Abstract
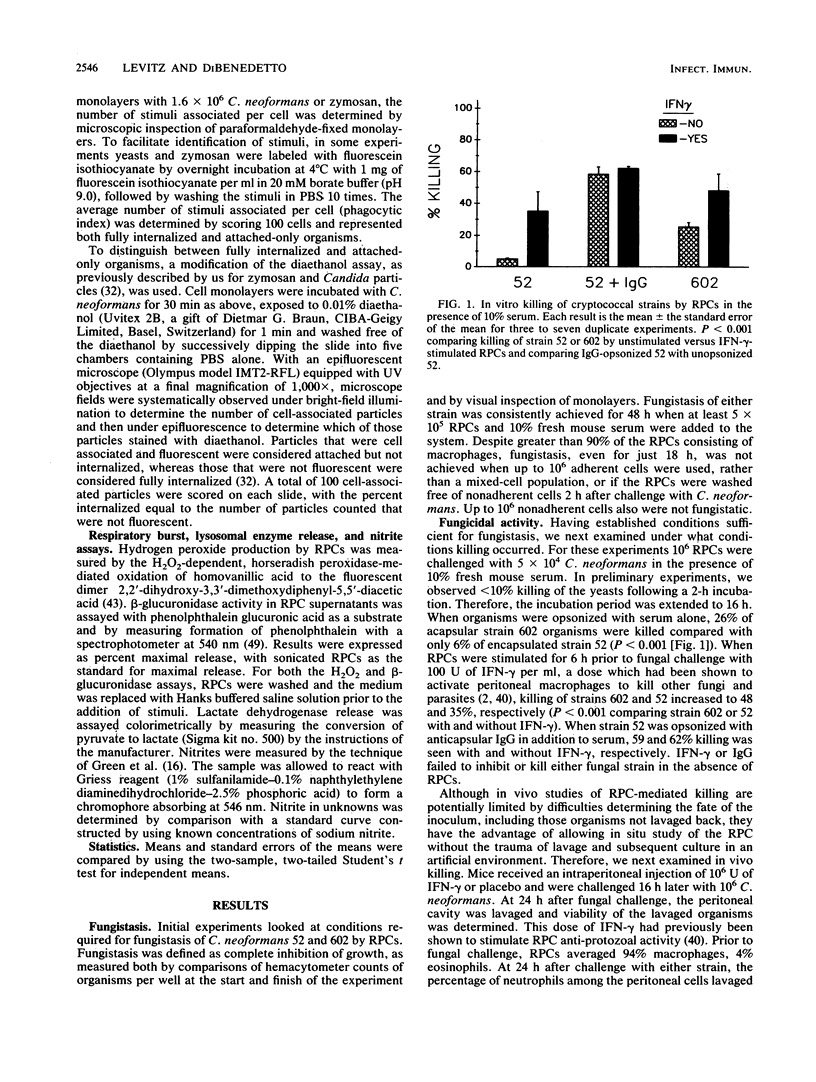
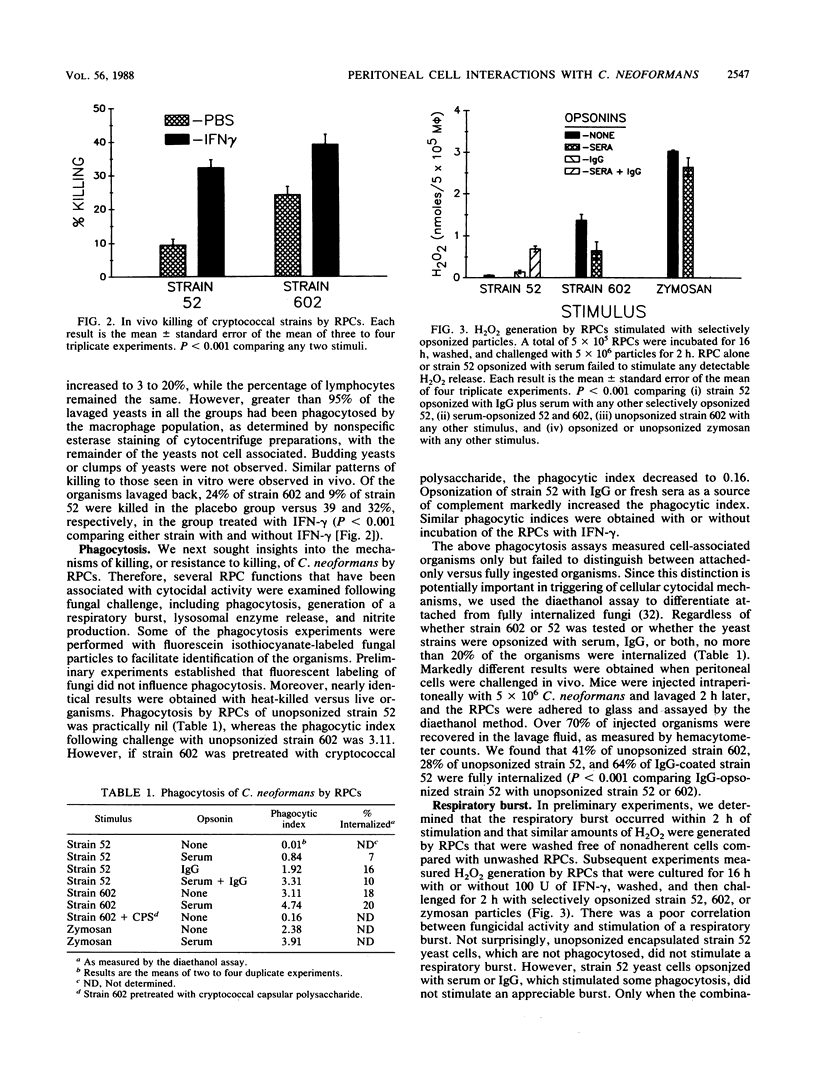
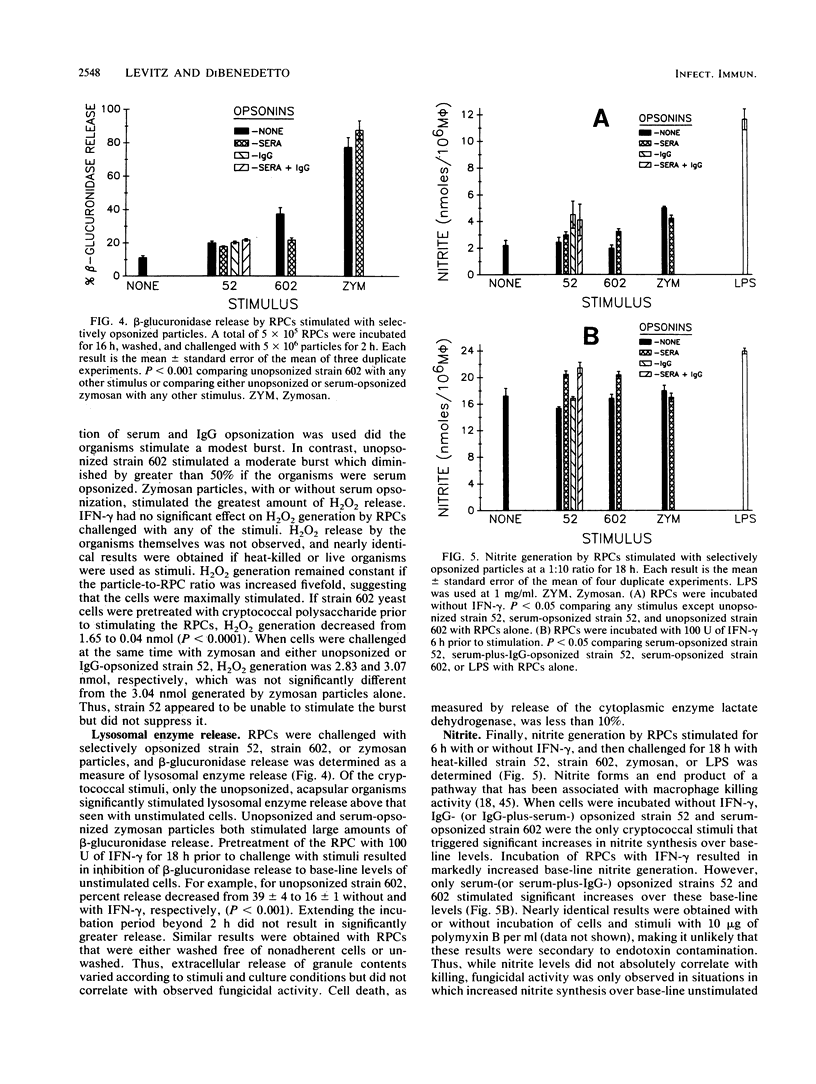
Stimulation of murine resident peritoneal cells (RPCs) by encapsulated strain 52 and acapsular strain 602 of Cryptococcus neoformans was compared. Fresh serum was required for fungistasis of both strains. Encapsulated organisms were killed only if the RPCs were activated with gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) or if the organisms were opsonized with anticapsular immunoglobulin G (IgG). In contrast, acapsular organisms were killed by unactivated RPCs, with enhanced killing seen if the cells were activated with IFN-gamma. Except for unopsonized strain 52, all organisms of both strains were phagocytosed. The respiratory burst was stimulated in unactivated and IFN-gamma-activated RPCs by encapsulated strain 52 only if organisms were opsonized with both IgG and serum. In contrast, the burst was stimulated by acapsular strain 602, with or without opsonization. Only unopsonized strain 602 stimulated significant lysosomal enzyme release. Nitrite synthesis by unactivated RPCs was seen only if strain 52 was opsonized with anticapsular IgG or if strain 602 was opsonized with serum. If RPCs were activated with IFN-gamma, then serum-opsonized strain 52 was also able to stimulate nitrite synthesis. Thus, RPC killing, phagocytosis, respiratory burst, lysosomal enzyme release, and nitrite synthesis following challenge by both unopsonized and opsonized with serum or anticapsular IgG strains 52 and 602 varied according to the surface properties of the organisms, the state of activation of the RPCs, and the particular RPC event studied. However, stimulation of nitrite synthesis was the only RPC event which correlated with killing of both strains.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharjee A. K., Bennett J. E., Glaudemans C. P. Capsular polysaccharides of Cryptococcus neoformans. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6(5):619–624. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.5.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummer E., Morrison C. J., Stevens D. A. Recombinant and natural gamma-interferon activation of macrophages in vitro: different dose requirements for induction of killing activity against phagocytizable and nonphagocytizable fungi. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):724–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.724-730.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer G. S., Tacker J. R. Phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans by alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):73–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.73-79.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauley L. K., Murphy J. W. Response of congenitally athymic (nude) and phenotypically normal mice to Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):644–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.644-651.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Allison A. C. Nature of the effector cells responsible for antibody-dependent cell-mediated killing of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):716–720. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.716-720.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Bennett J. E. Growth of Cryptococcus neoformans within human macrophages in vitro. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):231–236. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.231-236.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Bennett J. E. Prognostic factors in cryptococcal meningitis. A study in 111 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Feb;80(2):176–181. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-2-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D. Effects of stimulation and suppression of cell-mediated immunity on experimental cryptococcosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):187–194. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.187-194.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., May J. E., Kane M. A., Frank M. M., Bennett J. E. The role of the classical and alternate complement pathways in host defenses against Cryptococcus neoformans infection. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2260–2270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Root R. K., Bennett J. E. Factors influencing killing of Cryptococcus neoformans by human leukocytes in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):367–376. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dromer F., Charreire J., Contrepois A., Carbon C., Yeni P. Protection of mice against experimental cryptococcosis by anti-Cryptococcus neoformans monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):749–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.749-752.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. O., Remington J. S. Resistance against Cryptococcus conferred by intracellular bacteria and protozoa. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):22–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Specific amino acid (L-arginine) requirement for the microbiostatic activity of murine macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1129–1136. doi: 10.1172/JCI113427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Macrophage-mediated fungistasis in vitro: requirements for intracellular and extracellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):672–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr Roles of macrophage Fc and C3b receptors in phagocytosis of immunologically coated Cryptococcus neoformans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3853–3857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z. Macrophage cytotoxicity: role for L-arginine deiminase and imino nitrogen oxidation to nitrite. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):473–476. doi: 10.1126/science.2432665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janusz M. J., Austen K. F., Czop J. K. Lysosomal enzyme release from human monocytes by particulate activators is mediated by beta-glucan inhibitable receptors. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3897–3901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. Regulation of the Fc-receptor-mediated respiratory burst: treatment of primed murine peritoneal macrophages with lipopolysaccharide selectively inhibits H2O2 secretion stimulated by immune complexes. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):513–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitz D. J., Johnson C. R., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G., Little J. R. Growth inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans by cloned cultured murine macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 15;88(2):489–500. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Cazin J. Nonencapsulated Variant of Cryptococcus neoformans I. Virulence Studies and Characterization of Soluble Polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1971 Feb;3(2):287–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.2.287-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R. Dissociation of a hydrophobic surface from phagocytosis of encapsulated and non-encapsulated cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1214–1219. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1214-1219.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Gotschlich E. C. The capsule of cryptococcus neoformans passively inhibits phagocytosis of the yeast by macrophages. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1675–1680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Hermerath C. A. Binding of cryptococcal polysaccharide to Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):879–886. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.879-886.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Highison B., Stratton C. J. Localization on encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans of serum components opsonic for phagocytosis by macrophages and neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):574–579. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.574-579.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Mastroianni R. P. Inhibition of phagocytosis by cryptococcal polysaccharide: dissociation of the attachment and ingestion phases of phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):62–67. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.62-67.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., McGaw T. G. Opsonization of Cryptococcus neoformans by human immunoglobulin G: role of immunoglobulin G in phagocytosis by macrophages. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):255–261. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.255-261.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Polacheck I., Popkin T. J. Melanin-lacking mutants of Cryptococcus neoformans and their virulence for mice. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1414–1421. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1414-1421.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., DiBenedetto D. J., Diamond R. D. A rapid fluorescent assay to distinguish attached from phagocytized yeast particles. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Jul 16;101(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90213-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., Diamond R. D. Killing of Aspergillus fumigatus spores and Candida albicans yeast phase by the iron-hydrogen peroxide-iodide cytotoxic system: comparison with the myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-halide system. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1100–1102. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1100-1102.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim T. S., Murphy J. W. Transfer of immunity to cryptococcosis by T-enriched splenic lymphocytes from Cryptococcus neoformans-sensitized mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):5–11. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.5-11.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macher A. M., Bennett J. E., Gadek J. E., Frank M. M. Complement depletion in cryptococcal sepsis. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1686–1690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani B., Rabinovitch M., Nussenzweig V. Phagocytosis of immune complexes by macrophages. Different roles of the macrophage receptor sites for complement (C3) and for immunoglobulin (IgG). J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):780–792. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monga D. P. Role of macrophages in resistance of mice to experimental cryptococcosis. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):975–978. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.975-978.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., McDaniel D. O. In vitro reactivity of natural killer (NK) cells against Cryptococcus neoformans. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1577–1583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Moorhead J. W. Regulation of cell-mediated immunity in cryptococcosis. I. Induction of specific afferent T suppressor cells by cryptococcal antigen. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):276–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Mosley R. L., Moorhead J. W. Regulation of cell-mediated immunity in cryptococcosis. II. Characterization of first-order T suppressor cells (Ts1) and induction of second-order suppressor cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2876–2881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Spitalny G. L., Nathan C. F. Activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1619–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi N., Murphy J. W. Antibody-dependent natural killer cell-mediated growth inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):556–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.556-562.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Prendergast T. J., Wiebe M. E., Stanley E. R., Platzer E., Remold H. G., Welte K., Rubin B. Y., Murray H. W. Activation of human macrophages. Comparison of other cytokines with interferon-gamma. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):600–605. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruch W., Cooper P. H., Baggiolini M. Assay of H2O2 production by macrophages and neutrophils with homovanillic acid and horse-radish peroxidase. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Oct 28;63(3):347–357. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(83)80008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp A. K., Banerjee D. K. Effect of gamma interferon on hydrogen peroxide production by cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):597–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.597-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Induction of nitrite/nitrate synthesis in murine macrophages by BCG infection, lymphokines, or interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):518–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Mammalian nitrate biosynthesis: mouse macrophages produce nitrite and nitrate in response to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7738–7742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. S., Nelson R. S., Silverstein S. C. Mouse peritoneal macrophages plated on mannan- and horseradish peroxidase-coated substrates lose the ability to phagocytose by their Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3712–3717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacker J. R., Farhi F., Bulmer G. S. Intracellular fate of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):162–167. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.162-167.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valletta E. A., Berton G. Desensitization of macrophage oxygen metabolism on immobilized ligands: different effect of immunoglobulin G and complement. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4366–4373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. E., Bennett J. E., Bailey J. W. Serologic grouping of Cryptococcus neoformans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Mar;127(3):820–823. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Licht M. R., Craigmyle L. S., Silverstein S. C. Communication between receptors for different ligands on a single cell: ligation of fibronectin receptors induces a reversible alteration in the function of complement receptors on cultured human monocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):336–339. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Silverstein S. C. Receptors for C3b and C3bi promote phagocytosis but not the release of toxic oxygen from human phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2016–2023. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B. A., Howard D. H. Inhibition of the intracellular growth of Histoplasma capsulatum by recombinant murine gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1987 Apr;55(4):1014–1016. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.4.1014-1016.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


