Abstract
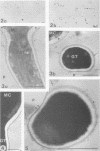
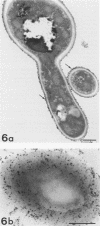
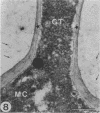
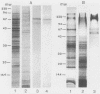
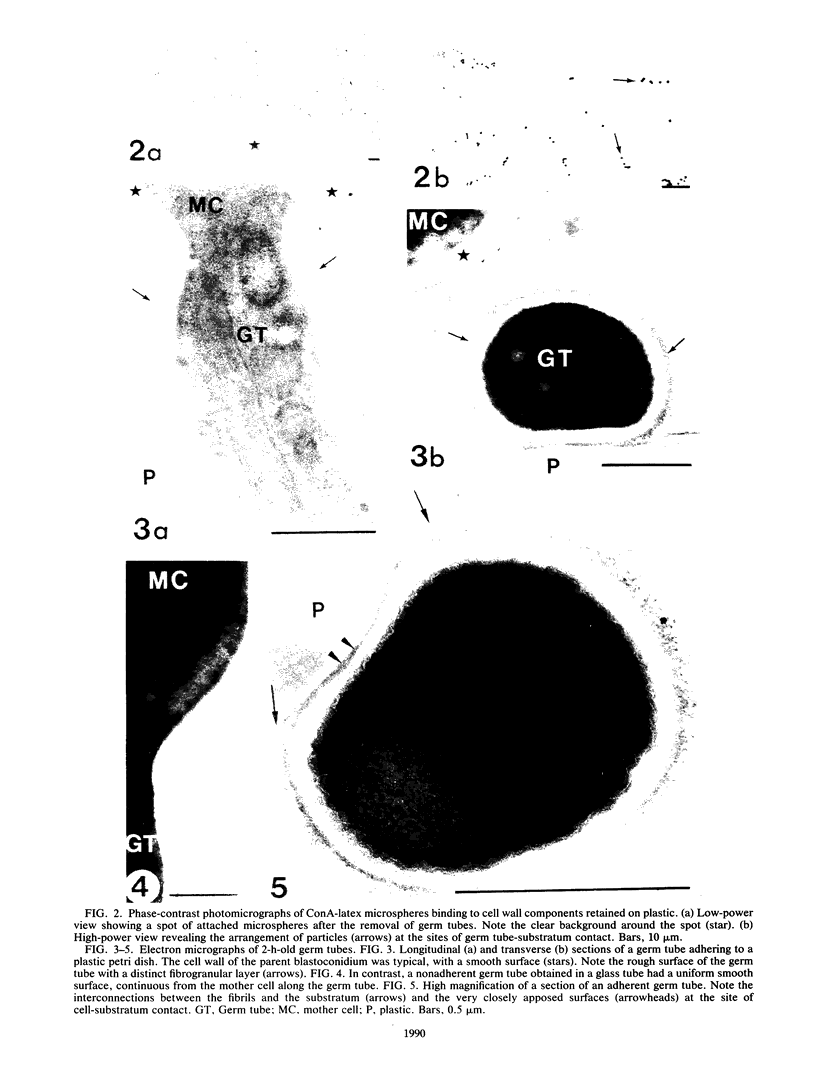
Germ tubes of Candida albicans produced an additional fibrillar surface layer responsible for enhanced adherence to plastic. The correlation between germination of C. albicans and adherence of germ tubes to a plastic matrix led us to consider the existence of germ tube-specific adhesive components involved in the attachment process. Using concanavalin A-sensitized latex microspheres, we first detected extracellular molecules on the plastic surface after removal of the adherent germ tubes. Electron microscopy confirmed that fibrils of the germ tube involved in cell-substratum interconnections were retained on the plastic surface. Cytochemistry with concanavalin A-gold labeling demonstrated that these fibrillar structures contained mannoproteins. Dithiothreitol and iodoacetamide treatment of washed plastic allowed us to further characterize these fibrillar adhesins. Through analysis by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, two components with molecular weights (MWs) of 68,000 and 60,000 were detected on the plastic surface. The 68,000-MW component appeared to be one of the major constituents of the germ tube surface layers. Biosynthetic labeling experiments performed with L-[35S]methionine revealed two additional proteins: a high-MW component (greater than 200,000), and a 200,000-MW component. These four proteins, strongly labeled on the plastic surface and on the germ tube cell wall layers, were in contrast slightly labeled or even nonidentified in the culture supernatant, suggesting their involvement in germ tube adherence.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calderone R. A., Linehan L., Wadsworth E., Sandberg A. L. Identification of C3d receptors on Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):252–258. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.252-258.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassone A., Mattia E., Boldrini L. Agglutination of blastospores of Candida albicans by concanavalin A and its relationship with the distribution of mannan polymers and the ultrastructure of the cell wall. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Apr;105(2):263–273. doi: 10.1099/00221287-105-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley I. A., Douglas L. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an adhesin from Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):629–636. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley I. A., Douglas L. J. Role of glycosides as epithelial cell receptors for Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):637–643. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowa N., Howard D. H., Landau J. W., Shechter Y. Synthesis of nueic acids and proteins in the dimorphic forms of Candida albicans. Sabouraudia. 1970 Nov;8(3):163–169. doi: 10.1080/00362177085190831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elorza M. V., Murgui A., Sentandreu R. Dimorphism in Candida albicans: contribution of mannoproteins to the architecture of yeast and mycelial cell walls. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2209–2216. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura L. H., Pearsall N. N. Relationship between germination of Candida albicans and increased adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):464–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.464-468.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. D., Lee J. C., Morris A. L. Adherence of Candida albicans and other Candida species to mucosal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):667–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.667-674.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A., Drutz D. J., Zajic J. E. Factors governing adherence of Candida species to plastic surfaces. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.97-101.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. L., Buckley H. R., Campbell C. C. An amino acid liquid synthetic medium for the development of mycelial and yeast forms of Candida Albicans. Sabouraudia. 1975 Jul;13(2):148–153. doi: 10.1080/00362177585190271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisch P. A., Calderone R. A. Role of surface mannan in the adherence of Candida albicans to fibrin-platelet clots formed in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):92–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.92-97.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCourtie J., Douglas L. J. Extracellular polymer of Candida albicans: isolation, analysis and role in adhesion. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Mar;131(3):495–503. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-3-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCourtie J., Douglas L. J. Relationship between cell surface composition of Candida albicans and adherence to acrylic after growth on different carbon sources. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1234–1241. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1234-1241.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCourtie J., MacFarlane T. W., Samaranayake L. P. Effect of saliva and serum on the adherence of Candida species to chlorhexidine-treated denture acrylic. J Med Microbiol. 1986 May;21(3):209–213. doi: 10.1099/00222615-21-3-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake Y., Fujita Y., Minagi S., Suginaka H. Surface hydrophobicity and adherence of Candida to acrylic surfaces. Microbios. 1986;46(186):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponton J., Jones J. M. Analysis of cell wall extracts of Candida albicans by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western blot techniques. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):565–572. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.565-572.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponton J., Jones J. M. Identification of two germ-tube-specific cell wall antigens of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):864–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.864-868.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Calderone R. A., Edwards J. E., Jr Adherence of Candida species to host tissues and plastic surfaces. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;8(1):73–85. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Edwards J. E., Jr, Gibson T. R., Moore J. C., Cohen A. H., Green I. Adherence of Candida to cultured vascular endothelial cells: mechanisms of attachment and endothelial cell penetration. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1264–1274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samaranayake L. P., MacFarlane T. W. An in-vitro study of the adherence of Candida albicans to acrylic surfaces. Arch Oral Biol. 1980;25(8-9):603–609. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(80)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samaranayake L. P., MacFarlane T. W. The adhesion of the yeast Candida albicans to epithelial cells of human origin in vitro. Arch Oral Biol. 1981;26(10):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(81)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smail E. H., Jones J. M. Demonstration and solubilization of antigens expressed primarily on the surfaces of Candida albicans germ tubes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.74-81.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P. M., Kenny G. E. Characterization of antigens specific to the surface of germ tubes of Candida albicans by immunofluorescence. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):850–855. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.850-855.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P. M., Kenny G. E. Enzymatic release of germ tube-specific antigens from cell walls of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):609–614. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.609-614.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom P. M., Nichols E. J., Kenny G. E. Antigenic differences between mannoproteins of germ tubes and blastospores of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):616–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.616-620.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin G., Poulain D., Herbaut J., Biguet J. Cytochemical and ultrastructural studies of Candida albicans. II. Evidence for a cell wall coat using concanavalin A. J Ultrastruct Res. 1981 Apr;75(1):50–59. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(81)80099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin G., Poulain D., Vernes A. Cytochemical and ultrastructural studies of Candida albicans. III. Evidence for modifications of the cell wall coat during adherence to human buccal epithelial cells. Arch Microbiol. 1984 Oct;139(2-3):221–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00402004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronchin G., Robert R., Bouali A., Senet J. M. Immunocytochemical localization of in vitro binding of human fibrinogen to Candida albicans germ tube and mycelium. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Mar-Apr;138(2):177–187. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90194-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]