Abstract
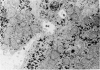
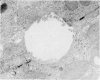
Choleretic infusions of taurocholate (40 μ moles for one hour) result in a significant increase in the number of lateral cell surface invaginations observed by scanning electron microscopy adjacent to the junctional complex of bile canaliculi in rat liver. Transmission electron microscopy indicates that these invaginations resemble “blisters” induced by osmotic gradients across epithelial tissues, a morphologic change which correlates with increases in ionic and hydraulic conductivity of the paracellular “shunt” pathway in such tissue. Since taurocholate infusions result in localization of ionic lanthanum chloride within hepatocyte junctional complexes, bile acids may also stimulate the movement of fluid and electrolytes across paracellular pathways during the process of bile formation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer J. L., Bloomer J. R. Canalicular bile secretion in man. Studies utilizing the biliary clearance of (14C)mannitol. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):773–781. doi: 10.1172/JCI107817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., DiBona D. Pathways for movement of ions and water across toad urinary bladder. II. Site and mode of action of vasopressin. J Membr Biol. 1974;19(3):195–220. doi: 10.1007/BF01869978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona D. R., Civan M. M. Pathways for movement of ions and water across toad urinary bladder. I. Anatomic site of transepithelial shunt pathways. J Membr Biol. 1973;12(2):101–128. doi: 10.1007/BF01869994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona D. R. Passive intercellular pathway in amphibian epithelia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 9;238(84):179–181. doi: 10.1038/newbio238179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L. Hepatocellular uptake of inulin, sucrose, and mannitol in rats. Am J Physiol. 1970 Dec;219(6):1568–1573. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.6.1568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L. The effect of estrogen on bile formation in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):654–663. doi: 10.1172/JCI106023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Gilula N. B. Variations in tight and gap junctions in mammalian tissues. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jun;53(3):758–776. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.3.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANZON V. Liver cell secretion under normal and pathologic conditions studied by fluorescence microscopy on living rats. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1952;28(101):1–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layden T. J., Boyer J. L. Influence of bile acids on bile canalicular membrane morphology and the lobular gradient in canalicular size. Lab Invest. 1978 Aug;39(2):110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layden T. J., Boyer J. L. Taurolithocholate-induced cholestasis: taurocholate but not dehydrocholate, reverses cholestasis and bile canalicular membrane injury. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jul;73(1):120–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layden T. J., Elias E., Boyer J. L. Bile formation in the rat: the role of the paracellular shunt pathway. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1375–1385. doi: 10.1172/JCI109258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layden T. J., Schwarz, Boyer J. L. Scanning electron microscopy of the rat liver. Studies of the effect of taurolithocholate and other models of cholestasis. Gastroenterology. 1975 Sep;69(3):724–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machen T. E., Erlij D., Wooding F. B. Permeable junctional complexes. The movement of lanthanum across rabbit gallbladder and intestine. J Cell Biol. 1972 Aug;54(2):302–312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Palomo A., Erlij D., Bracho H. Localization of permeability barriers in the frog skin epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1971 Aug;50(2):277–287. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter A., Orci L., Rouiller C. A study on the permeability barriers between Disse's space and the bile canaliculus. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Oct;11:1–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzki P. F. Bile canaliculus and space of Disse. Electron microscopic relationships as delineated by lanthanum. Lab Invest. 1969 Jan;20(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisher C. C., Yarger W. E. Lanthanum permeability of the tight junction (zonula occludens) in the renal tubule of the rat. Kidney Int. 1973 Apr;3(4):238–250. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. B., Karnovsky M. J. Fracture faces of osmotically disrupted zonulae occludentes. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):344–350. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. B., Revel J. P., DiScala V. A. Effect of osmotic gradients on intercellular junctions of the toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1973 Feb;224(2):407–415. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]