Abstract
In a model of pneumonia caused by murine Chlamydia trachomatis, depletion experiments with monoclonal antibody to gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) made mice more susceptible. Repletion experiments giving exogenous recombinant murine IFN-gamma were not consistently protective. IFN-gamma may be necessary but not sufficient in host defense against the organism.
Full text
PDF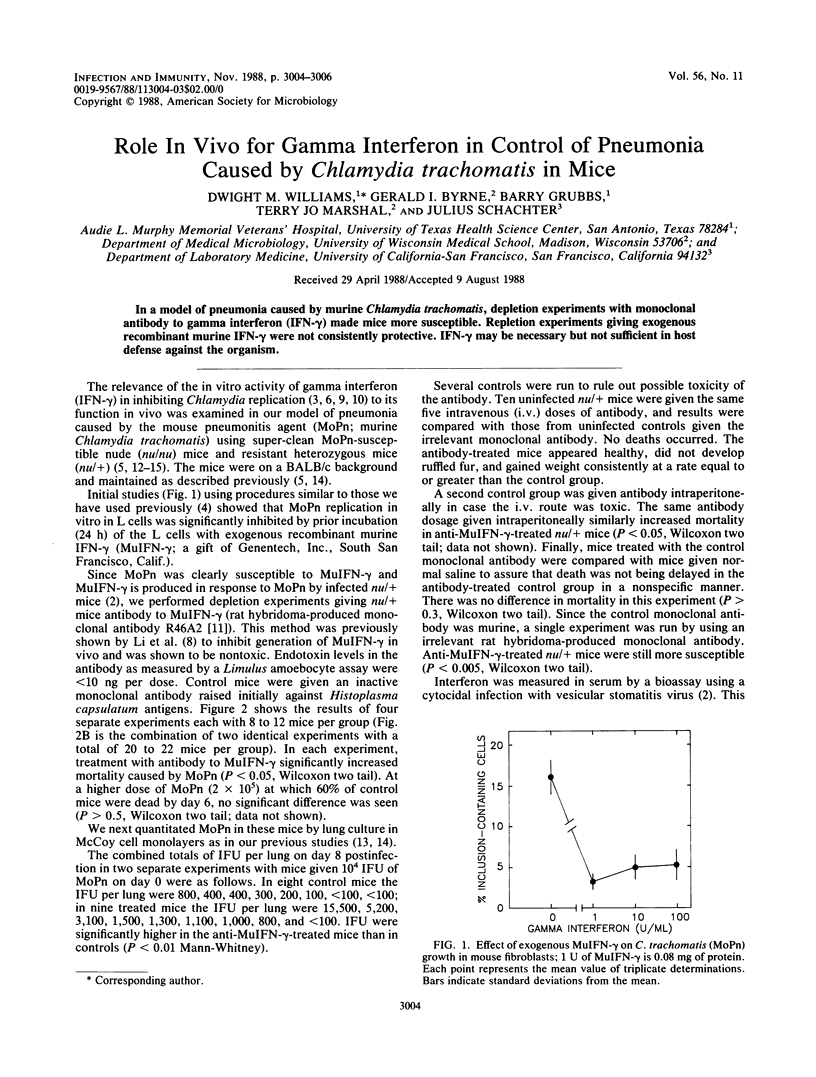
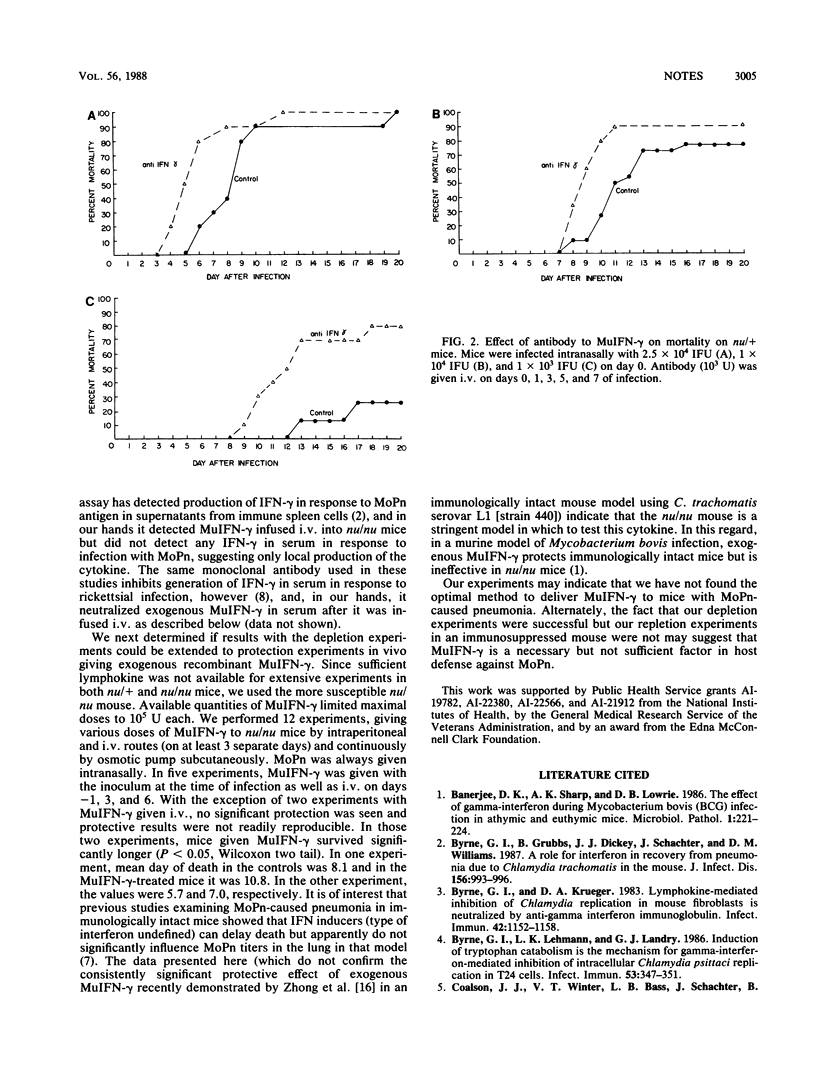

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee D. K., Sharp A. K., Lowrie D. B. The effect of gamma-interferon during Mycobacterium bovis (BCG) infection in athymic and euthymic mice. Microb Pathog. 1986 Apr;1(2):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Grubbs B., Dickey T. J., Schachter J., Williams D. M. Interferon in recovery from pneumonia due to Chlamydia trachomatis in the mouse. J Infect Dis. 1987 Dec;156(6):993–996. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.6.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Krueger D. A. Lymphokine-mediated inhibition of Chlamydia replication in mouse fibroblasts is neutralized by anti-gamma interferon immunoglobulin. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1152–1158. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1152-1158.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Lehmann L. K., Landry G. J. Induction of tryptophan catabolism is the mechanism for gamma-interferon-mediated inhibition of intracellular Chlamydia psittaci replication in T24 cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):347–351. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.347-351.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coalson J. J., Winter V. T., Bass L. B., Schachter J., Grubbs B. G., Williams D. M. Chlamydia trachomatis pneumonia in the immune, athymic and normal BALB mouse. Br J Exp Pathol. 1987 Jun;68(3):399–411. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazar J., Gillmore J. D., Gordon F. B. Effect of Interferon and Interferon Inducers on Infections with a Nonviral Intracellular Microorganism, Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):825–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.825-832.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Jerrells T. R., Spitalny G. L., Walker D. H. Gamma interferon as a crucial host defense against Rickettsia conorii in vivo. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1252–1255. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1252-1255.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothermel C. D., Rubin B. Y., Murray H. W. Gamma-interferon is the factor in lymphokine that activates human macrophages to inhibit intracellular Chlamydia psittaci replication. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2542–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer Y., Sarov I. Inhibition of growth of Chlamydia trachomatis by human gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):592–596. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.592-596.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitalny G. L., Havell E. A. Monoclonal antibody to murine gamma interferon inhibits lymphokine-induced antiviral and macrophage tumoricidal activities. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1560–1565. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Schachter J., Coalson J. J., Grubbs B. Cellular immunity to the mouse pneumonitis agent. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):630–639. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Schachter J., Drutz D. J., Sumaya C. V. Pneumonia due to Chlamydia trachomatis in the immunocompromised (nude) mouse. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):238–241. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Schachter J., Grubbs B. Role of natural killer cells in infection with the mouse pneumonitis agent (murine Chlamydia trachomatis). Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):223–226. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.223-226.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Schachter J., Grubbs B., Sumaya C. V. The role of antibody in host defense against the agent of mouse pneumonitis. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):200–205. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong G. M., Peterson E. M., Czarniecki C. W., de la Maza L. M. Recombinant murine gamma interferon inhibits Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L1 in vivo. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):283–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.283-286.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Maza L. M., Peterson E. M., Fennie C. W., Czarniecki C. W. The anti-chlamydial and anti-proliferative activities of recombinant murine interferon-gamma are not dependent on tryptophan concentrations. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4198–4200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


