Abstract
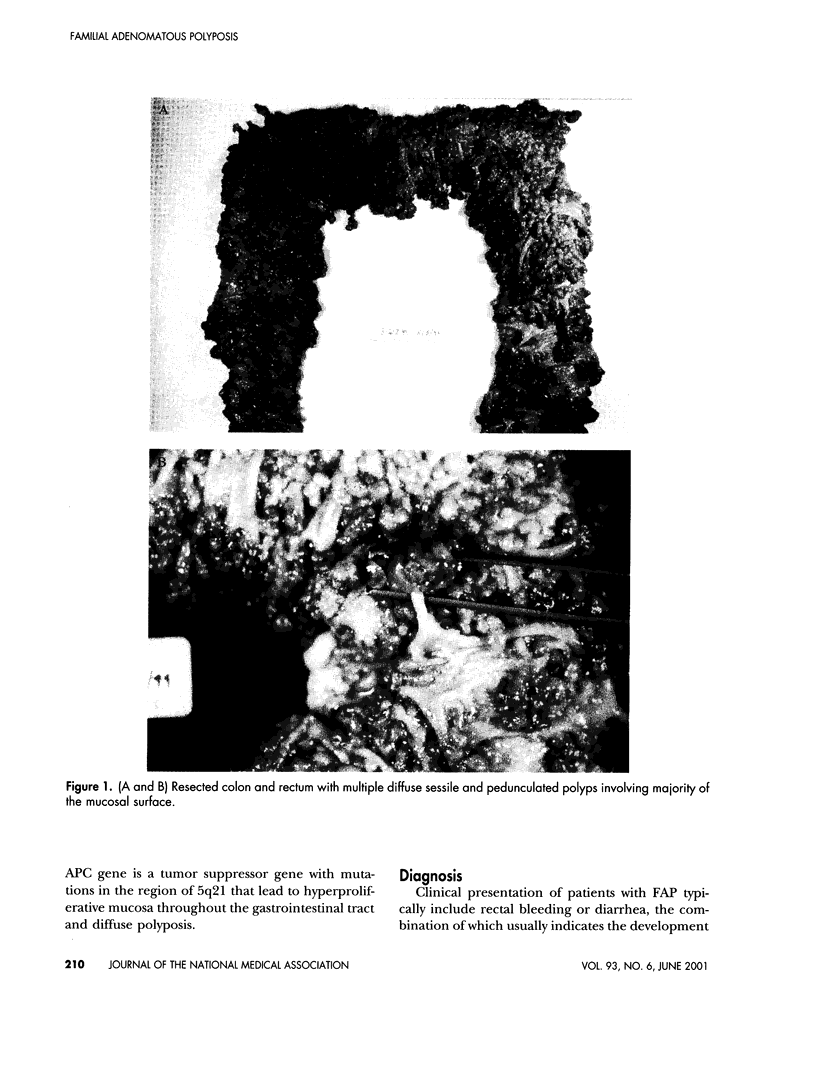
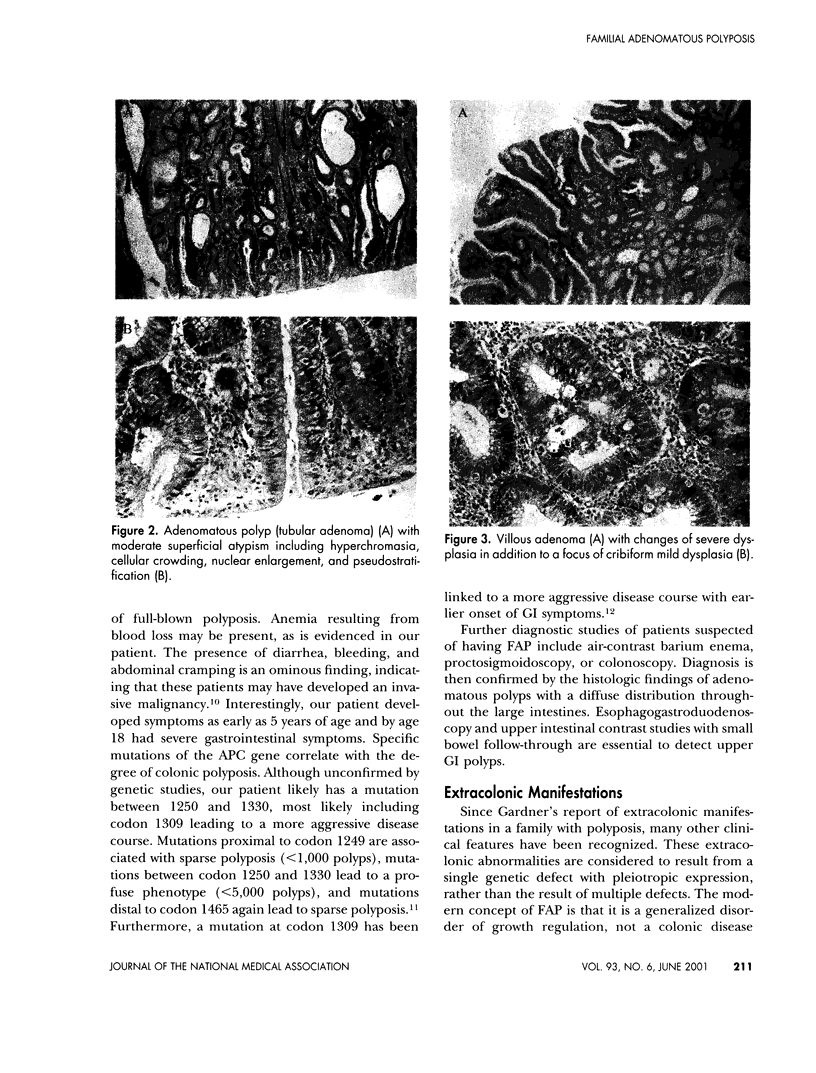
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by diffuse intestinal polyposis, specific gene mutation, and predisposition for developing colon cancer. Left untreated, patients with FAP will develop colorectal carcinoma during early adulthood. Hence, early detection and surgical intervention are of the utmost importance. Colectomy is required and may include an ileal pouch with ileoanal anastomosis, which eliminates the colon and rectal disease while preserving fecal continence and avoidance of a permanent ileostomy. Advances in the treatment of FAP with associated reduction in mortality from colorectal carcinoma make extracolonic manifestations of the disease more common and life-long surveillance is mandatory. The most life-threatening extracolonic manifestations of FAP are periampullary carcinoma and desmoid tumors. The upper gastrointestinal tract should be monitored endoscopically at the time of diagnosis and assessed regularly thereafter. Duodenal adenomas should be resected so as to avoid the devastating effects of invasive periampullary carcinoma. Additionally, the development of desmoid tumors needs to be monitored (by CT or MRI), so as to avoid the severe complications of local invasion. Further research is indicated in the development of effective screening and treatment for this condition.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvanitis M. L., Jagelman D. G., Fazio V. W., Lavery I. C., McGannon E. Mortality in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1990 Aug;33(8):639–642. doi: 10.1007/BF02150736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk T., Bülow S., Cohen Z., DeCosse J. J., Hawley P. R., Jagelman D. G., Järvinen H. J., Macrae F. A. Surgical aspects of familial adenomatous polyposis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1988 Mar;3(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF01649676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaard M. L., Fenger K., Bülow S., Niebuhr E., Mohr J. Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP): frequency, penetrance, and mutation rate. Hum Mutat. 1994;3(2):121–125. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380030206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F., Bailey C. J., Bodmer J., Bussey H. J., Ellis A., Gorman P., Lucibello F. C., Murday V. A., Rider S. H., Scambler P. Localization of the gene for familial adenomatous polyposis on chromosome 5. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):614–616. doi: 10.1038/328614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow S., Holm N. V., Hauge M. The incidence and prevalence of familial polyposis coli in Denmark. Scand J Soc Med. 1986;14(2):67–74. doi: 10.1177/140349488601400205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W. J., Spence R. A., Parks T. G. Familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg. 1994 Dec;81(12):1722–1733. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800811207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspari R., Friedl W., Mandl M., Möslein G., Kadmon M., Knapp M., Jacobasch K. H., Ecker K. W., Kreissler-Haag D., Timmermanns G. Familial adenomatous polyposis: mutation at codon 1309 and early onset of colon cancer. Lancet. 1994 Mar 12;343(8898):629–632. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92634-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole N. M., Guiss L. W. Extra-abdominal desmoid tumors. Arch Surg. 1969 Apr;98(4):530–533. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1969.01340100146020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera L., Kakati S., Gibas L., Pietrzak E., Sandberg A. A. Gardner syndrome in a man with an interstitial deletion of 5q. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Nov;25(3):473–476. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320250309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagelman D. G. Extracolonic manifestations of familial polyposis coli. Semin Surg Oncol. 1987;3(2):88–91. doi: 10.1002/ssu.2980030208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiot W. A., Williams M. R., Keighley M. R. Pouchitis following colectomy and ileal reservoir construction for familial adenomatous polyposis. Br J Surg. 1990 Nov;77(11):1283–1283. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800771128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konsker K. A. Familial adenomatous polyposis: case report and review of extracolonic manifestations. Mt Sinai J Med. 1992 Jan;59(1):85–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Dobbs M., Scambler P., O'Connell P., Nakamura Y., Stauffer D., Woodward S., Burt R., Hughes J., Gardner E. The gene for familial polyposis coli maps to the long arm of chromosome 5. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1411–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.3479843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moertel C. G., Hill J. R., Adson M. A. Surgical management of multiple polyposis. The problem of cancer in the retained bowel segment. Arch Surg. 1970 Apr;100(4):521–526. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1970.01340220197033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan M. J., McCarthy T. V., Doyle C. T. Familial adenomatous polyposis: from bedside to benchside. Am J Clin Pathol. 1998 May;109(5):521–526. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/109.5.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar P. M., Pemberton J. H. Operations for familial adenomatous polyposis. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 1996 Jul;5(3):675–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarre R. G., Frost A. G., Jagelman D. G., Petras R. E., Sivak M. V., McGannon E. Gastric and duodenal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis: a prospective study of the nature and prevalence of upper gastrointestinal polyps. Gut. 1987 Mar;28(3):306–314. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.3.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]