Abstract
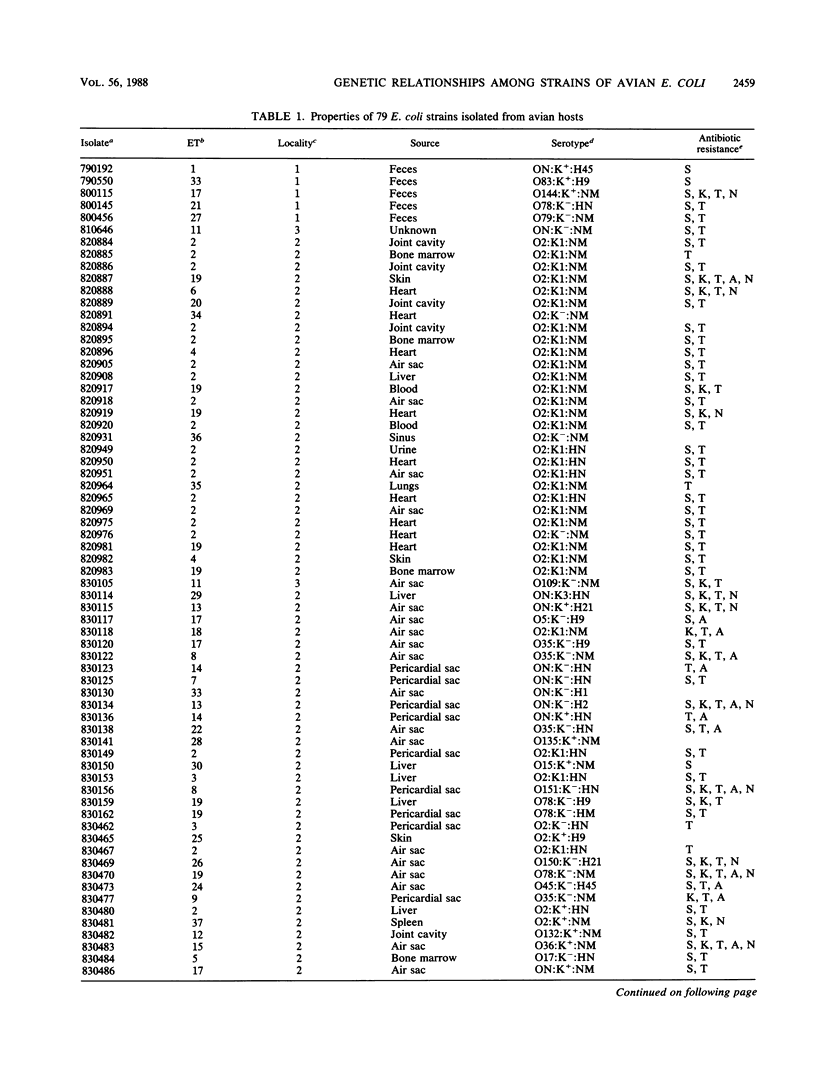
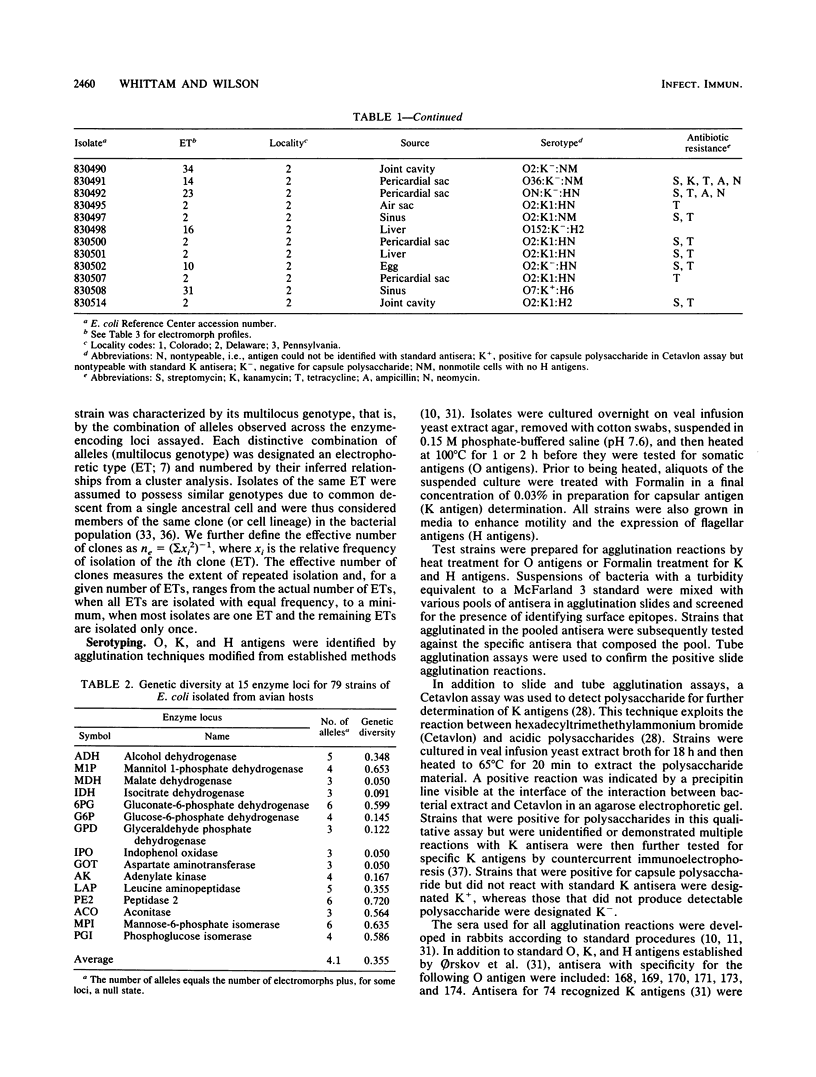
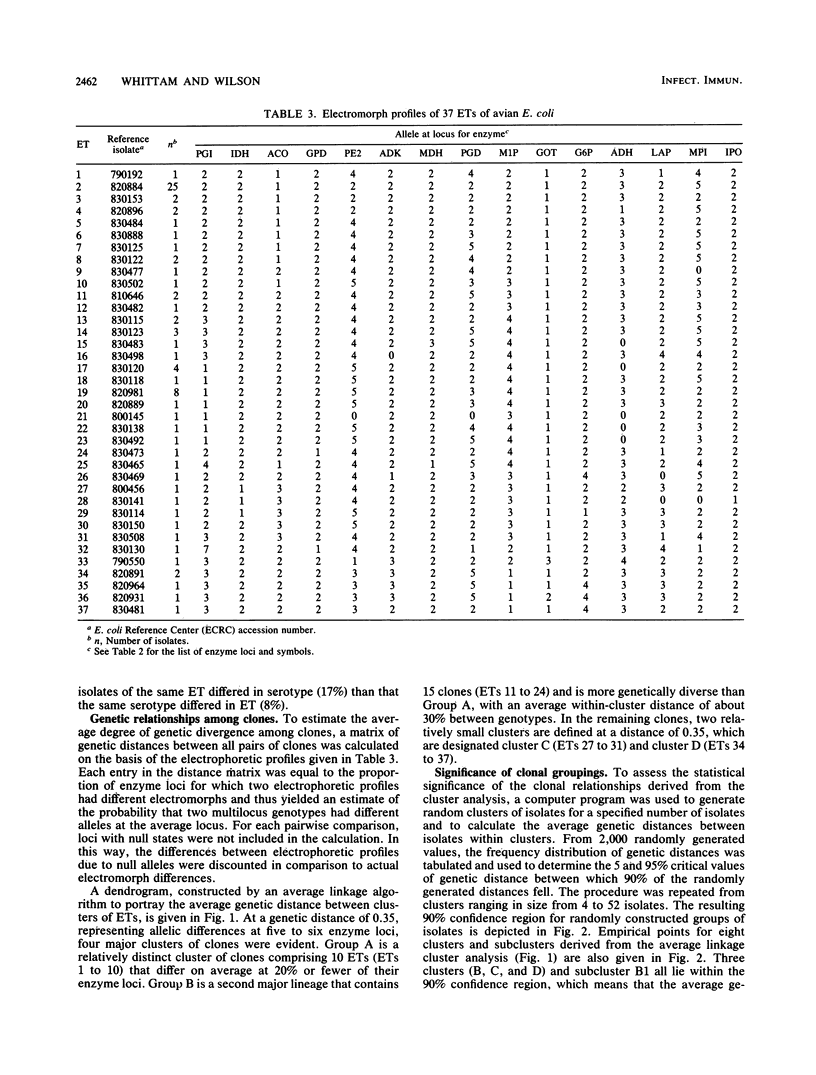
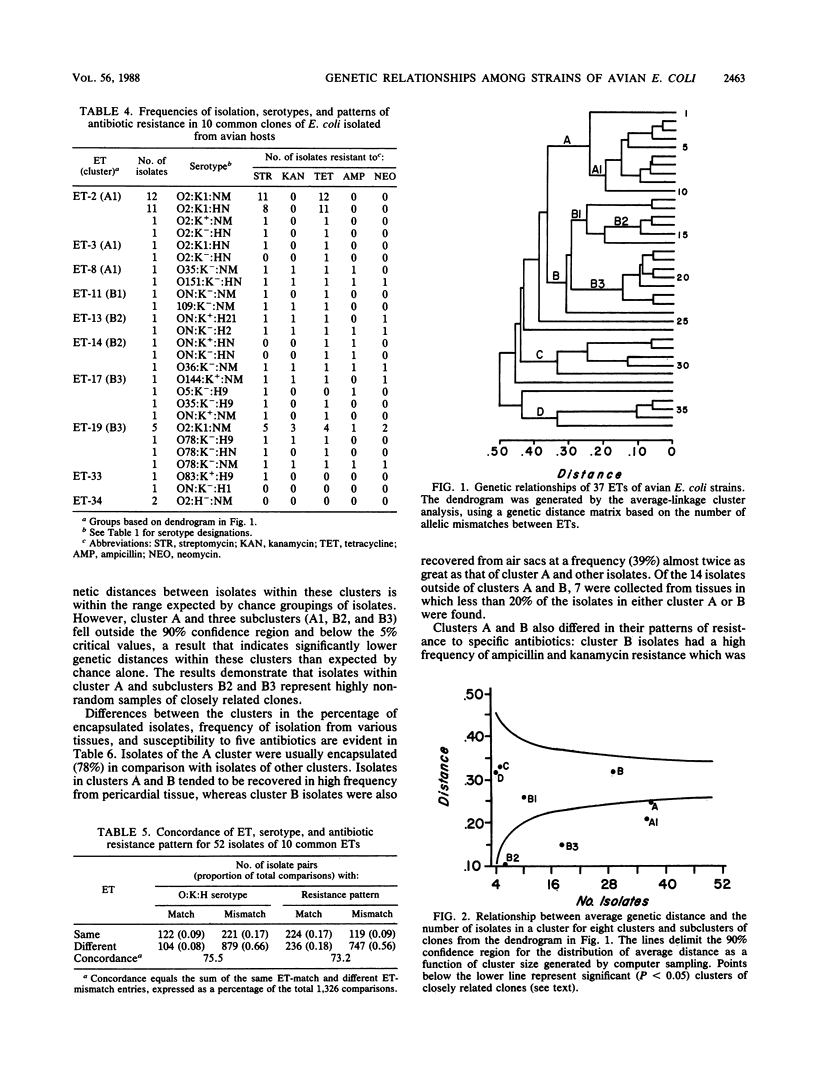
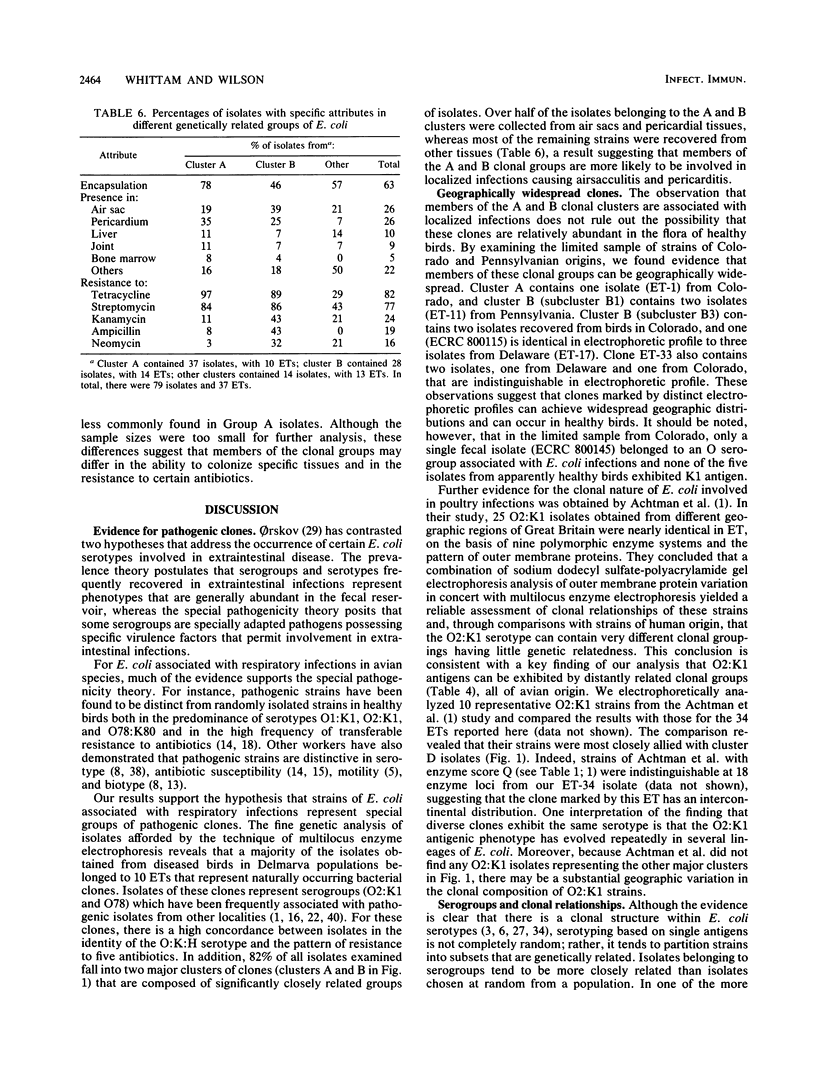
Genetic relationships among 79 strains of Escherichia coli, isolated mostly from diseased chickens, were estimated on the basis of allelic variation at 15 enzyme-encoding loci, determined by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. All 15 loci were polymorphic, with an average of 4.1 allelic states per locus. Comparisons of the observed combinations of alleles among strains revealed 37 distinct multilocus genotypes that were used to define naturally occurring cell lineages or clones. Two-thirds of the isolates were classified into 10 clones, including a single multilocus genotype that accounted for about a third of all isolates. For isolates of these clones, there was a high concordance (76%) between identity in multilocus genotype, O:K:H serotype, and pattern of resistance to five antibiotics. Cluster analysis disclosed two major complexes of closely related clones, in which more than 50% of the isolates were associated with localized infections (airsacculitis and pericarditis). Both complexes contained isolates with serotype O2:K1, indicating that this serotype can occur on diverse chromosomal backgrounds. The results suggest that colibacillosis within avian populations is caused by a relatively limited number of pathogenic clones representing at least two distinct clone complexes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Heuzenroeder M., Kusecek B., Ochman H., Caugant D., Selander R. K., Väisanen-Rhen V., Korhonen T. K., Stuart S., Orskov F. Clonal analysis of Escherichia coli O2:K1 isolated from diseased humans and animals. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):268–276. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.268-276.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achtman M., Mercer A., Kusecek B., Pohl A., Heuzenroeder M., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Silver R. P. Six widespread bacterial clones among Escherichia coli K1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):315–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.315-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achtman M., Pluschke G. Clonal analysis of descent and virulence among selected Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:185–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Levin B. R., Orskov I., Orskov F., Svanborg Eden C., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity in relation to serotype in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):407–413. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.407-413.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caugant D. A., Levin B. R., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and temporal variation in the E. coli population of a human host. Genetics. 1981 Jul;98(3):467–490. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloud S. S., Rosenberger J. K., Fries P. A., Wilson R. A., Odor E. M. In vitro and in vivo characterization of avian Escherichia coli. I. Serotypes, metabolic activity, and antibiotic sensitivity. Avian Dis. 1985 Oct-Dec;29(4):1084–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominick M. A., Schmerr M. J., Jensen A. E. Expression of type 1 pili by Escherichia coli strains of high and low virulence in the intestinal tract of gnotobiotic turkeys. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Jan;46(1):270–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyimah J. E., Panigrahy B. Adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of pathogenic Escherichia coli to chicken tracheal epithelium. Avian Dis. 1988 Jan-Mar;32(1):74–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyimah J. E., Panigrahy B. Immunogenicity of an Escherichia coli (serotype O1) pili vaccine in chickens. Avian Dis. 1985 Oct-Dec;29(4):1078–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRY E. G., CHUBB L. G. RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN CERTAIN BIOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND PATHOLOGICAL ACTIVITY IN AVIAN STRAINS OF E. COLI. J Comp Pathol. 1964 Apr;74:180–187. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1742(64)80022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller E. D., Drabkin N. Some characteristics of pathogenic E. coli strains. Br Vet J. 1977 Nov-Dec;133(6):572–578. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)33936-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller E. D., Smith H. W. The incidence of antibiotic resistance and other characteristics amongst Escherichia coli strains causing fatal infection in chickens: the utilization of these characteristics to study the epidemiology of the infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Dec;71(4):771–781. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400023032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsley R. V., Barnum D. A., Ingram D. G. Biochemical and serological studies of avian strains of Escherichia coli. Avian Dis. 1967 Feb;11(1):90–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai H., Hashimoto H., Mitsuhashi S. Drug resistance and conjugative R plasmids in fecal Escherichia coli strains isolated from healthy younger animals (chickens, piglets, calves) and children. Microbiol Immunol. 1983;27(12):1031–1041. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1983.tb02937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H., Howe K., Bennett P. M., Richmond M. H., Whiteside E. J. The colonization of the human gut by antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli from chickens. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;43(3):465–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraja K. V., Emery D. A., Newman J. A., Pomeroy B. S. Identification and isolation of somatic pili from pathogenic Escherichia coli of turkeys. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Feb;44(2):284–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naveh M. W., Zusman T., Skutelsky E., Ron E. Z. Adherence pili in avian strains of Escherichia coli: effect on pathogenicity. Avian Dis. 1984 Jul-Sep;28(3):651–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Selander R. K. Evidence for clonal population structure in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):198–201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Whittam T. S., Caugant D. A., Selander R. K. Enzyme polymorphism and genetic population structure in Escherichia coli and Shigella. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2715–2726. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger J. K., Fries P. A., Cloud S. S., Wilson R. A. In vitro and in vivo characterization of avian Escherichia coli. II. Factors associated with pathogenicity. Avian Dis. 1985 Oct-Dec;29(4):1094–1107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Caugant D. A., Ochman H., Musser J. M., Gilmour M. N., Whittam T. S. Methods of multilocus enzyme electrophoresis for bacterial population genetics and systematics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):873–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.873-884.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Korhonen T. K., Väisänen-Rhen V., Williams P. H., Pattison P. E., Caugant D. A. Genetic relationships and clonal structure of strains of Escherichia coli causing neonatal septicemia and meningitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):213–222. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.213-222.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Levin B. R. Genetic diversity and structure in Escherichia coli populations. Science. 1980 Oct 31;210(4469):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6999623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenderup J., Orskov F. The clonal nature of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1019–1024. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwanichkul A., Panigrahy B. Biological and immunological characterization of pili of Escherichia coli serotypes O1, O2, and O78 pathogenic to poultry. Avian Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;30(4):781–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Ochman H., Selander R. K. Geographic components of linkage disequilibrium in natural populations of Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Evol. 1983 Dec;1(1):67–83. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Ochman H., Selander R. K. Multilocus genetic structure in natural populations of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1751–1755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam T. S., Wachsmuth I. K., Wilson R. A. Genetic evidence of clonal descent of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1124–1133. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


