Abstract
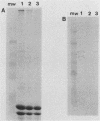
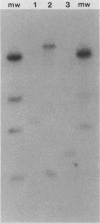
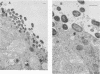
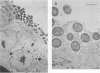
The ability to attach to epithelial cells, efface the microvillus surface, and disrupt the underlying cytoskeleton is characteristic of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC). Recently, eae, a gene necessary for this phenomenon, was described (A. E. Jerse, J. Yu, B. D. Tall, and J. B. Kaper, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:7839-7843, 1990). We report the use of a novel suicide vector containing the pir-dependent R6K replicon and the sacB gene of Bacillus subtilis to construct an eae deletion mutant of EPEC. This system enables positive selection for the loss of vector sequences. The resulting mutant, CVD206, is indistinguishable from the wild-type strain except for the loss of a 94-kDa outer membrane protein and attaching and effacing ability. Both the 94-kDa outer membrane protein and attaching and effacing ability are restored upon reintroduction of the eae gene on a plasmid. These results confirm the role of the eae gene in the attaching and effacing activity of EPEC and establish the utility of a new system for the construction of deletion mutations.
Full text
PDF
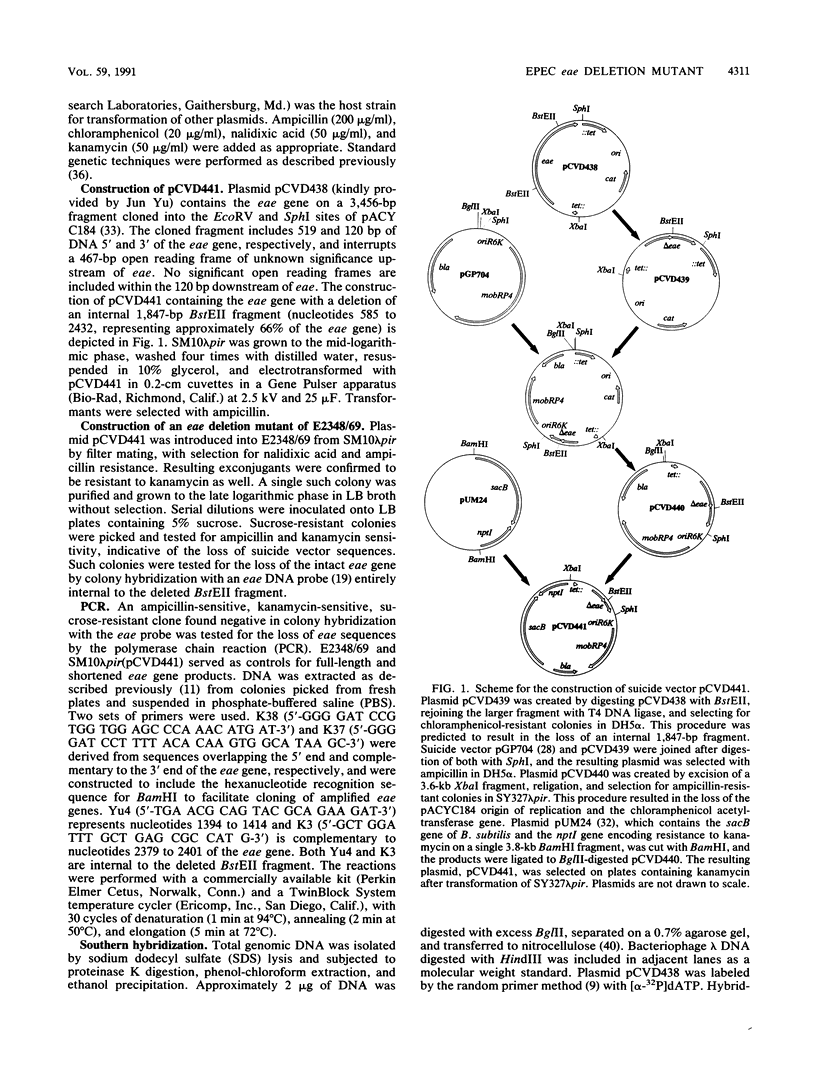


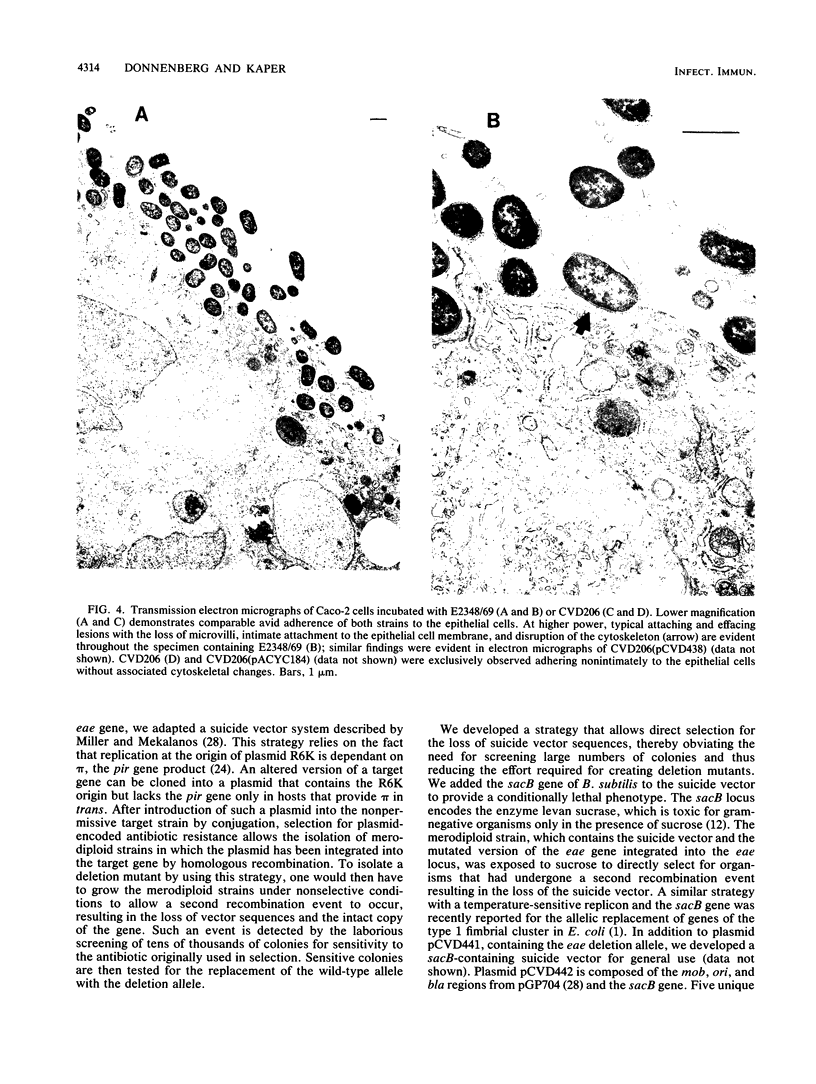
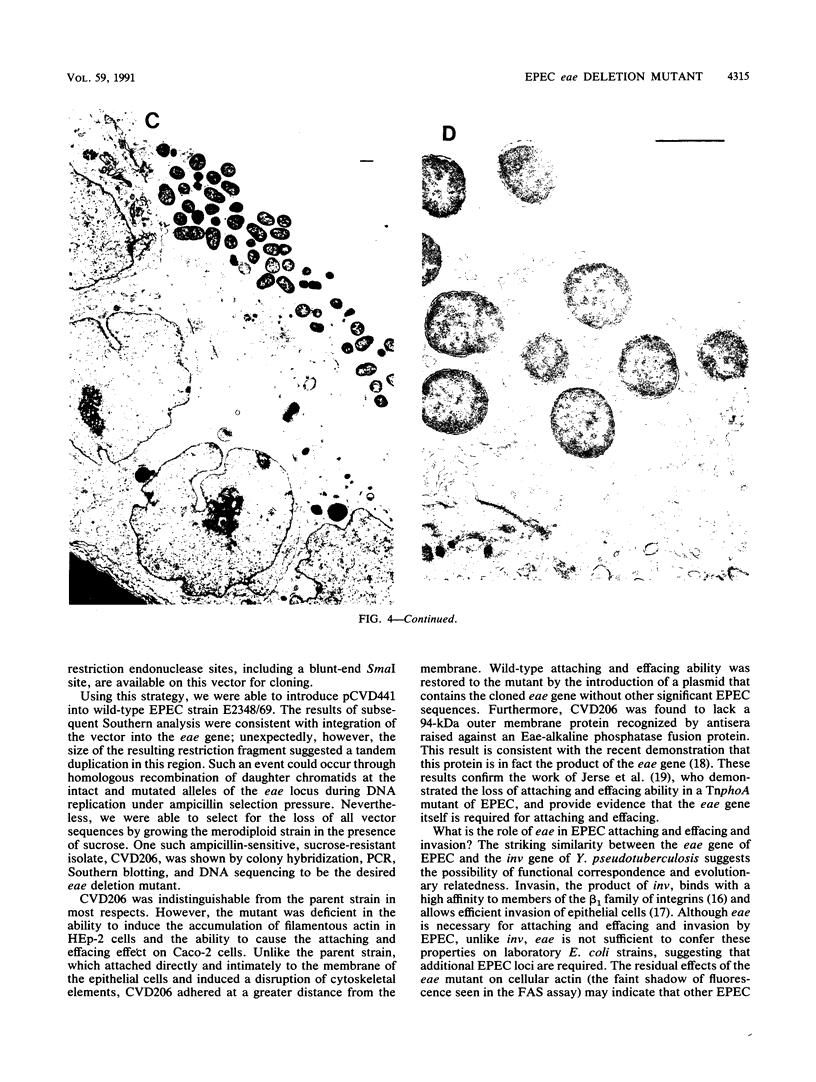


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blomfield I. C., Vaughn V., Rest R. F., Eisenstein B. I. Allelic exchange in Escherichia coli using the Bacillus subtilis sacB gene and a temperature-sensitive pSC101 replicon. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1447–1457. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chart H., Scotland S. M., Willshaw G. A., Rowe B. HEp-2 adhesion and the expression of a 94 kDa outer-membrane protein by strains of Escherichia coli belonging to enteropathogenic serogroups. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 May;134(5):1315–1321. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-5-1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobeljić M., Mel D., Arsić B., Krstić L., Sokolovski B., Nikolovski B., Sopovski E., Kulauzov M., Kalenić S. The association of enterotoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and other enteric pathogens with childhood diarrhoea in Yugoslavia. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Aug;103(1):53–62. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800030351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cravioto A., Tello A., Navarro A., Ruiz J., Villafán H., Uribe F., Eslava C. Association of Escherichia coli HEp-2 adherence patterns with type and duration of diarrhoea. Lancet. 1991 Feb 2;337(8736):262–264. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90868-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Calderwood S. B., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T., Kaper J. B. Construction and analysis of TnphoA mutants of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli unable to invade HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1565–1571. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1565-1571.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. H., Collins J. E., Duimstra J. R. Infection of gnotobiotic pigs with an Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain associated with an outbreak of hemorrhagic colitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):953–956. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.953-956.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel G., Riley L., Giron J. A., Valmassoi J., Friedmann A., Strockbine N., Falkow S., Schoolnik G. K. Detection of Shigella in feces using DNA amplification. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1252–1256. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay P., Le Coq D., Steinmetz M., Berkelman T., Kado C. I. Positive selection procedure for entrapment of insertion sequence elements in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):918–921. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.918-921.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes T. A., Blake P. A., Trabulsi L. R. Prevalence of Escherichia coli strains with localized, diffuse, and aggregative adherence to HeLa cells in infants with diarrhea and matched controls. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Feb;27(2):266–269. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.2.266-269.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Leong J. M. Multiple beta 1 chain integrins are receptors for invasin, a protein that promotes bacterial penetration into mammalian cells. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):861–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90099-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Voorhis D. L., Falkow S. Identification of invasin: a protein that allows enteric bacteria to penetrate cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Kaper J. B. The eae gene of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli encodes a 94-kilodalton membrane protein, the expression of which is influenced by the EAF plasmid. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4302–4309. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4302-4309.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerse A. E., Yu J., Tall B. D., Kaper J. B. A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7839–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kain K. C., Barteluk R. L., Kelly M. T., He X., de Hua G., Ge Y. A., Proctor E. M., Byrne S., Stiver H. G. Etiology of childhood diarrhea in Beijing, China. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jan;29(1):90–95. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.1.90-95.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., McNeish A. S. Role of plasmid-encoded adherence factors in adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):78–85. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.78-85.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Baldwin T., Williams P. H., McNeish A. S. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1290–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1290-1298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutton S., Lloyd D. R., McNeish A. S. Adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to human intestinal enterocytes and cultured human intestinal mucosa. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.69-77.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Inuzuka M., Helinski D. R. Trans-complementation-dependent replication of a low molecular weight origin fragment from plasmid R6K. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1199–1208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Bergquist E. J., Nalin D. R., Waterman D. H., Hornick R. B., Young C. R., Sotman S. Escherichia coli strains that cause diarrhoea but do not produce heat-labile or heat-stable enterotoxins and are non-invasive. Lancet. 1978 May 27;1(8074):1119–1122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nataro J. P., Karch H., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Clements M. L., O'Brien A. D. The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):550–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Synthesis of cholera toxin is positively regulated at the transcriptional level by toxR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3471–3475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Argenzio R. A., Levine M. M., Giannella R. A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1340-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Scaletsky I. C., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M., Trabulsi L. R. Plasmid-mediated factors conferring diffuse and localized adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):378–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.378-383.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polotsky Y. E., Dragunskaya E. M., Seliverstova V. G., Avdeeva T. A., Chakhutinskaya M. G., Kétyi I., Vertényl A., Ralovich B., Emödy L., Málovics I. Pathogenic effect of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Escherichia coli causing infantile diarrhoea. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1977;24(3):221–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ried J. L., Collmer A. An nptI-sacB-sacR cartridge for constructing directed, unmarked mutations in gram-negative bacteria by marker exchange-eviction mutagenesis. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose R. E. The nucleotide sequence of pACYC184. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):355–355. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbaum R., McAdams A. J., Giannella R., Partin J. C. A clinicopathologic study of enterocyte-adherent Escherichia coli: a cause of protracted diarrhea in infants. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):441–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset M. The human colon carcinoma cell lines HT-29 and Caco-2: two in vitro models for the study of intestinal differentiation. Biochimie. 1986 Sep;68(9):1035–1040. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaletsky I. C., Silva M. L., Trabulsi L. R. Distinctive patterns of adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):534–536. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.534-536.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senerwa D., Olsvik O., Mutanda L. N., Lindqvist K. J., Gathuma J. M., Fossum K., Wachsmuth K. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli serotype O111:HNT isolated from preterm neonates in Nairobi, Kenya. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1307–1311. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1307-1311.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staley T. E., Jones E. W., Corley L. D. Attachment and penetration of Escherichia coli into intestinal epithelium of the ileum in newborn pigs. Am J Pathol. 1969 Sep;56(3):371–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Robins-Browne R. M., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., McCartney E. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli enteritis: evaluation of the gnotobiotic piglet as a model of human infection. Gut. 1985 Jun;26(6):570–578. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.6.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulshen M. H., Rollo J. L. Pathogenesis of escherichia coli gastroenteritis in man--another mechanism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):99–101. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]