pt 3):303–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1986.tb02724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., Handley P. S., Baars A., Slot J. W. Negative staining and immunoelectron microscopy of adhesion-deficient mutants of Streptococcus salivarius reveal that the adhesive protein antigens are separate classes of cell surface fibril. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):746–755. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.746-755.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]