Abstract
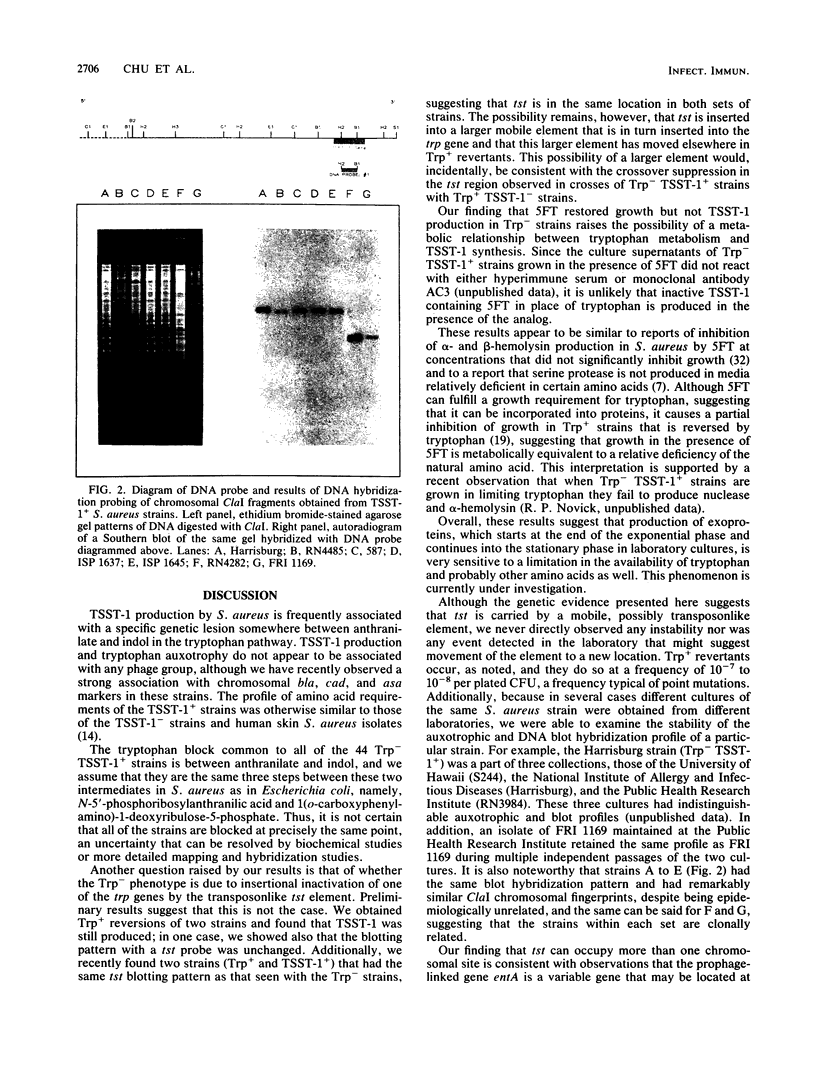
Most Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic shock syndrome and producing toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1) require tryptophan because of a genetic defect in tryptophan biosynthesis. The association between TSST-1 production and tryptophan auxotrophy was not correlated with the phage type, the colonization site, or the disease status of the patient from whom the isolate came. Protoplast fusion and transformation mapping located the genetic determinant of TSST-1 production (tst) very close to the trp operon in such strains and very close to tyrB in a Trp+ TSST-1+ strain. Southern blot hybridization of ClaI-restricted chromosomal DNA with a tst-specific probe revealed a common homologous segment in all of the Trp+ strains with tst linked to tyrB. These results confirmed that the tst determinant in Trp- strains is located at one site, whereas in Trp+ TSST-1+ strains the determinant is located elsewhere on the S. aureus chromosome. It is suggested that the TSST-1 determinant is associated with the insertion of a transposonlike segment into several sites on the S. aureus chromosome.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altemeier W. A., Lewis S. A., Schlievert P. M., Bergdoll M. S., Bjornson H. S., Staneck J. L., Crass B. A. Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome: phage typing and toxin capability testing. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):978–982. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altemeier W. A., Lewis S. A., Schlievert P. M., Bergdoll M. S., Bjornson H. S., Staneck J. L., Crass B. A. Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome: phage typing and toxin capability testing. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jun;96(6 Pt 2):978–982. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-6-978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Vaginal isolates of Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):442–449. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.442-449.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergdoll M. S., Crass B. A., Reiser R. F., Robbins R. N., Davis J. P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981 May 9;1(8228):1017–1021. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best G. K., Scott D. F., Kling J. M., Crowell W. F., Kirkland J. J. Enhanced susceptibility of male rabbits to infection with a toxic shock strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):727–732. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.727-732.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betley M. J., Löfdahl S., Kreiswirth B. N., Bergdoll M. S., Novick R. P. Staphylococcal enterotoxin A gene is associated with a variable genetic element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5179–5183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomster-Hautamaa D. A., Kreiswirth B. N., Kornblum J. S., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M. The nucleotide and partial amino acid sequence of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15783–15786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney P. J., Bergdoll M. S., Davis J. P., Vergeront J. M. The disease spectrum, epidemiology, and etiology of toxic-shock syndrome. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:315–338. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Bartlett K. H., Percival-Smith R., Morrison B. J. Vaginal colonization with Staphylococcus aureus, positive for toxic-shock marker protein, and Escherichia coli in healthy women. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):80–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. C., Melish M. E., James J. F. Tryptophan auxotypy associated with Staphylococcus aureus that produce toxic-shock-syndrome toxin. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1157–1158. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmett M., Kloos W. E. Amino acid requirements of staphylococci isolated from human skin. Can J Microbiol. 1975 May;21(5):729–733. doi: 10.1139/m75-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Antibody production by hybridomas. J Immunol Methods. 1980;39(4):285–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B. N., Kravitz G. R., Schlievert P. M., Novick R. P. Nosocomial transmission of a strain of Staphylococcus aureus causing toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Nov;105(5):704–707. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-5-704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiswirth B. N., Löfdahl S., Betley M. J., O'Reilly M., Schlievert P. M., Bergdoll M. S., Novick R. P. The toxic shock syndrome exotoxin structural gene is not detectably transmitted by a prophage. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):709–712. doi: 10.1038/305709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leboeuf-Trudeau T., de Repentigny J., Frenette R. M., Sonea S. Tryptophan metabolism and toxin formation in Staphylococcus aureus Wood 46 strain. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Jan;15(1):1–7. doi: 10.1139/m69-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. C., Bergdoll M. S. Spontaneous occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus mutants with different pigmentation and ability to produce toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):308–309. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.308-309.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupski J. R. Molecular mechanisms for transposition of drug-resistance genes and other movable genetic elements. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Mar-Apr;9(2):357–368. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.2.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheieu L. G., de Repentigny J., Trudeau T. Effects of amino acid analogs on growth and toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Rev Can Biol. 1970 Sep;29(3):271–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A. Distribution of Tn551 insertion sites responsible for auxotrophy on the Staphylococcus aureus chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):479–488. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.479-488.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Neveln D. S. Transformation analysis of three linkage groups in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):201–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.201-211.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor A. R., Kloos W. E. The tryptophan gene cluster of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(3):319–327. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-3-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quimby F., Nguyen H. T. Animal studies of toxic shock syndrome. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;12(1):1–44. doi: 10.3109/10408418509104424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed J. K., Arko R. J., Feeley J. C., Chandler F. W., Thornsberry C., Gibson R. J., Cohen M. L., Jeffries C. D., Broome C. V. Acquired ability of Staphylococcus aureus to produce toxic shock-associated protein and resulting illness in a rabbit model. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):598–604. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.598-604.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves M. W., Pine L., Feeley J. C., Wells D. E. Presence of toxic shock toxin in toxic shock and other clinical strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):590–597. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.590-597.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritz H. L., Kirkland J. J., Bond G. G., Warner E. K., Petty G. P. Association of high levels of serum antibody to staphylococcal toxic shock antigen with nasal carriage of toxic shock antigen-producing strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):954–958. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.954-958.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma B. S., Haque R. Effect of tryptophan analogues on synthesis of staphylococcal beta-haemolysin. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jul;77(1):221–224. doi: 10.1099/00221287-77-1-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Pattee P. A. Computer-assisted chromosome mapping by protoplast fusion in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):395–405. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.395-405.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Pattee P. A. Confirmation of protoplast fusion-derived linkages in Staphylococcus aureus by transformation with protoplast DNA. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):406–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.406-412.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. K., Franco-Buff A., Lawellin D. W., Vasil M. L. Phenotypic distinctiveness of Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):339–344. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.339-344.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J., Fishaut M., Kapral F., Welch T. Toxic-shock syndrome associated with phage-group-I Staphylococci. Lancet. 1978 Nov 25;2(8100):1116–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92274-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Azavedo J. C., Foster T. J., Hartigan P. J., Arbuthnott J. P., O'Reilly M., Kreiswirth B. N., Novick R. P. Expression of the cloned toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene (tst) in vivo with a rabbit uterine model. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):304–309. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.304-309.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



