Abstract
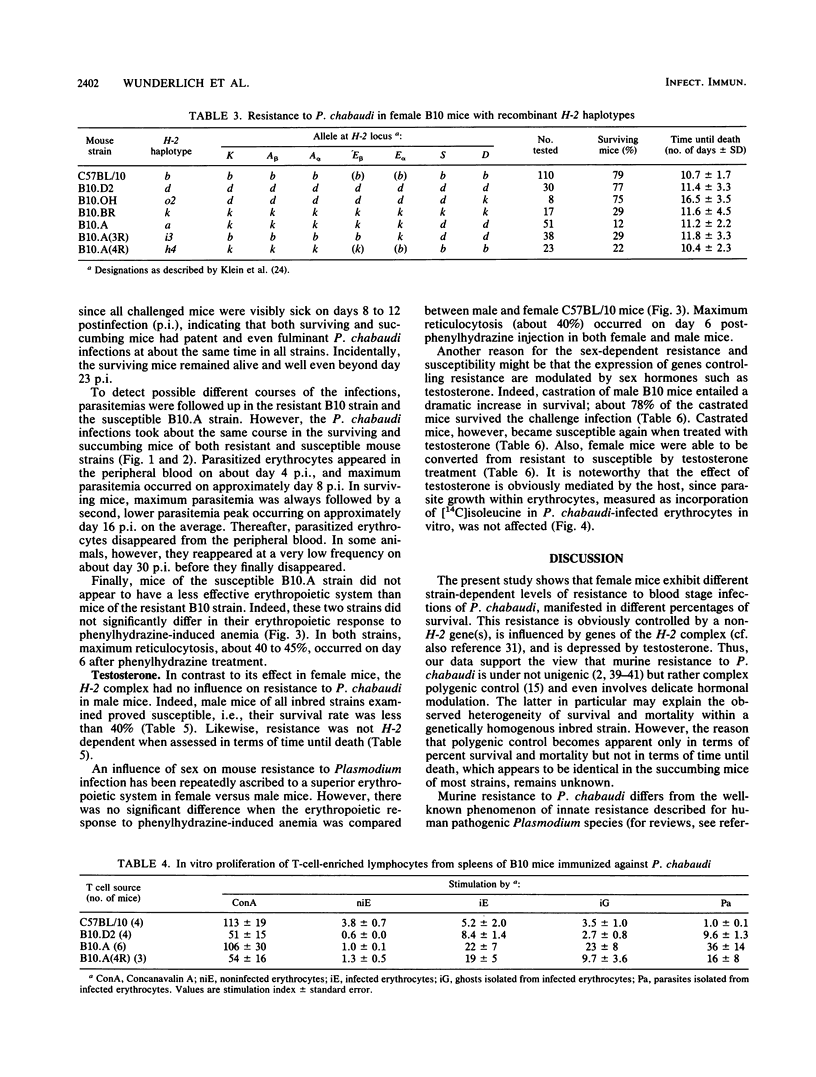
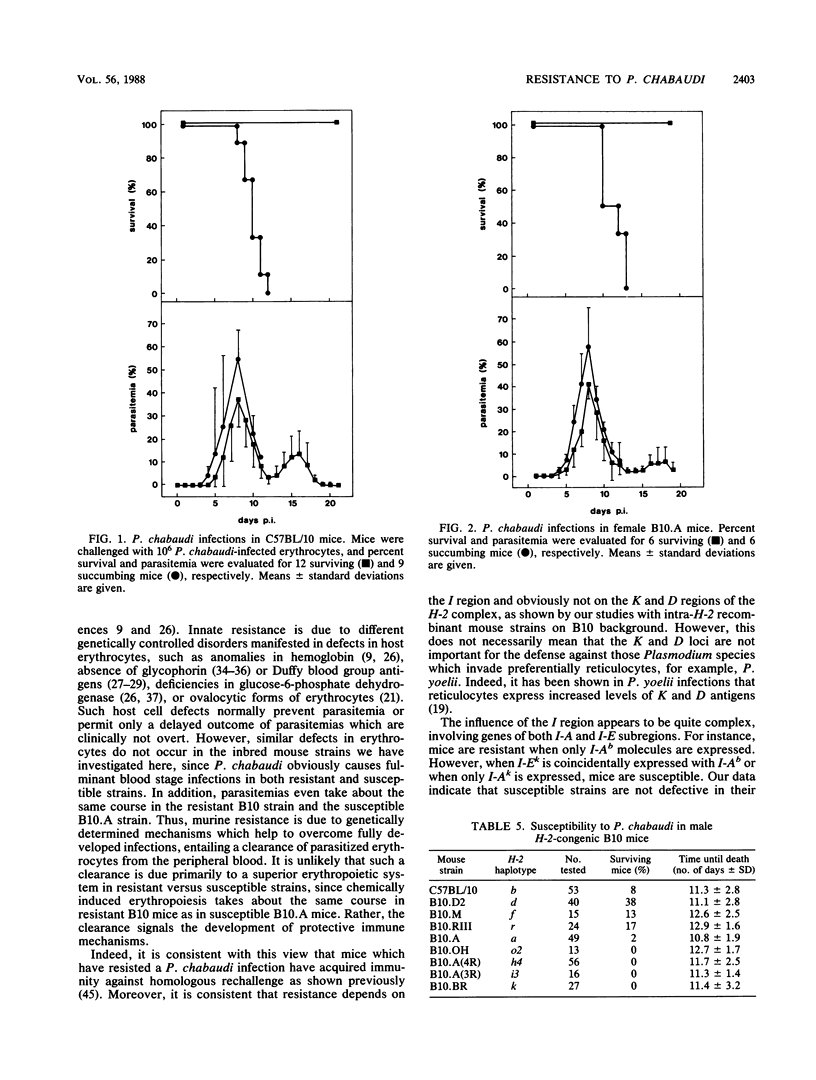
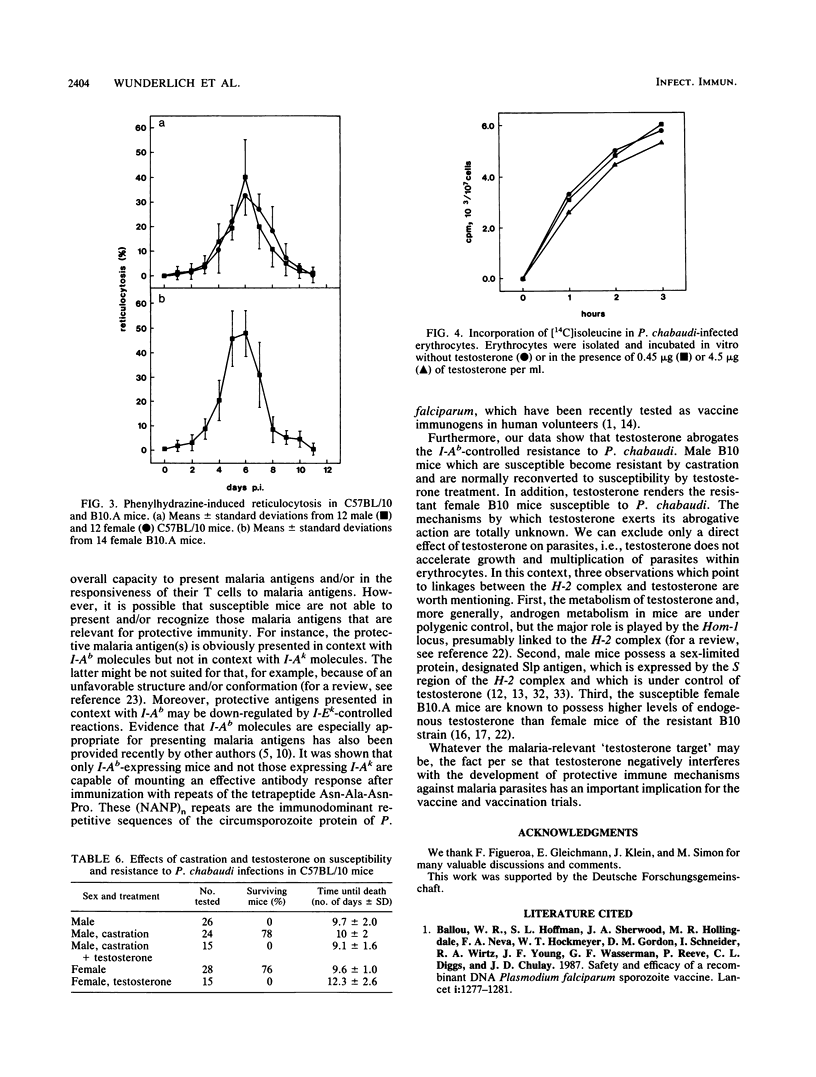
Resistance to Plasmodium chabaudi has been examined in different inbred mouse strains bearing identical H-2 haplotypes on different genetic backgrounds as well as in H-2-congenic mouse strains on B10 background. Resistance is expressed in terms of percent survival after a challenge with 10(6) P. chabaudi-infected erythrocytes. We can show that murine resistance to P. chabaudi is under complex polygenic control involving a non-H-2 gene(s) as well as genes in both I-A and I-E subregions of the H-2 complex. Our data indicate in particular that malaria protective antigens can be presented in context with I-Ab molecules but not in context with I-Ak molecules. Resistance controlled by I-Ab does not become apparent when I-Ek molecules are coincidentally expressed. Moreover, testosterone abrogates I-Ab-controlled resistance to P. chabaudi.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballou W. R., Hoffman S. L., Sherwood J. A., Hollingdale M. R., Neva F. A., Hockmeyer W. T., Gordon D. M., Schneider I., Wirtz R. A., Young J. F. Safety and efficacy of a recombinant DNA Plasmodium falciparum sporozoite vaccine. Lancet. 1987 Jun 6;1(8545):1277–1281. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90540-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büngener W. Malariaplasmodien in der Maus. Befall von reifen und unreifen Erythrozyten durch Plasmodium berghei, Plasmodium yoelii und Plasmodium chabaudi. Tropenmed Parasitol. 1979 Jun;30(2):198–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Giudice G., Cooper J. A., Merino J., Verdini A. S., Pessi A., Togna A. R., Engers H. D., Corradin G., Lambert P. H. The antibody response in mice to carrier-free synthetic polymers of Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite repetitive epitope is I-Ab-restricted: possible implications for malaria vaccines. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2952–2955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eling W., van Zon A., Jerusalem C. The course of a Plasmodium berghei infection in six different mouse strains. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Dec 13;54(1):29–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00380634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eugui E. M., Allison A. C. Differences in susceptibility of various mouse strains to haemoprotozoan infections: possible correlation with natural killer activity. Parasite Immunol. 1980 Winter;2(4):277–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1980.tb00059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey J. R., Spitalny G. L. Virulent and nonvirulent forms of Plasmodium yoelii are not restricted to growth within a single erythrocyte type. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):151–156. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.151-156.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBERG J., NADEL E. M., COATNEY G. R. [The influence of strain, sex and age of mice on infection with Plasmodium berghei]. J Infect Dis. 1953 Jul-Aug;93(1):96–100. doi: 10.1093/infdis/93.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good M. F., Berzofsky J. A., Maloy W. L., Hayashi Y., Fujii N., Hockmeyer W. T., Miller L. H. Genetic control of the immune response in mice to a Plasmodium falciparum sporozoite vaccine. Widespread nonresponsiveness to single malaria T epitope in highly repetitive vaccine. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):655–660. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampl R., Iványi P., Stárka L. Testosterone and testosterone binding in murine plasma. Steroidologia. 1971;2(2):113–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Krasteff T. N., Shreffler D. C. Quantitative variations in the expression of the mouse serum antigen Ss and its sex-limited allotype Slp. Biochem Genet. 1974 Oct;12(4):281–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00485949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Clyde D. F., Losonsky G., Cortesia M., Murphy J. R., Davis J., Baqar S., Felix A. M., Heimer E. P., Gillessen D. Safety and immunogenicity in man of a synthetic peptide malaria vaccine against Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):257–259. doi: 10.1038/328257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann E. J., Weidanz W. P., Long C. A. Susceptibility of CXB recombinant inbred mice to murine plasmodia. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):981–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.981-985.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iványi P., Gregorová S., Micková M., Hampl R., Stárka L. Genetic association between a histocompatibility gene (H-2) and androgen metabolism in mice. Transplant Proc. 1973 Mar;5(1):189–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iványi P., Hámpl R., Stárka L., Micková M. Genetic association between H-2 gene and testosterone metabolism in mice. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 30;238(87):280–281. doi: 10.1038/newbio238280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardena A. N., Mogil R., Murphy D. B., Burger D., Gershon R. K. Enhanced expression of H-2K and H-2D antigens on reticulocytes infected with Plasmodium yoelii. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):623–626. doi: 10.1038/302623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidson C., Lamont G., Saul A., Nurse G. T. Ovalocytic erythrocytes from Melanesians are resistant to invasion by malaria parasites in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5829–5832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F., David C. S. H-2 haplotypes, genes and antigens: second listing. II. The H-2 complex. Immunogenetics. 1983;17(6):553–596. doi: 10.1007/BF00366126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Juretic A., Baxevanis C. N., Nagy Z. A. The traditional and a new version of the mouse H-2 complex. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):455–460. doi: 10.1038/291455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L. Genetics of red cells and susceptibility to malaria. Blood. 1979 Nov;54(5):961–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason S. J., Miller L. H., Shiroishi T., Dvorak J. A., McGinniss M. H. The Duffy blood group determinants: their role in the susceptibility of human and animal erythrocytes to Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. Br J Haematol. 1977 Jul;36(3):327–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Haynes J. D., McAuliffe F. M., Shiroishi T., Durocher J. R., McGinniss M. H. Evidence for differences in erythrocyte surface receptors for the malarial parasites, Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium knowlesi. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):277–281. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Mason S. J., Dvorak J. A., McGinniss M. H., Rothman I. K. Erythrocyte receptors for (Plasmodium knowlesi) malaria: Duffy blood group determinants. Science. 1975 Aug 15;189(4202):561–563. doi: 10.1126/science.1145213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott K. J. Influence of reticulocytosis on the course of infection of Plasmodium chabaudi and P. berghei. J Protozool. 1968 May;15(2):365–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish C. R., Freeman R. R., McKenzie I. F., Cheers C., Cole G. A. Ia antigens in serum during different murine infections. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):422–426. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.422-426.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore H. C., Shreffler D. C. A sex-limited serum protein variant in the mouse: hormonal control of phenotypic expression. Biochem Genet. 1971 Apr;5(2):201–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00485645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore H. C., Shreffler D. C. A sex-limited serum protein variant in the mouse: inheritance and association with the H-2 region. Biochem Genet. 1970 Jun;4(3):351–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00485752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasvol G., Wainscoat J. S., Weatherall D. J. Erythrocytes deficiency in glycophorin resist invasion by the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):64–66. doi: 10.1038/297064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasvol G., Wilson R. J. The interaction of malaria parasites with red blood cells. Br Med Bull. 1982 May;38(2):133–140. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. Inhibitory effects of erythrocyte membrane proteins on the in vitro invasion of the human malarial parasite (Plasmodium falciparum) into its host cell. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):563–567. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth E. F., Jr, Raventos-Suarez C., Rinaldi A., Nagel R. L. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency inhibits in vitro growth of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):298–299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M. M., Lyanga J. J., Skamene E. Murine malaria: genetic control of resistance to Plasmodium chabaudi. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):80–88. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.80-88.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M. M., Skamene E. Murine malaria: resistance of AXB/BXA recombinant inbred mice to Plasmodium chabaudi. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):452–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.452-456.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Lemieux S., Skamene E. Genetic control of resistance to murine malaria. J Cell Biochem. 1984;24(1):91–102. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240240108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trischmann T. M., Bloom B. R. Genetics of murine resistance to Trypanosoma cruzi. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):546–551. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.546-551.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viens P., Chevalier J. L., Sonea S., Yoeli M. The effect of reticulocytosis on Plasmodium vinckei infection in white mice. Action of phenylhydrazine and of repeated bleedings. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Feb;17(2):257–261. doi: 10.1139/m71-043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Grumet F. C., Remington J. S. Genetic control of murine resistance to Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):416–420. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.416-420.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlich F., Helwig M. Plasmodium chabaudi malaria: red blood cells with altered membrane proteins in immune mice. Eur J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;43(3):499–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlich F., Helwig M., Schillinger G., Vial H., Philippot J., Speth V. Isolation and characterization of parasites and host cell ghosts from erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium chabaudi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Mar;23(2):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlich F., Schillinger G., Helwig M. Fractionation of Plasmodium chabaudi-infected erythrocytes into parasites and ghosts. Z Parasitenkd. 1985;71(4):545–551. doi: 10.1007/BF00928358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlich F., Stübig H., Königk E. Development of Plasmodium chabaudi in mouse red blood cells: structural properties of the host and parasite membranes. J Protozool. 1982 Feb;29(1):60–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1982.tb02880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


