Abstract
A major virulence factor of group A streptococci is M protein, a surface-exposed fibrillar molecule of which there exist more than 80 distinct serological types. Antigenic variability resides largely in the amino-terminal region of M protein, whereas the carboxy-terminal half of the molecule is highly conserved among different M serotypes. We sought to determine whether mucosal immunization with conserved epitopes of M protein influences the course of mucosal colonization by group A streptococci in a mouse model. Synthetic peptides corresponding to sequences in the conserved region of M protein were covalently linked to the mucosal adjuvant cholera toxin B subunit. Mice were immunized intranasally with the peptide-cholera toxin B subunit conjugate or with cholera toxin B subunit alone and then challenged intranasally with live streptococci. Pharyngeal colonization by streptococci was measured for up to 15 days postchallenge. Mice immunized with synthetic peptides showed a significant reduction in colonization compared with the control group. The data demonstrate that immunity evoked by conserved portions of M protein influences the outcome of group A streptococcal infection at the nasopharyngeal mucosa in a mouse model.
Full text
PDF


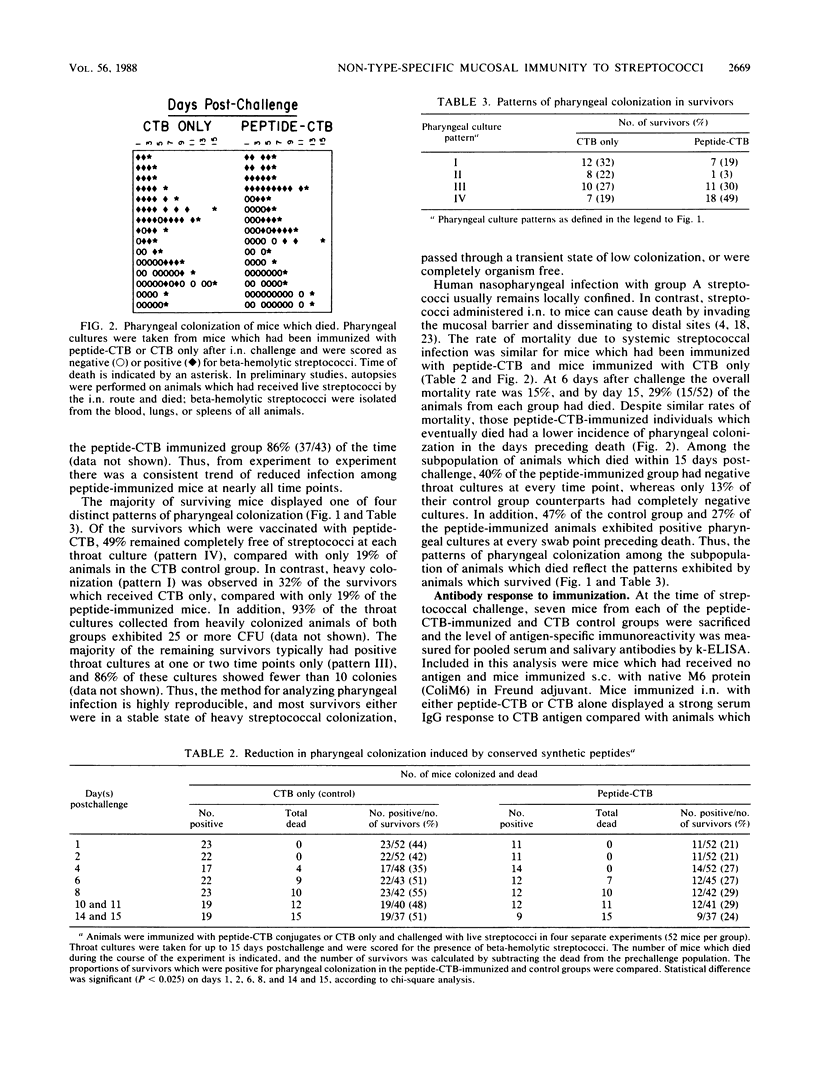
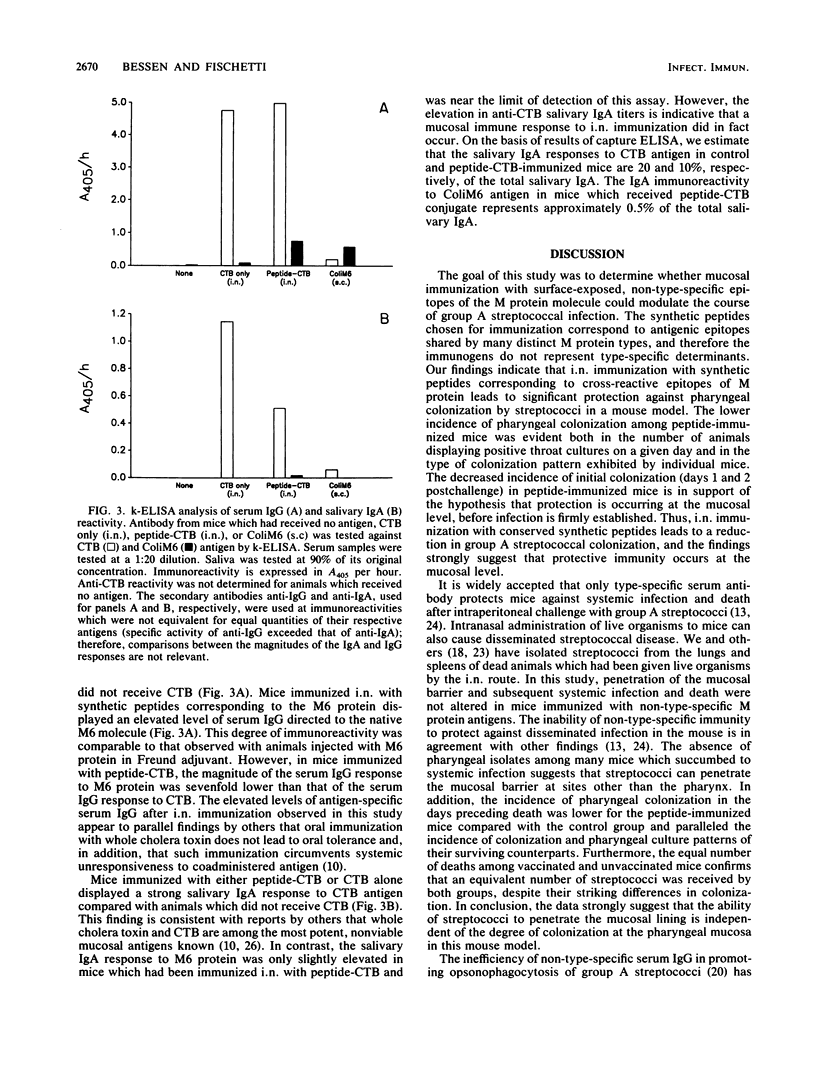


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H., Seyer J. M., Dale J. B. Protective immunogenicity and T lymphocyte specificity of a trivalent hybrid peptide containing NH2-terminal sequences of types 5, 6, and 24 M proteins synthesized in tandem. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):647–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Seyer J. M., Dale J. B., Simpson W. A., Kang A. H. Type-specific protective immunity evoked by synthetic peptide of Streptococcus pyogenes M protein. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):457–459. doi: 10.1038/292457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessen D., Fischetti V. A. Passive acquired mucosal immunity to group A streptococci by secretory immunoglobulin A. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1945–1950. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisno A. L. Alternate complement pathway activation by group A streptococci: role of M-protein. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1172–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1172-1176.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Drevin H., Axén R. Protein thiolation and reversible protein-protein conjugation. N-Succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio)propionate, a new heterobifunctional reagent. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):723–737. doi: 10.1042/bj1730723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessandri R., Plotkin G., Kluge R. M., Wittner M. K., Fox E. N., Dorfman A., Waldman R. H. Protective studies with group A streptococcal M protein vaccine. III. Challenge of volunteers after systemic or intranasal immunization with Type 3 or Type 12 group A Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1978 Dec;138(6):712–718. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.6.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale J. B., Beachey E. H. Sequence of myosin-crossreactive epitopes of streptococcal M protein. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1785–1790. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Cholera toxin feeding did not induce oral tolerance in mice and abrogated oral tolerance to an unrelated protein antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2892–2897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Jones K. F., Manjula B. N., Scott J. R. Streptococcal M6 protein expressed in Escherichia coli. Localization, purification, and comparison with streptococcal-derived M protein. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1083–1095. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Parry D. A., Trus B. L., Hollingshead S. K., Scott J. R., Manjula B. N. Conformational characteristics of the complete sequence of group A streptococcal M6 protein. Proteins. 1988;3(1):60–69. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N. M proteins of group A streptococci. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):57–86. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.57-86.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Waldman R. H., Wittner M. K., Mauceri A. A., Dorfman A. Protective study with a group A streptococcal M protein vaccine. Infectivity challenge of human volunteers. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):1885–1892. doi: 10.1172/JCI107372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOOK E. W., WAGNER R. R., LANCEFIELD R. C. An epizootic in Swiss mice caused by a group A Streptococcus, newly designated type 50. Am J Hyg. 1960 Jul;72:111–119. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. A highly conserved region present in transcripts encoding heterologous M proteins of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3237–3239. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3237-3239.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of type 6 M protein of the group A Streptococcus. Repetitive structure and membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1677–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Size variation in group A streptococcal M protein is generated by homologous recombination between intragenic repeats. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):196–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00331578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks-Weis J., Kim Y., Cleary P. P. Restricted deposition of C3 on M+ group A streptococci: correlation with resistance to phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1897–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. F., Fischetti V. A. The importance of the location of antibody binding on the M6 protein for opsonization and phagocytosis of group A M6 streptococci. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1114–1123. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. F., Khan S. A., Erickson B. W., Hollingshead S. K., Scott J. R., Fischetti V. A. Immunochemical localization and amino acid sequences of crossreactive epitopes within the group A streptococcal M6 protein. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1226–1238. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. F., Manjula B. N., Johnston K. H., Hollingshead S. K., Scott J. R., Fischetti V. A. Location of variable and conserved epitopes among the multiple serotypes of streptococcal M protein. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):623–628. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurl D. N., Stjernquist-Desatnik A., Schalén C., Christensen P. Induction of local immunity to group A streptococci type M50 in mice by non-type-specific mechanisms. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Dec;93(6):401–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig D. S., Holmes R. K., Schoolnik G. K. Chemical and immunochemical studies on the receptor binding domain of cholera toxin B subunit. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12528–12534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. J., Halsey J. F. Cholera toxin B subunit as a carrier protein to stimulate a mucosal immune response. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1818–1824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancholi V., Fischetti V. A. Isolation and characterization of the cell-associated region of group A streptococcal M6 protein. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2618–2624. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2618-2624.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Schmeling D., Cleary P. P., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Quie P. G. Inhibition of alternative complement pathway opsonization by group A streptococcal M protein. J Infect Dis. 1979 May;139(5):575–585. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.5.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. N., Jr, Flicker P. F., Cohen C., Manjula B. N., Fischetti V. A. Streptococcal M protein: alpha-helical coiled-coil structure and arrangement on the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4689–4693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polly S. M., Waldman R. H., High P., Wittner M. K., Dorfman A. Protective studies with a group A streptococcal M protein vaccine. II. Challange of volenteers after local immunization in the upper respiratory tract. J Infect Dis. 1975 Mar;131(3):217–224. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.3.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. R., Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A. Homologous regions within M protein genes in group A streptococci of different serotypes. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):609–612. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.609-612.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Wilson B. C., Peralta J. M. Quantitative, single-tube, kinetic-dependent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (k-ELISA). Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:391–403. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


