Abstract
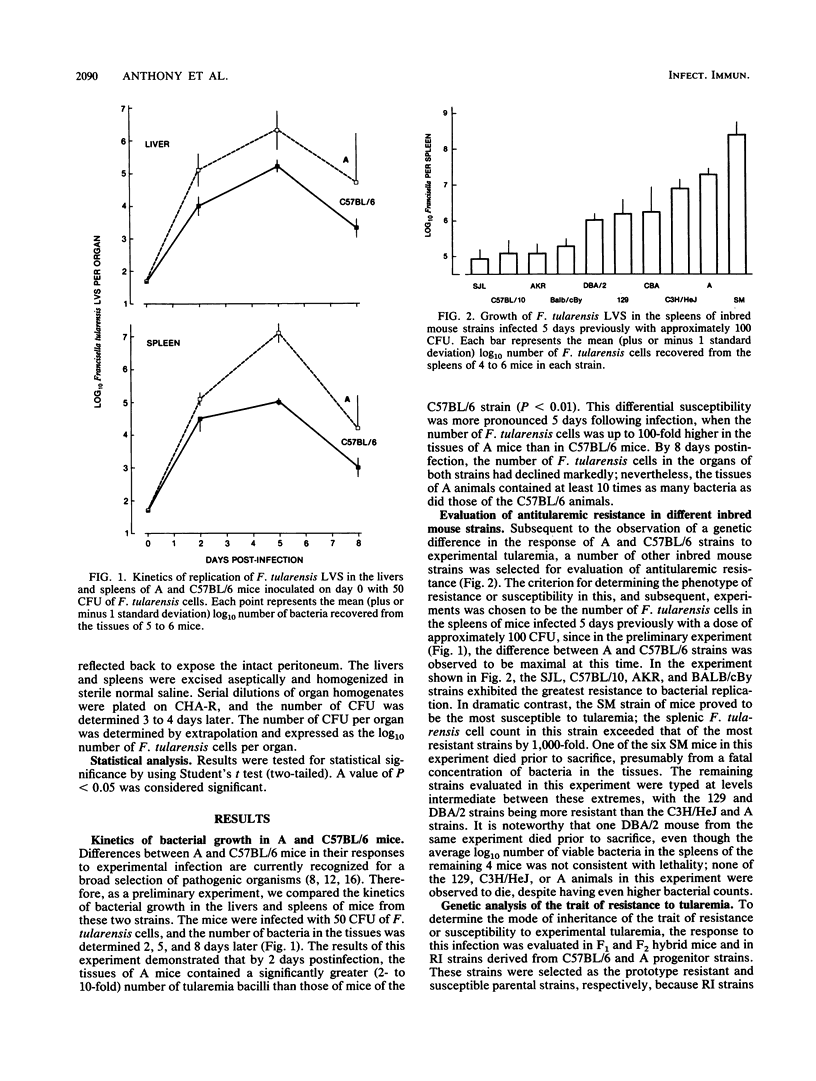
The host response to experimental murine tularemia was examined in different inbred mouse strains. The kinetics of growth of Francisella tularensis live vaccine strain (LVS) in the livers and spleens of A and C57BL/6 mice were monitored, and it was observed that mice of the A strain were more susceptible to the proliferation of LVS than were C57BL/6 mice. The difference was most marked 5 days following infection, when the number of bacteria isolated from the spleens of A mice was found to exceed that of C57BL/6 mice by 100-fold. In addition, the C57BL/6 strain exhibited a more pronounced splenomegaly 8 days after infection than did the A strain. When the response of other inbred strains was evaluated by determining the splenic count of LVS on day 5 postinfection, several levels of antiularemic resistance were observed. Mice of the AKR, BALB/cBy, C57BL/10, and SJL strains were found to be most resistant, while SM mice were most susceptible to the proliferation of LVS. The DBA/2, CBA, 129, C3H/HeJ, and A strains expressed a resistance phenotype which was intermediate between the two extremes, with A and C3H/HeJ mice being somewhat more susceptible than DBA/2, CBA, or 129 mice. The trait of resistance or susceptibility was analyzed genetically in (C57BL/6 x A)F1 hybrid mice and in F2 generation and recombinant inbred (RI) mouse strains derived from C57BL/6 (resistant) and A (susceptible) strain progenitors. The F1 progeny exhibited a level of resistance to infection which was similar to that of the resistant parent. In both the F2 generation mice and the RI strains, a continuous spectrum of resistance levels was observed. The results of these experiments indicate that the genetic background of the host influences host resistance to experimental murine tularemia and that multiple genetic loci are involved in this response.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN W. P. Immunity against tularemia: passive protection of mice by transfer of immune tissues. J Exp Med. 1962 Feb 1;115:411–420. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
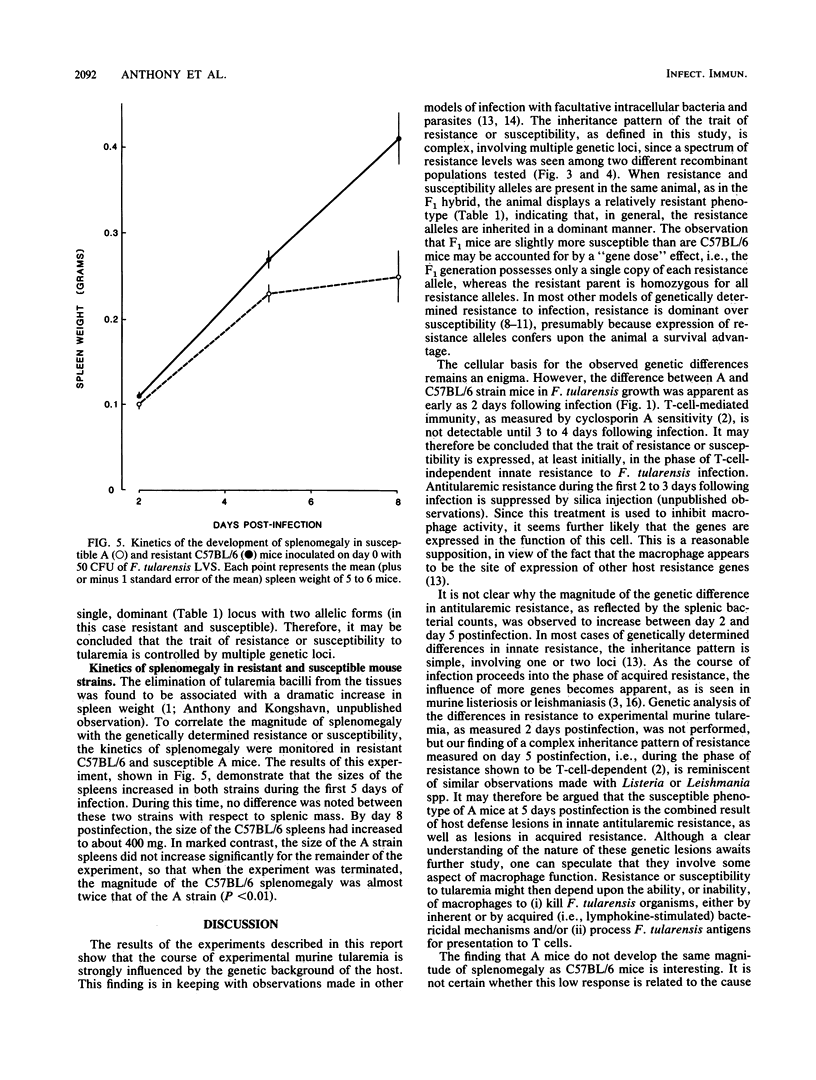
- Anthony L. S., Kongshavn P. A. Experimental murine tularemia caused by Francisella tularensis, live vaccine strain: a model of acquired cellular resistance. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jan;2(1):3–14. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J., Freeman J., Bradley D. Influence of H-2 complex on acquired resistance to Leishmania donovani infection in mice. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):72–74. doi: 10.1038/283072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CINADER B., DUBISKI S., WARDLAW A. C. DISTRIBUTION, INHERITANCE, AND PROPERTIES OF AN ANTIGEN, MUB1, AND ITS RELATION TO HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:897–924. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigelsbach H. T., Hunter D. H., Janssen W. A., Dangerfield H. G., Rabinowitz S. G. Murine model for study of cell-mediated immunity: protection against death from fully virulent Francisella tularensis infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.999-1005.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan S. P. 'Nude', a new hairless gene with pleiotropic effects in the mouse. Genet Res. 1966 Dec;8(3):295–309. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300010168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervais F., Stevenson M., Skamene E. Genetic control of resistance to Listeria monocytogenes: regulation of leukocyte inflammatory responses by the Hc locus. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):2078–2083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Skamene E., Forget A. Genetic control of natural resistance to Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) in mice. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2417–2421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. G., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: genetics of natural resistance to infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):583–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.583-588.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst R. G., Wallace M. E. Inherited resistance to Corynebacterium kutscheri in mice. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):475–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.475-482.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Genetics of resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):72–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson H. G., Vas S. I. Resistance of inbred mice to Salmonella typhimurium. J Infect Dis. 1972 Oct;126(4):378–386. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.4.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Weinblatt A. C., O'Brien A. D. Genetic control of resistance to infection in mice. Crit Rev Immunol. 1982 Jun;3(4):263–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E. Genetic regulation of host resistance to bacterial infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S823–S832. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Gros P., Forget A., Kongshavn P. A., St Charles C., Taylor B. A. Genetic regulation of resistance to intracellular pathogens. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):506–509. doi: 10.1038/297506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Kongshavn P. A., Sachs D. H. Resistance to Listeria monocytogenes in mice: genetic control by genes that are not linked to the H-2 complex. J Infect Dis. 1979 Feb;139(2):228–231. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M. M., Kongshavn P. A., Skamene E. Genetic linkage of resistance to Listeria monocytogenes with macrophage inflammatory responses. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):402–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M. Genetic control of leucocyte responses to endotoxin. Nature. 1968 Sep 21;219(5160):1253–1254. doi: 10.1038/2191253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


