Abstract
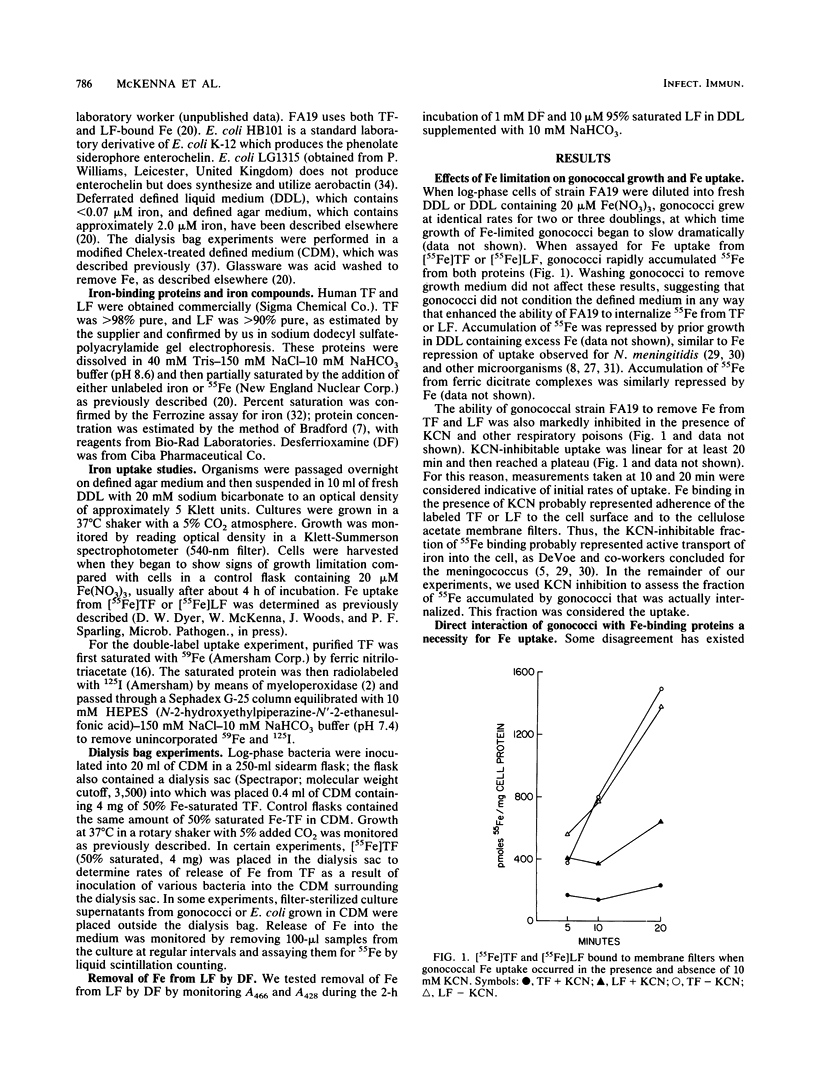
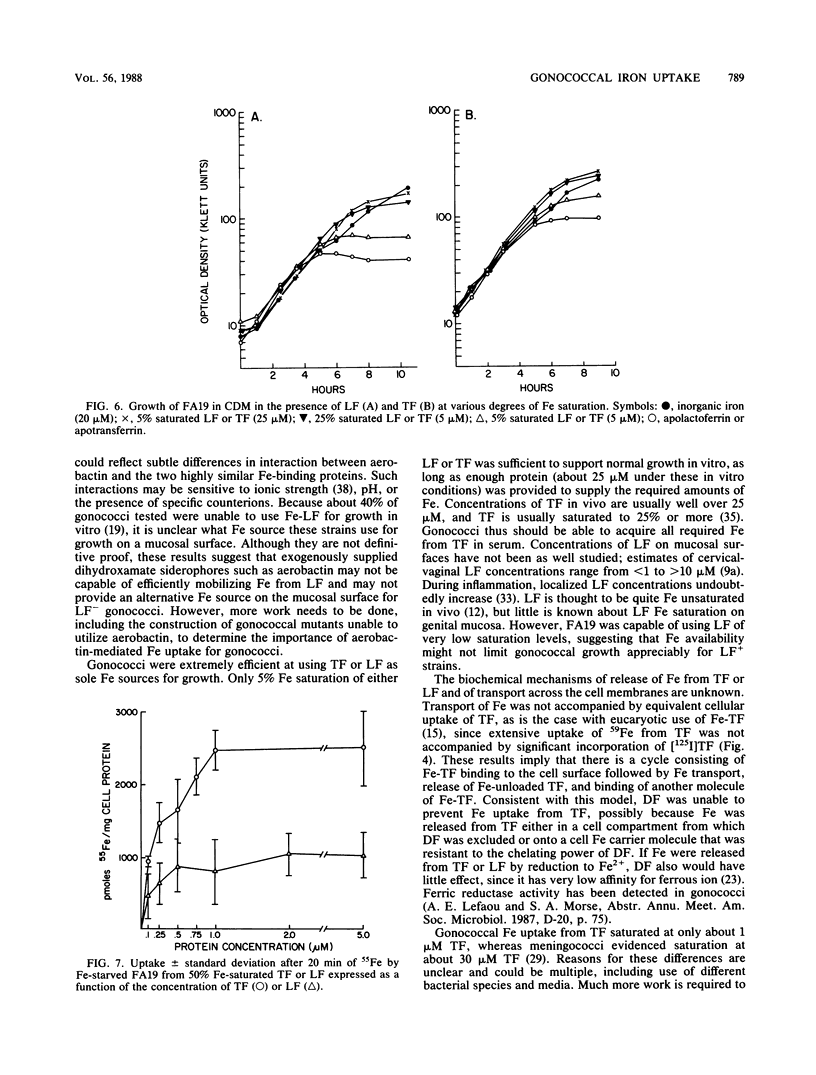
The major iron (Fe) sources available to Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the human host are probably transferrin (TF) and lactoferrin (LF). Although a number of studies have examined Fe uptake by Neisseria meningitidis, no comparable studies have been done on Fe uptake by the gonococcus from TF and LF. We found that, like meningococci, gonococci removed Fe from TF and LF in an energy-dependent manner; uptake was repressed by Fe and did not proceed by a siderophore-mediated uptake system. Unlike published studies examining meningococcal Fe uptake from TF, our study showed that gonococcal Fe uptake from both TF and LF was highly efficient; uptake saturated at 1 microM protein, and growth with 5% saturated TF and LF occurred at maximal rates when the protein was present in appreciable concentrations. We conclude that the availability of protein-bound Fe probably does not limit growth of N. gonorrhoeae in the human body.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Leibman A. Lactoferrin and transferrin: a comparative study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):314–323. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90283-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface characterization of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):814–823. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.814-823.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald F. S., DeVoe I. W. Iron acquisition by Neisseria meningitidis in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):322–334. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.322-334.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald F. S., Simonson C., DeVoe I. W. Comparison of iron binding and uptake from FeCl3 and Fe-citrated by Neisseria meningitidis. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Oct;27(10):1066–1070. doi: 10.1139/m81-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. R., Dyer D. W., Thompson M. K., Sparling P. F. Human immune response to iron-repressible outer membrane proteins of Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):710–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.710-713.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Burkhardt R. Regulation of the ColV plasmid-determined iron (III)-aerobactin transport system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):223–231. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.223-231.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brener D., DeVoe I. W., Holbein B. E. Increased virulence of Neisseria meningitidis after in vitro iron-limited growth at low pH. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):59–66. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.59-66.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Britigan B. E., French M., Bean K. Preliminary observations on lactoferrin secretion in human vaginal mucus: variation during the menstrual cycle, evidence of hormonal regulation, and implications for infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Nov;157(5):1122–1125. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(87)80274-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson D., Faruki H., Dyer D., Sparling P. F. Recombination near the antibiotic resistance locus penB results in antigenic variation of gonococcal outer membrane protein I. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):529–533. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.529-533.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer D. W., West E. P., Sparling P. F. Effects of serum carrier proteins on the growth of pathogenic neisseriae with heme-bound iron. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2171–2175. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2171-2175.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Yancey R. J. Effect of siderophores on virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):609–613. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.609-613.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbein B. E. Iron-controlled infection with Neisseria meningitidis in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):886–891. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.886-891.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Ashwell G., van Renswoude J., Harford J. B., Bridges K. R. Binding of apotransferrin to K562 cells: explanation of the transferrin cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2263–2266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima N., Bates G. W. The reduction and release of iron from Fe3+ .transferrin.CO3(2-). J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8847–8854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka K., Mareschal J. C., Crichton R. R. Iron transfer form transferrin to ferritin mediated by polyphosphate compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 5;677(3-4):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90255-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka K., Mareschal J. C., Crichton R. R. Iron transfer from transferrin to ferritin mediated by pyrophosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 16;96(3):1408–1413. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from lactoferrin. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):915–920. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.915-920.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., Sparling P. F. Ability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and commensal Neisseria species to obtain iron from transferrin and iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):555–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.555-564.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietzner T. A., Barnes R. C., JeanLouis Y. A., Shafer W. M., Morse S. A. Distribution of an antigenically related iron-regulated protein among the Neisseria spp. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):60–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.60-68.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietzner T. A., Bolan G., Schoolnik G. K., Morse S. A. Purification and characterization of the major iron-regulated protein expressed by pathogenic Neisseriae. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):1041–1057. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial envelope proteins related to iron. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A., Gotschlich E. C. Isolation of a high molecular weight polyphosphate from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):2049–2060. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.2049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. M., Cryz S. J., Jr, Holmes R. K. Genetic and biochemical evidence for a siderophore-dependent iron transport system in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):143–149. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.143-149.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Genetic mapping of linked antibiotic resistance loci in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1284–1292. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1284-1292.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C., Brener D., DeVoe I. W. Expression of a high-affinity mechanism for acquisition of transferrin iron by Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.107-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson C., Trivett T., DeVoe I. W. Energy-independent uptake of iron from citrate by isolated outer membranes of Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):547–553. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.547-553.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol P. A., Woods D. E. Demonstration of an iron-siderophore-binding protein in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):665–669. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.665-669.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. L., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. The involvement of lactoferrin in the hyposideremia of acute inflammation. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):1068–1084. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner P. J., Williams P. H., Bindereif A., Neilands J. B. ColV plasmid-specific aerobactin synthesis by invasive strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):540–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.540-545.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. D. Iron and infection. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):45–66. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.45-66.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Sparling P. F. Aerobactin utilization by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and cloning of a genomic DNA fragment that complements Escherichia coli fhuB mutations. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3414–3421. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3414-3421.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Sparling P. F. Response of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to iron limitation: alterations in expression of membrane proteins without apparent siderophore production. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):388–394. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.388-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J., Chasteen N. D., Moreton K. The effect of salt concentration on the iron-binding properties of human transferrin. Biochem J. 1982 Mar 1;201(3):527–532. doi: 10.1042/bj2010527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Finkelstein R. A. Assmilation of iron by pathogenic Neisseria spp. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):592–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.592-599.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Finkelstein R. A. Siderophore production by pathogenic Neisseria spp. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):600–608. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.600-608.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


