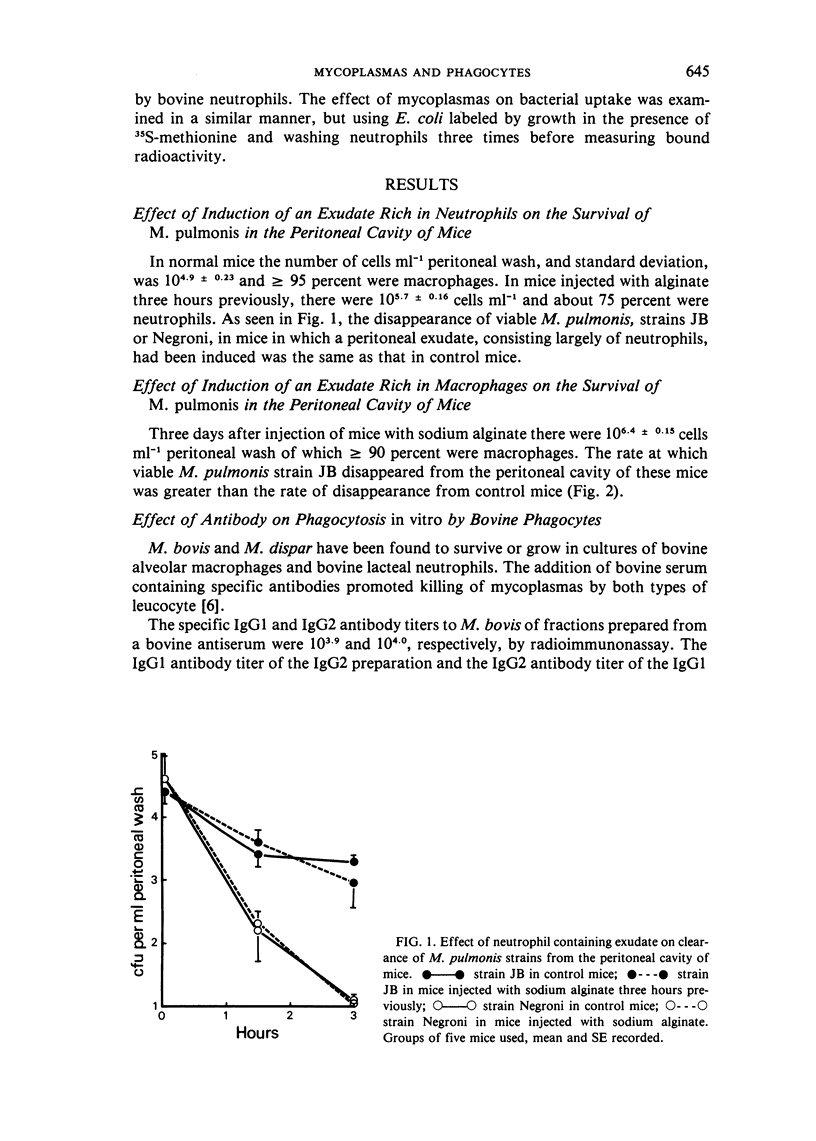
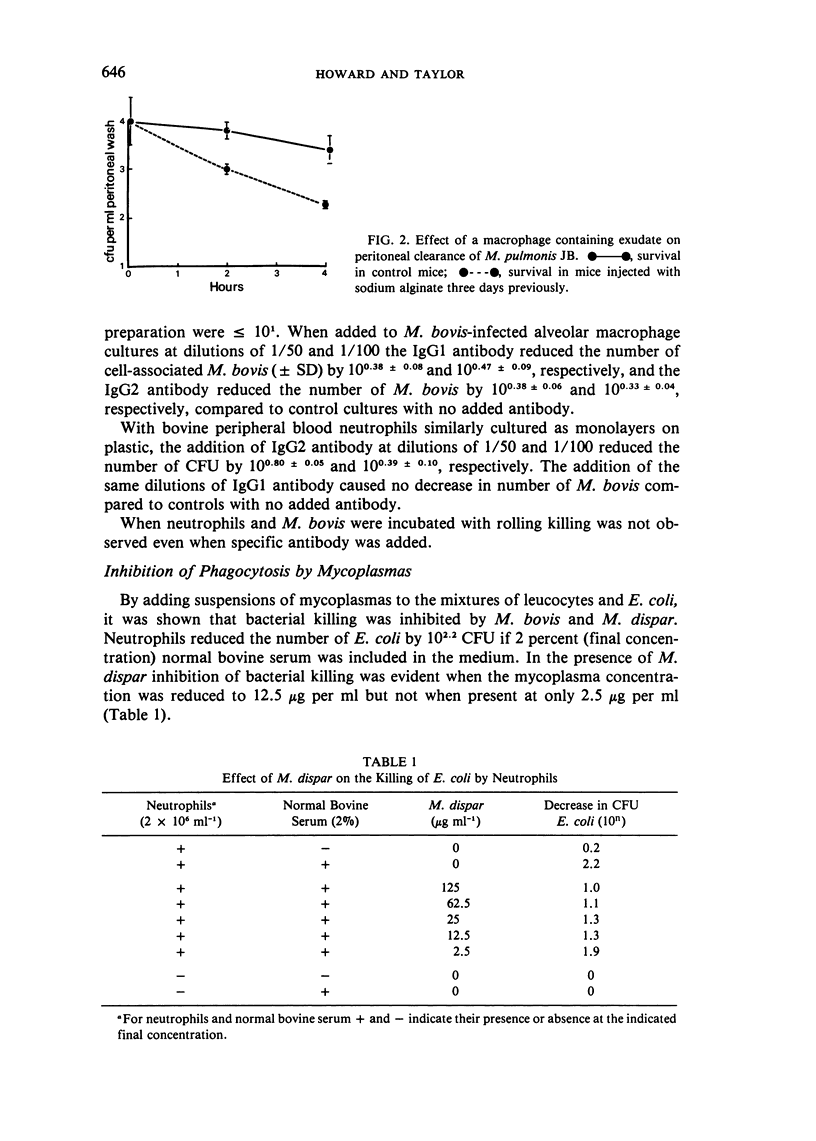
Abstract
Aspects of the interaction of certain mycoplasmas with macrophages and neutrophils in vivo and in vitro have been studied using two systems, one involving M. pulmonis in mice and the other involving M. bovis with bovine leucocytes. Studies with M. pulmonis indicated that the disappearance of viable organisms from the peritoneal cavity was not enhanced in SPF mice in which a peritoneal exudate rich in neutrophils had been induced. However, viable M. pulmonis organisms disappeared more rapidly from the peritoneal cavities with exudates containing increased numbers of macrophages. Experiments in vitro studied the opsonic effect of bovine IgG isotypes for bovine neutrophils and alveolar macrophages. Both IgG1 and IgG2 promoted killing of M. bovis by alveolar macrophages but IgG2 was more effective than IgG1 at promoting mycoplasma killing by neutrophils. Further studies in vitro indicated that certain bovine mycoplasma could inhibit killing of Escherichia coli by bovine neutrophils.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brownlie J., Howard C. J., Gourlay R. N. The effect of an intramammary infusion of endotoxin on experimentally induced mycoplasmal mastitis. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Dec;83(3):501–505. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson G. P., Kaneko J. J. Isolation of leukocytes from bovine peripheral blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Mar;142(3):853–856. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Ward J. R. Interaction of Mycoplasma arthritidis and other mycoplasmas with murine peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):691–699. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.691-699.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. K., Delozier K. M., Asa D. K., Minion F. C., Cassell G. H. Interactions between murine alveolar macrophages and Mycoplasma pulmonis in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):590–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.590-599.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey H., Pfister H., Messerli J., Sturzenegger N., Grolimund F. Methods of isolation, purification and quantitation of bovine immunoglobulins: a technical review. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1976 May;23(4):269–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1976.tb00682.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Taylor G., Brownlie J. Surface receptors for immunoglobulin on bovine polymorphonuclear neutrophils and macrophages. Res Vet Sci. 1980 Jul;29(1):128–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Taylor G., Collins J., Gourlay R. N. Interaction of Mycoplasma dispar and Mycoplasma agalactiae subsp. bovis with bovine alveolar macrophages and bovine lacteal polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):11–17. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.11-17.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Taylor G. Variation in the virulence of strains of Mycoplasma pulmonis related to susceptibility to killing by macrophages in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):289–294. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Hirsch J. G. The interaction in vitro of Mycoplasma pulmonis with mouse peritoneal macrophages and L-cells. J Exp Med. 1971 Feb 1;133(2):231–259. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Musoke A. J., Kurtti T. Functional properties of bovine IgG1 and IgG2: interaction with complement, macrophages, neutrophils and skin. Immunology. 1979 Oct;38(2):249–256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossmann H., Schmitz B., Possart P., Hammer D. K. Antibody-dependent, cell-mediated cytotoxicity in cattle: transfer of IgG subclasses in relation to the protection of the newborn calf. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;137:279–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simberkoff M. S., Elsbach P. The interaction in vitro between polymorphonuclear leukocytes and mycoplasma. J Exp Med. 1971 Dec 1;134(6):1417–1430. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.6.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Howard C. J. Class-specific antibody responses to Mycoplasma pulmonis in sera and lungs of infected and vaccinated mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1160–1168. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1160-1168.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Howard C. J. Interaction of Mycoplasma pulmonis with mouse peritoneal macrophages and polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):19–30. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Howard C. J. Protection of mice against Mycoplasma pulmonis infection using purified mouse immunoglobulins: comparison between protective effect and biological properties of immunoglobulin classes. Immunology. 1981 Jul;43(3):519–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


