Abstract
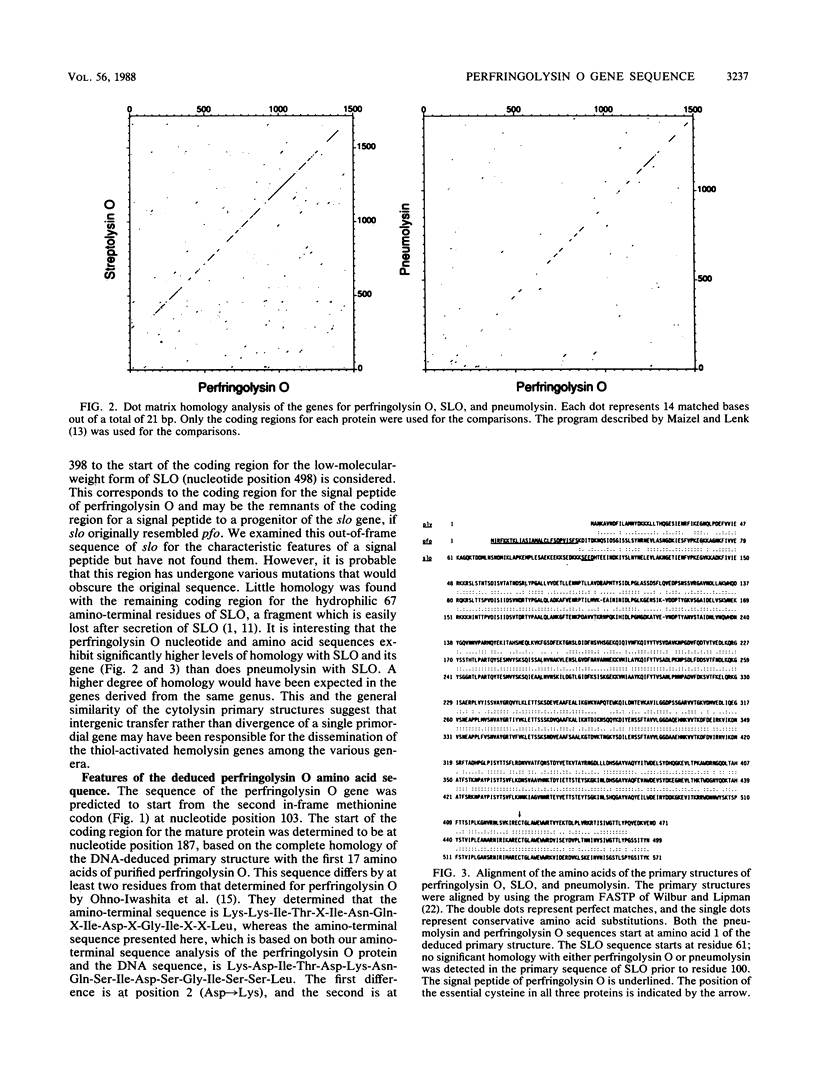
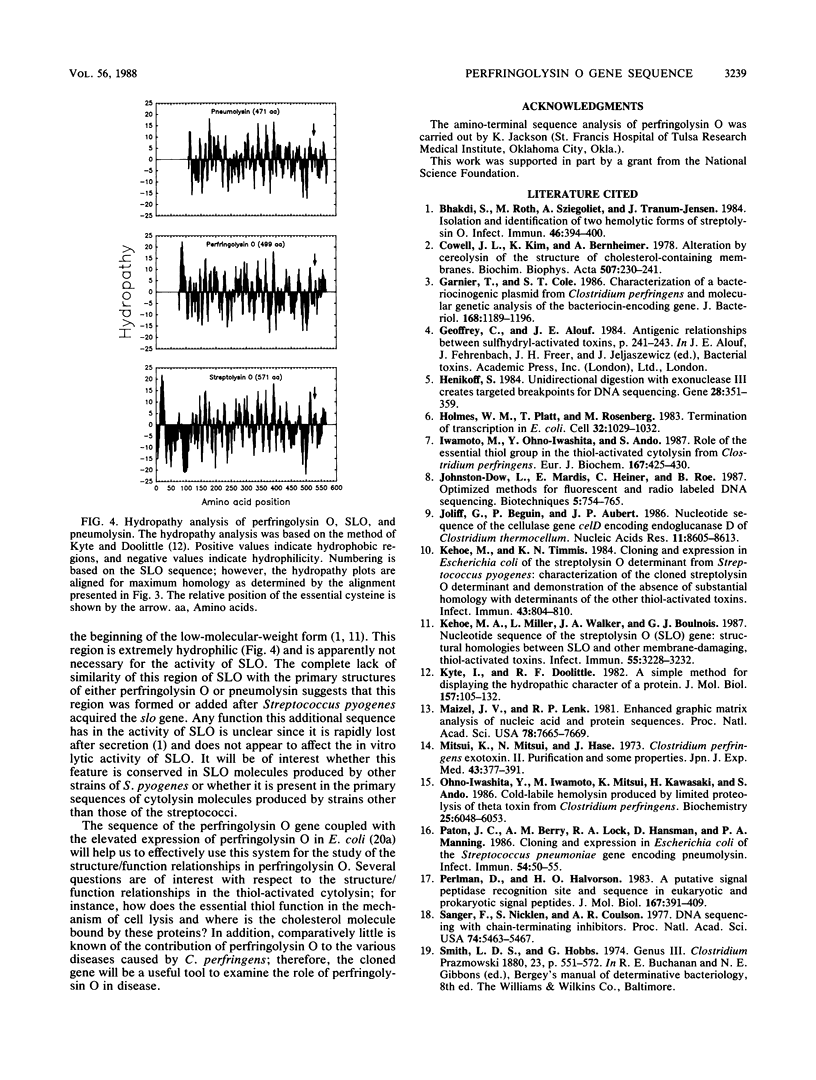
The nucleotide sequence was determined for the gene encoding the thiol-activated cytolysin, perfringolysin O (theta-toxin), from Clostridium perfringens. The nucleotide-sequence-derived primary structure of perfringolysin O is 499 residues long and exhibits a 27-amino-acid signal peptide. The calculated molecular weight of the secreted (mature) form of perfringolysin O is 52,469. The deduced amino-terminal sequence of perfringolysin O is identical to that determined for purified perfringolysin O. Hydropathy analysis indicated that, except for the signal peptide, no major stretches of hydrophobic residues are present. Extensive amino acid sequence homology (65%) was detected with the low-molecular-weight form of streptolysin O, and a lesser amount (42%) was detected with pneumolysin. The nucleotide sequence of the perfringolysin O gene (pfo) exhibits approximately 60% homology with the streptolysin O gene (slo) and 48% homology with the pneumolysin gene (ply). All three toxins contain an identical region of 12 amino acids, which includes the essential cysteine of all three toxins. The location of these 12 residues was conserved in all three toxins when the primary sequences were aligned for maximum homology.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Roth M., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J. Isolation and identification of two hemolytic forms of streptolysin-O. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):394–400. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.394-400.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. L., Kim K. S., Bernheimer A. W. Alteration by cereolysin of the structure of cholesterol-containing membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 21;507(2):230–241. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90419-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier T., Cole S. T. Characterization of a bacteriocinogenic plasmid from Clostridium perfringens and molecular genetic analysis of the bacteriocin-encoding gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1189–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1189-1196.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. M., Platt T., Rosenberg M. Termination of transcription in E. coli. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1029–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto M., Ohno-Iwashita Y., Ando S. Role of the essential thiol group in the thiol-activated cytolysin from Clostridium perfringens. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 15;167(3):425–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joliff G., Béguin P., Aubert J. P. Nucleotide sequence of the cellulase gene celD encoding endoglucanase D of Clostridium thermocellum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8605–8613. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M. A., Miller L., Walker J. A., Boulnois G. J. Nucleotide sequence of the streptolysin O (SLO) gene: structural homologies between SLO and other membrane-damaging, thiol-activated toxins. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3228–3232. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3228-3232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M., Timmis K. N. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the streptolysin O determinant from Streptococcus pyogenes: characterization of the cloned streptolysin O determinant and demonstration of the absence of substantial homology with determinants of other thiol-activated toxins. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):804–810. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.804-810.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, Lenk R. P. Enhanced graphic matrix analysis of nucleic acid and protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7665–7669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Mitsui N., Hase J. Clostridium perfringens exotoxins. II. Purification and some properties of theta-toxin. Jpn J Exp Med. 1973 Oct;43(5):377–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Iwashita Y., Iwamoto M., Mitsui K., Kawasaki H., Ando S. Cold-labile hemolysin produced by limited proteolysis of theta-toxin from Clostridium perfringens. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6048–6053. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. C., Berry A. M., Lock R. A., Hansman D., Manning P. A. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the Streptococcus pneumoniae gene encoding pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the perfringolysin O (theta-toxin) gene from Clostridium perfringens and characterization of the gene product. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3228–3234. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3228-3234.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. A., Allen R. L., Falmagne P., Johnson M. K., Boulnois G. J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for pneumolysin, the sulfhydryl-activated toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1184–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1184-1189.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamakawa Y., Ito A., Sato H. Theta-toxin of Clostridium perfringens. I. Purification and some properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 26;494(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


