Abstract
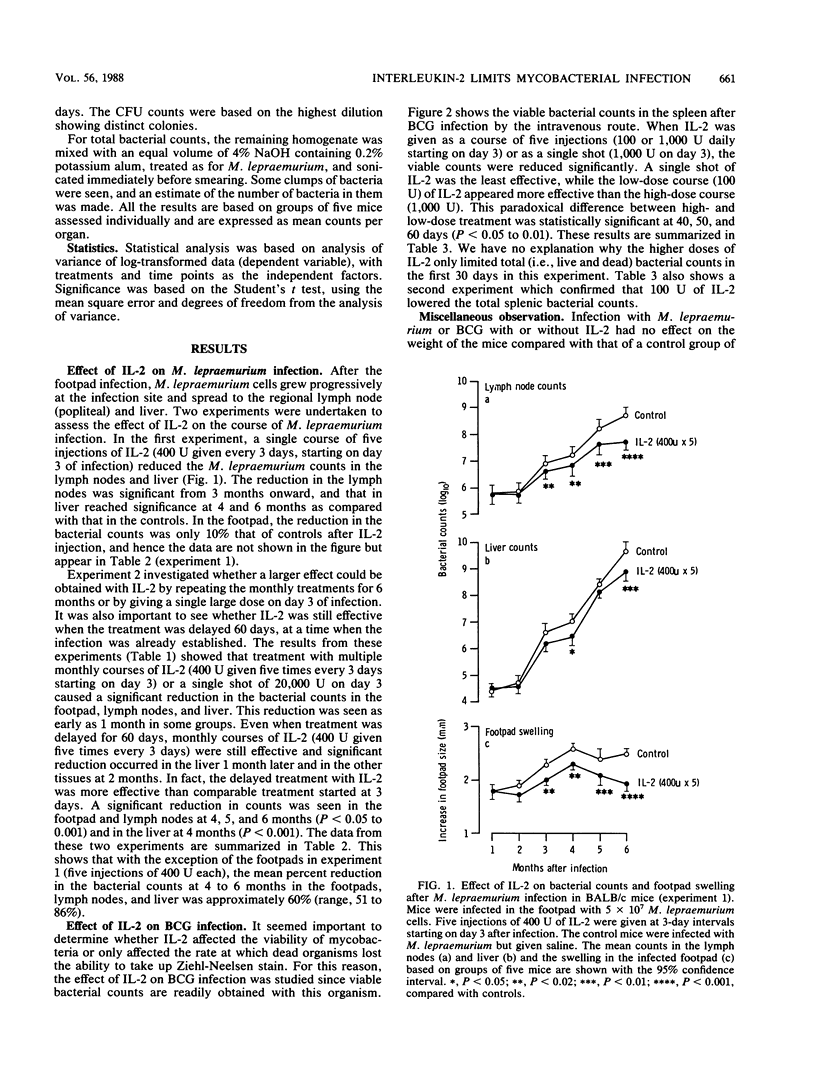
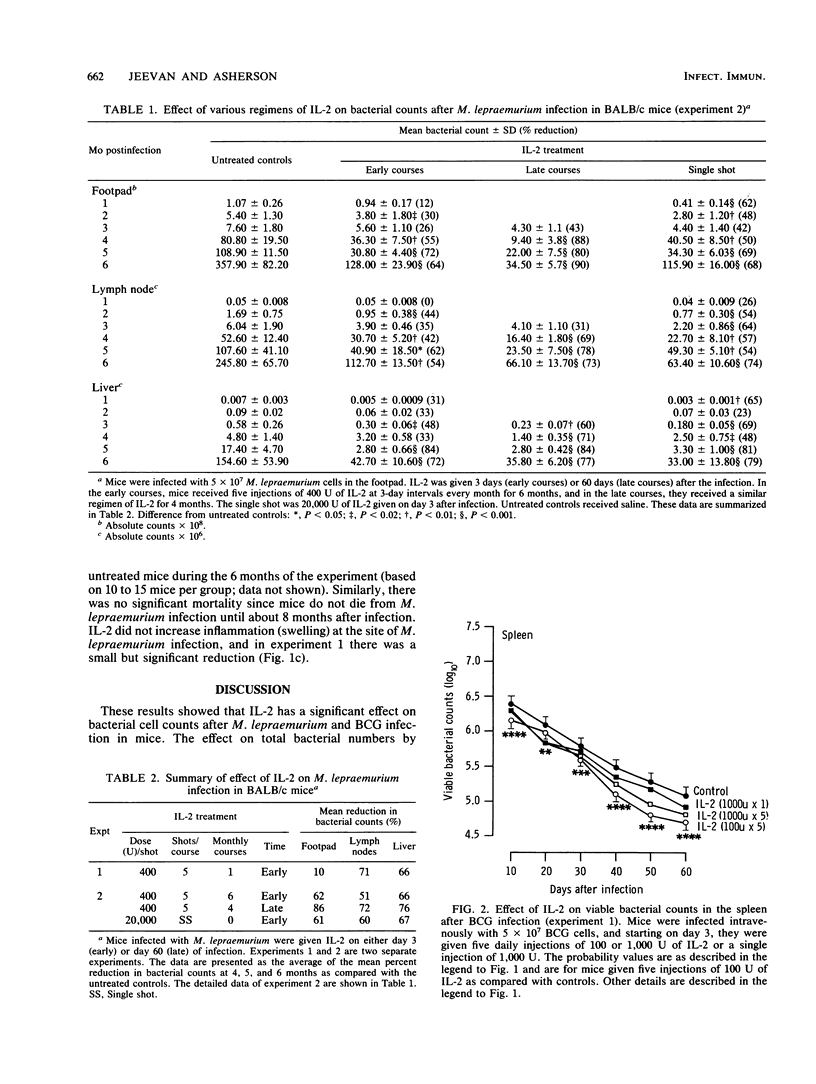
BALB/c mice were infected with Mycobacterium lepraemurium in the footpad or with Mycobacterium bovis BCG intravenously with 5 x 10(7) bacilli. Recombinant interleukin-2 (IL-2) was injected intraperitoneally as a single dose (20,000 U), as a single course of five injections (400 U each), or as a 6-month course starting 3 days after the M. lepraemurium infection. BCG-infected mice received a single dose (1,000 U) or five daily injections of 100 or 1,000 U each. IL-2 significantly reduced the total bacterial counts in the footpad, lymph nodes, and liver of M. lepraemurium-infected mice (50 to 85%) by 6 months and viable counts in the spleen (30 to 50%) by 60 days after BCG infection. The courses of IL-2 started at 60 days were more effective than those started at 3 days after M. lepraemurium infection (P less than 0.05 to 0.001), and for BCG, 100 U of IL-2 was better than 1,000 U (P less than 0.05 to 0.01). These results indicate that IL-2 limits mycobacterial infections in mice and raise the question of its possible use in humans.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnass S., Mace J., Steele J., Torres P., Gervasoni B., Ravioli R., Terencio J., Rook G. A., Waters M. F. Prevalence and specificity of the enhancing effect of three types of interleukin 2 on T cell responsiveness in 97 lepromatous leprosy patients of mixed ethnic origin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Apr;64(1):41–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Mehra V. Immunological unresponsiveness in leprosy. Immunol Rev. 1984 Aug;80:5–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett S. J. T-cell responsiveness in Mycobacterium lepraemurium infections in a "resistant" (CBA) and a "susceptible" (BALB/c) mouse strain. Cell Immunol. 1984 Nov;89(1):132–143. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colizzi V. In vivo and in vitro administration of interleukin 2-containing preparation reverses T-cell unresponsiveness in Mycobacterium bovis BCG-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):25–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.25-28.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colizzi V., Malkovsky M., Lang G., Asherson G. L. In vivo activity of interleukin-2: conversion of a stimulus causing unresponsiveness to a stimulus causing contact hypersensitivity by the injection of interleukin-2. Immunology. 1985 Dec;56(4):653–658. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Plaetinck G., Cheroutre H., Simons G., Degrave W., Tavernier J., Remaut E., Fiers W. Molecular cloning of human interleukin 2 cDNA and its expression in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4307–4323. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper P. The walls of Mycobacterium lepraemurium: chemistry and ultrastructure. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(3):313–324. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-3-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Johnson H. M., Farrar J. J. Regulation of the production of immune interferon and cytotoxic T lymphocytes by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1120–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haregewoin A., Mustafa A. S., Helle I., Waters M. F., Leiker D. L., Godal T. Reversal by interleukin-2 of the T cell unresponsiveness of lepromatous leprosy to Mycobacterium leprae. Immunol Rev. 1984 Aug;80:77–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb00495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye P. M., Sims M., Feldmann M. Regulation of macrophage accessory cell activity by mycobacteria. II. In vitro inhibition of Ia expression by Mycobacterium microti. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Apr;64(1):28–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khor M., Lowrie D. B., Mitchison D. A. Effects of recombinant interferon-gamma and chemotherapy with isoniazid and rifampicin on infections of mouse peritoneal macrophages with Listeria monocytogenes and Mycobacterium microti in vitro. Br J Exp Pathol. 1986 Oct;67(5):707–717. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovský M., Loveland B., North M., Asherson G. L., Gao L., Ward P., Fiers W. Recombinant interleukin-2 directly augments the cytotoxicity of human monocytes. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):262–265. doi: 10.1038/325262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Steele J., Ainsworth M., Champion B. R. Activation of macrophages to inhibit proliferation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: comparison of the effects of recombinant gamma-interferon on human monocytes and murine peritoneal macrophages. Immunology. 1986 Nov;59(3):333–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., McRae D. H. A method for counting acid-fast bacteria. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1968 Jan-Mar;36(1):78–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toossi Z., Kleinhenz M. E., Ellner J. J. Defective interleukin 2 production and responsiveness in human pulmonary tuberculosis. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1162–1172. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldschmidt T. J., Layton J. E., McFadden S. F., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. sIgD- and sIgD+ B cells responding to thymus-independent antigens have a different lymphokine requirement. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):865–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F., Nicola N. A., Metcalf D., Burgess A. W. Hierarchical down-modulation of hemopoietic growth factor receptors. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L., Lowrie D. B. Killing of Mycobacterium microti by immunologically activated macrophages. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):69–71. doi: 10.1038/293069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg A., Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Regulation of guinea-pig immune functions by interleukin 2: critical role of natural killer activity in acute HSV-2 genital infection. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3310–3317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


