Abstract
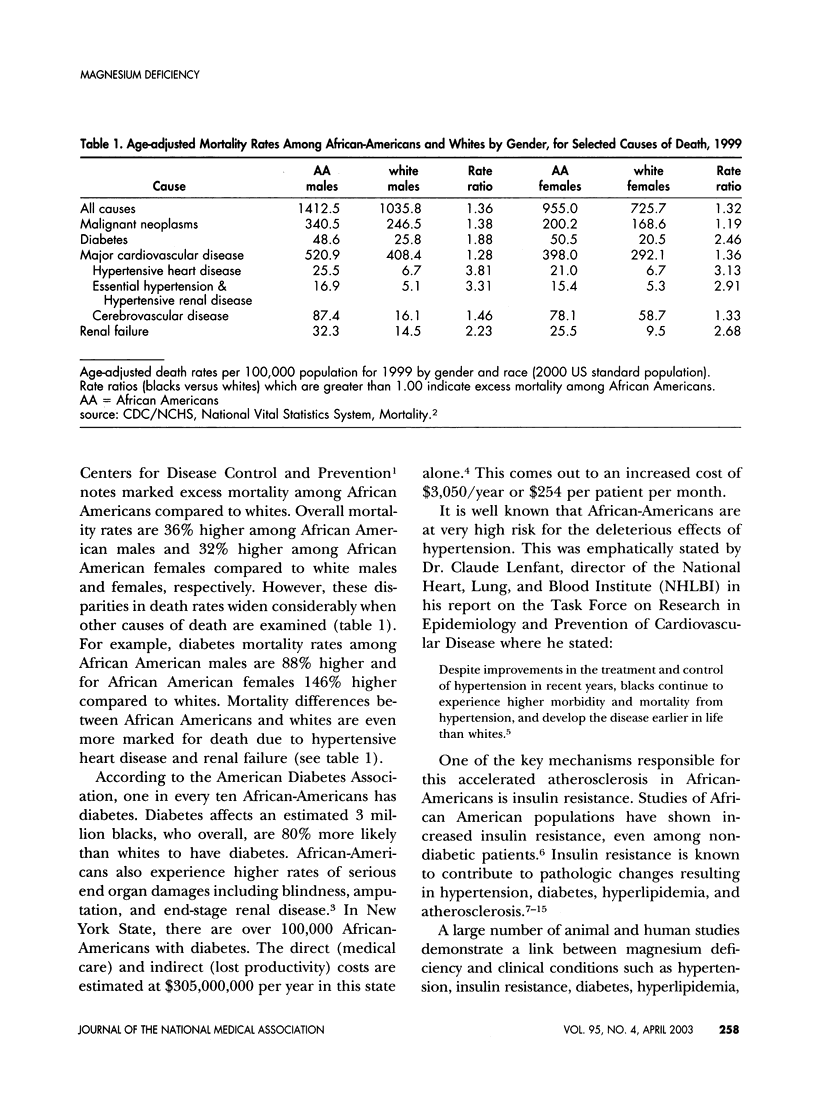
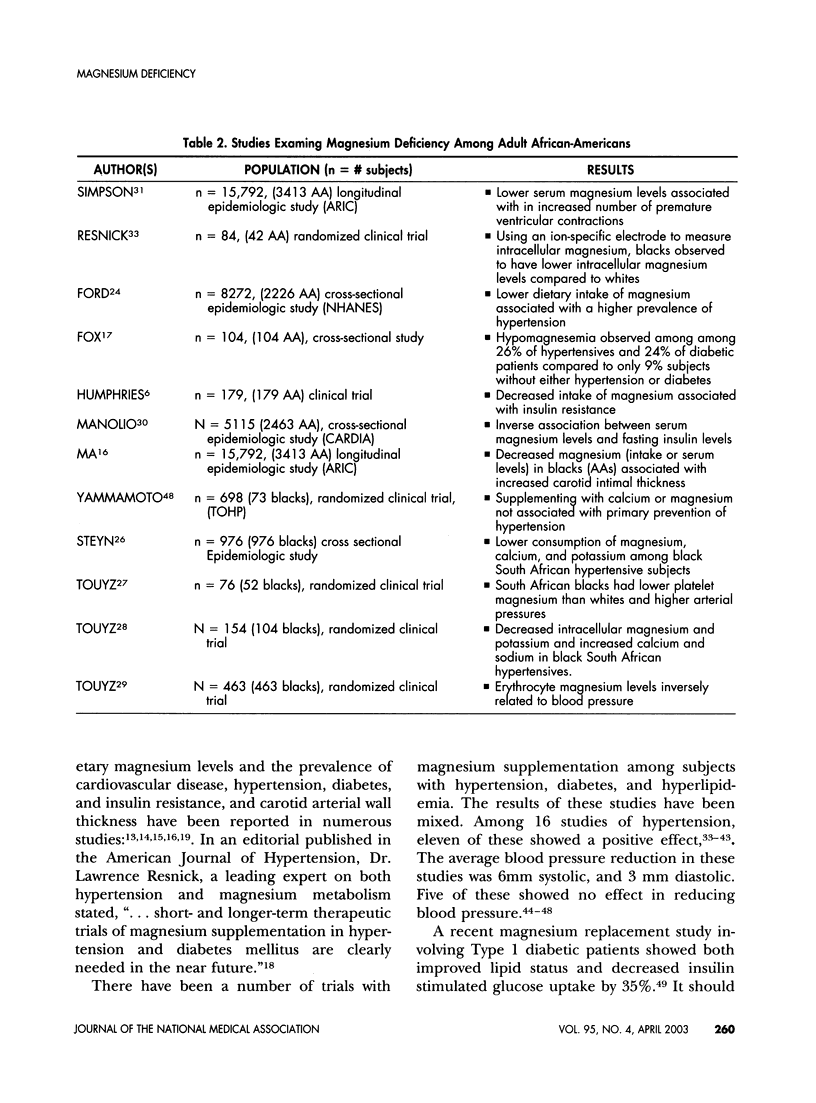
African-Americans are known to be disproportionately impacted by many chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular, and renal disease. Lower levels of dietary and serum magnesium have been associated with an increased prevalence of hypertension, insulin resistance, and diabetes. Studies suggest a greater prevalence of occult magnesium deficiency among African-Americans compared to other populations. This increased prevalence of hypomagnesemia may contribute to increased insulin resistance leading to accelerated atherosclerosis and premature death. Trials that correct magnesium status/levels among African-Americans, whether through dietary intervention or direct magnesium replacement/supplementation need to be completed to characterize this relationship more completely.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altura B. M., Zhang A., Altura B. T. Magnesium, hypertensive vascular diseases, atherogenesis, subcellular compartmentation of Ca2+ and Mg2+ and vascular contractility. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1993;19(4-5):323–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascherio A., Rimm E. B., Giovannucci E. L., Colditz G. A., Rosner B., Willett W. C., Sacks F., Stampfer M. J. A prospective study of nutritional factors and hypertension among US men. Circulation. 1992 Nov;86(5):1475–1484. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.5.1475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bild D. E., Folsom A. R., Lowe L. P., Sidney S., Kiefe C., Westfall A. O., Zheng Z. J., Rumberger J. Prevalence and correlates of coronary calcification in black and white young adults: the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001 May;21(5):852–857. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.21.5.852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappuccio F. P., Markandu N. D., Beynon G. W., Shore A. C., Sampson B., MacGregor G. A. Lack of effect of oral magnesium on high blood pressure: a double blind study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Jul 27;291(6490):235–238. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6490.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien K. L., Sung F. C., Hsu H. C., Su T. C., Lee Y. T. Left ventricular mass and correlated atherosclerotic risk factors in young adolescents: report from Chin-Shan community cardiovascular study in Taiwan. Atherosclerosis. 2001 Apr;155(2):431–437. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(00)00579-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colditz G. A., Manson J. E., Stampfer M. J., Rosner B., Willett W. C., Speizer F. E. Diet and risk of clinical diabetes in women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992 May;55(5):1018–1023. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/55.5.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djurhuus M. S., Klitgaard N. A., Pedersen K. K., Blaabjerg O., Altura B. M., Altura B. T., Henriksen J. E. Magnesium reduces insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and serum lipid concentrations in type 1 diabetes. Metabolism. 2001 Dec;50(12):1409–1417. doi: 10.1053/meta.2001.28072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyckner T., Wester P. O. Effect of magnesium on blood pressure. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Jun 11;286(6381):1847–1849. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6381.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara L. A., Iannuzzi R., Castaldo A., Iannuzzi A., Dello Russo A., Mancini M. Long-term magnesium supplementation in essential hypertension. Cardiology. 1992;81(1):25–33. doi: 10.1159/000175772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford E. S. Race, education, and dietary cations: findings from the Third National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey. Ethn Dis. 1998 Winter;8(1):10–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. H., Ramsoomair D., Mahoney M. C., Carter C., Young B., Graham R. An investigation of hypomagnesemia among ambulatory urban African Americans. J Fam Pract. 1999 Aug;48(8):636–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga H. Effects of dietary magnesium supplementation on diurnal variations of blood pressure and plasma Na+, K(+)-ATPase activity in essential hypertension. Jpn Heart J. 1992 Nov;33(6):785–800. doi: 10.1536/ihj.33.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori K., Saito K., Sano H., Fukuzaki H. Intracellular magnesium deficiency and effect of oral magnesium on blood pressure and red cell sodium transport in diuretic-treated hypertensive patients. Jpn Circ J. 1988 Nov;52(11):1249–1256. doi: 10.1253/jcj.52.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries S., Kushner H., Falkner B. Low dietary magnesium is associated with insulin resistance in a sample of young, nondiabetic Black Americans. Am J Hypertens. 1999 Aug;12(8 Pt 1):747–756. doi: 10.1016/s0895-7061(99)00041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joffres M. R., Reed D. M., Yano K. Relationship of magnesium intake and other dietary factors to blood pressure: the Honolulu heart study. Am J Clin Nutr. 1987 Feb;45(2):469–475. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/45.2.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano Y., Matsuoka H., Takishita S., Omae T. Effects of magnesium supplementation in hypertensive patients: assessment by office, home, and ambulatory blood pressures. Hypertension. 1998 Aug;32(2):260–265. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.32.2.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurant P., Touyz R. M. Physiological and pathophysiological role of magnesium in the cardiovascular system: implications in hypertension. J Hypertens. 2000 Sep;18(9):1177–1191. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200018090-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenfant C. Task Force on Research in Epidemiology and Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases: a revisit. Circulation. 1996 May 1;93(9):1605–1607. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.93.9.1605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind L., Lithell H., Pollare T., Ljunghall S. Blood pressure response during long-term treatment with magnesium is dependent on magnesium status. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study in essential hypertension and in subjects with high-normal blood pressure. Am J Hypertens. 1991 Aug;4(8):674–679. doi: 10.1093/ajh/4.8.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Folsom A. R., Melnick S. L., Eckfeldt J. H., Sharrett A. R., Nabulsi A. A., Hutchinson R. G., Metcalf P. A. Associations of serum and dietary magnesium with cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes, insulin, and carotid arterial wall thickness: the ARIC study. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. J Clin Epidemiol. 1995 Jul;48(7):927–940. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(94)00200-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolio T. A., Savage P. J., Burke G. L., Hilner J. E., Liu K., Orchard T. J., Sidney S., Oberman A. Correlates of fasting insulin levels in young adults: the CARDIA study. J Clin Epidemiol. 1991;44(6):571–578. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(91)90221-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather H. M., Nisbet J. A., Burton G. H., Poston G. J., Bland J. M., Bailey P. A., Pilkington T. R. Hypomagnesaemia in diabetes. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Jul 16;95(2):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90364-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motoyama T., Sano H., Fukuzaki H. Oral magnesium supplementation in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1989 Mar;13(3):227–232. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.13.3.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowson C. A., Morgan T. O. Magnesium supplementation in mild hypertensive patients on a moderately low sodium diet. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1989 Apr;16(4):299–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1989.tb01561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolisso G., Passariello N., Sgambato S., Torecca R., Buoninconti R., Varricchio M., D'Onofrio F. Impaired insulin-mediated erythrocyte magnesium accumulation in essential hypertension. Clin Sci (Lond) 1987 Nov;73(5):535–539. doi: 10.1042/cs0730535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolisso G., Ravussin E. Intracellular magnesium and insulin resistance: results in Pima Indians and Caucasians. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995 Apr;80(4):1382–1385. doi: 10.1210/jcem.80.4.7714114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Lithell H., Landsberg L. Hypertension and associated metabolic abnormalities--the role of insulin resistance and the sympathoadrenal system. N Engl J Med. 1996 Feb 8;334(6):374–381. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199602083340607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M., Bardicef O., Altura B. T., Alderman M. H., Altura B. M. Serum ionized magnesium: relation to blood pressure and racial factors. Am J Hypertens. 1997 Dec;10(12 Pt 1):1420–1424. doi: 10.1016/s0895-7061(97)00364-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L. M. Magnesium in the pathophysiology and treatment of hypertension and diabetes mellitus: where are we in 1997? Am J Hypertens. 1997 Mar;10(3):368–370. doi: 10.1016/s0895-7061(97)00021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks F. M., Svetkey L. P., Vollmer W. M., Appel L. J., Bray G. A., Harsha D., Obarzanek E., Conlin P. R., Miller E. R., 3rd, Simons-Morton D. G. Effects on blood pressure of reduced dietary sodium and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. DASH-Sodium Collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med. 2001 Jan 4;344(1):3–10. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200101043440101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Hattori K., Omatsu T., Hirouchi H., Sano H., Fukuzaki H. Effects of oral magnesium on blood pressure and red cell sodium transport in patients receiving long-term thiazide diuretics for hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 1988 Jul;1(3 Pt 3):71S–74S. doi: 10.1093/ajh/1.3.71s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanjuliani A. F., de Abreu Fagundes V. G., Francischetti E. A. Effects of magnesium on blood pressure and intracellular ion levels of Brazilian hypertensive patients. Int J Cardiol. 1996 Oct 11;56(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0167-5273(96)02716-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steyn K., Jooste P. L., Fourie J. M., Parry C. D., Rossouw J. E. Hypertension in the coloured population of the Cape Peninsula. S Afr Med J. 1986 Feb 1;69(3):165–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touyz R. M., Milne F. J., Reinach S. G. Intracellular Mg2+, Ca2+, Na2+ and K+ in platelets and erythrocytes of essential hypertension patients: relation to blood pressure. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1992;14(6):1189–1209. doi: 10.3109/10641969209038200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touyz R. M., Milne F. J., Reinach S. G. Racial differences in cell membrane ATPases and cellular cation content in urban South African normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Am J Hypertens. 1993 Aug;6(8):693–700. doi: 10.1093/ajh/6.8.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touyz R. M., Rathakrishnan S., Adam E., Sonnekus M., Reinach S. G., Milne F. J. The relationship between magnesium, calcium, sodium, potassium and blood pressure in South African adult males. Magnesium. 1989;8(3-4):145–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widman L., Wester P. O., Stegmayr B. K., Wirell M. The dose-dependent reduction in blood pressure through administration of magnesium. A double blind placebo controlled cross-over study. Am J Hypertens. 1993 Jan;6(1):41–45. doi: 10.1093/ajh/6.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirell M. P., Wester P. O., Stegmayr B. G. Nutritional dose of magnesium in hypertensive patients on beta blockers lowers systolic blood pressure: a double-blind, cross-over study. J Intern Med. 1994 Aug;236(2):189–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1994.tb01282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witteman J. C., Grobbee D. E., Derkx F. H., Bouillon R., de Bruijn A. M., Hofman A. Reduction of blood pressure with oral magnesium supplementation in women with mild to moderate hypertension. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994 Jul;60(1):129–135. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/60.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M. E., Applegate W. B., Klag M. J., Borhani N. O., Cohen J. D., Kirchner K. A., Lakatos E., Sacks F. M., Taylor J. O., Hennekens C. H. Lack of blood pressure effect with calcium and magnesium supplementation in adults with high-normal blood pressure. Results from Phase I of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention (TOHP). Trials of Hypertension Prevention (TOHP) Collaborative Research Group. Ann Epidemiol. 1995 Mar;5(2):96–107. doi: 10.1016/1047-2797(94)00054-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


