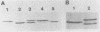Abstract
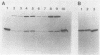
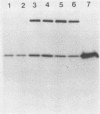
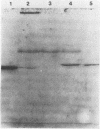
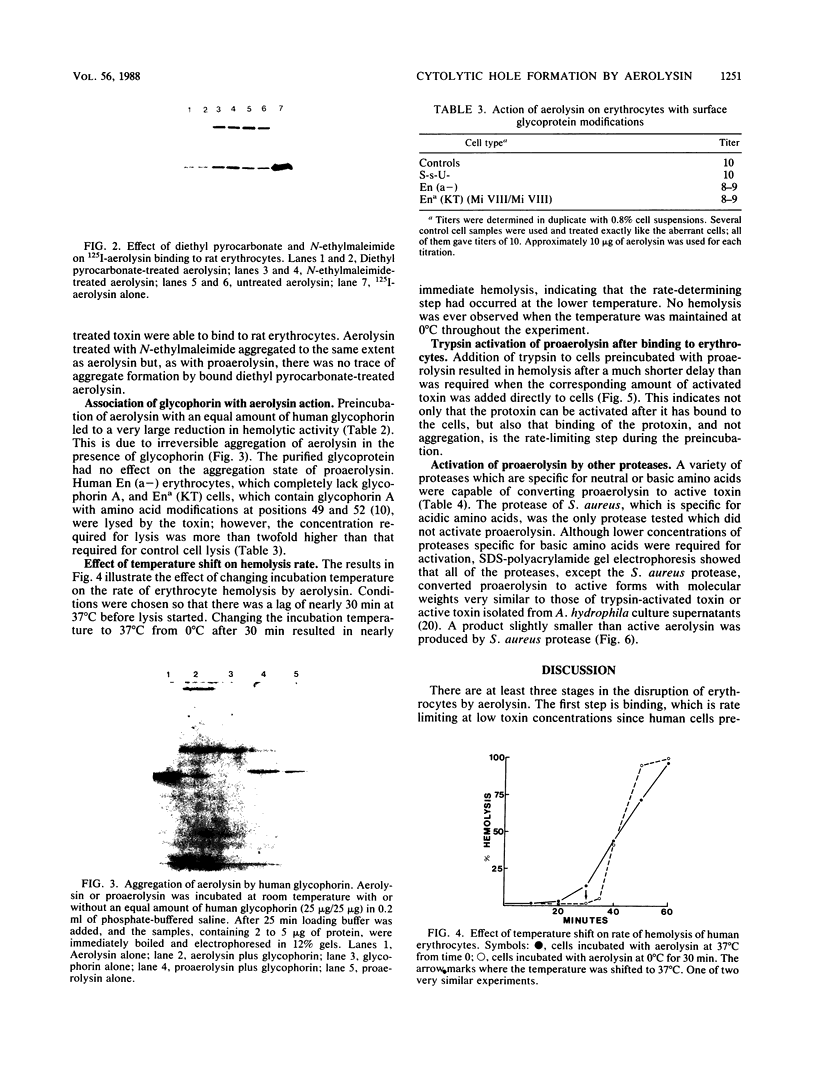
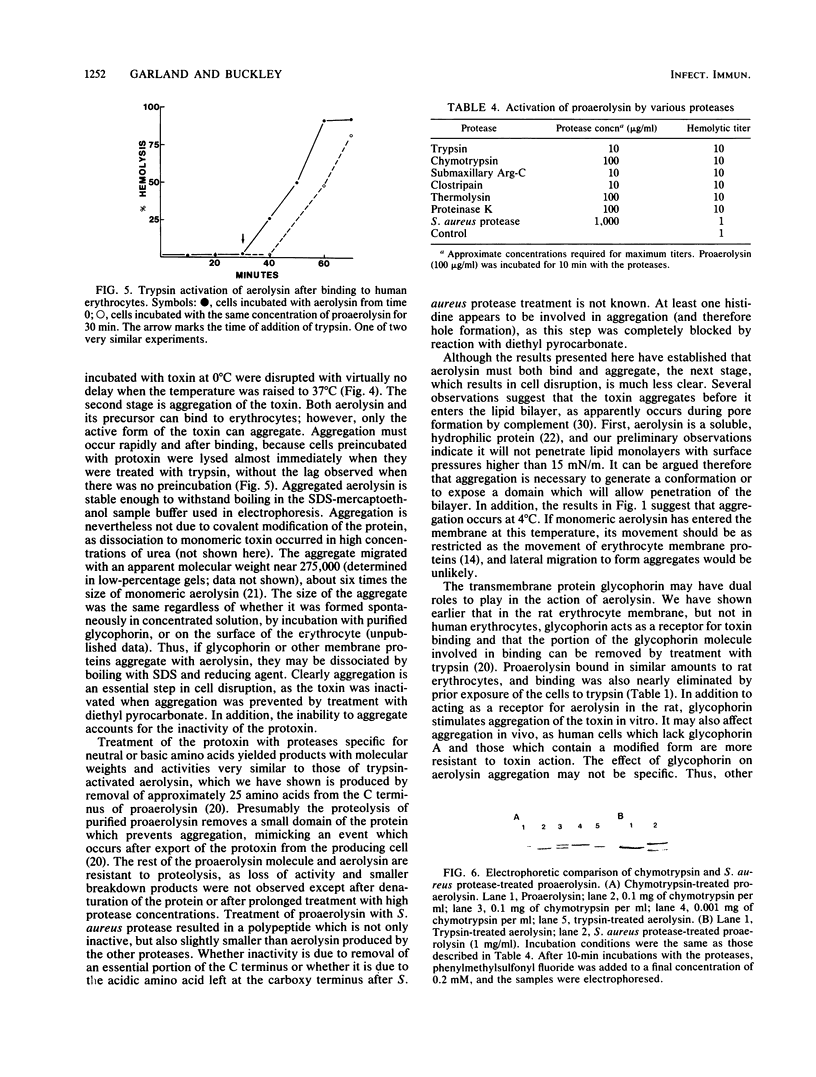
The hole-forming toxin aerolysin was shown to aggregate after binding to erythrocytes at 37 degrees C. Although the protein also bound and aggregated at 4 degrees C, hole formation was not observed, indicating that aggregation preceded penetration of the lipid bilayer. Aggregation, but not binding, could be blocked by pretreatment of the toxin with diethyl pyrocarbonate, a histidine-reactive reagent. This resulted in inactivation of the toxin. Incubation of aerolysin with glycophorin purified from human erythrocytes caused aggregation and complete inactivation. Erythrocytes which lacked glycophorin were less sensitive to the toxin. Proaerolysin, the inactive precursor of aerolysin, also bound to erythrocytes; however, it did not aggregate, nor did it aggregate when preincubated with glycophorin. The protoxin could be activated by treatment with trypsin even after it had bound to erythrocytes. Activation could also be achieved by reaction of proaerolysin with a variety of other proteases, each of which brought about a similar reduction in protein molecular weight. The activated protein was resistant to further proteolysis. These results indicate that aggregation is a necessary step in hole formation and that the sites on aerolysin required for binding and for aggregation and hole formation are separate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alouf J. E. Streptococcal toxins (streptolysin O, streptolysin S, erythrogenic toxin). Pharmacol Ther. 1980;11(3):661–717. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford C. L., Alder G. M., Menestrina G., Micklem K. J., Murphy J. J., Pasternak C. A. Membrane damage by hemolytic viruses, toxins, complement, and other cytotoxic agents. A common mechanism blocked by divalent cations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9300–9308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S. Partial characterization of aerolysin, a lytic exotoxin from Aeromonas hydrophila. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1016–1021. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1016-1021.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Rudy B. Interactions between membranes and cytolytic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 12;864(1):123–141. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Füssle R., Tranum-Jensen J. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin: oligomerization of hydrophilic monomers to form amphiphilic hexamers induced through contact with deoxycholate detergent micelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5475–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. Escherichia coli hemolysin may damage target cell membranes by generating transmembrane pores. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.63-69.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J., Utermann G., Füssle R. Binding and partial inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin by human plasma low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5899–5904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calton G. J. Immunosorbent separations. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:381–387. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahr W., Beyreuther K., Moulds J. J. Structural analysis of the major human erythrocyte membrane sialoglycoprotein from Miltenberger class VII cells. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):27–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahr W., Issitt P., Moulds P., Pavone B. Further studies on the membrane glycoprotein defects of S--s--and En(a--)-erythrocytes. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Sep;359(9):1217–1224. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufourc E. J., Smith I. C., Dufourcq J. Molecular details of melittin-induced lysis of phospholipid membranes as revealed by deuterium and phosphorus NMR. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6448–6455. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler V., Branton D. Lateral mobility of human erythrocyte integral membrane proteins. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):23–26. doi: 10.1038/268023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Birkbeck T. H. Possible conformation of delta-lysin, a membrane-damaging peptide of Staphylococcus aureus. J Theor Biol. 1982 Feb 7;94(3):535–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(82)90299-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H. Structural comparison of glycophorins and immunochemical analysis of genetic variants. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):519–524. doi: 10.1038/271519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman S., Bondurant M. Susceptibility to staphylococcal alpha-toxin of Friend virus-infected murine erythroblasts during differentiation. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):114–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.114-118.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard S. P., Buckley J. T. Activation of the hole-forming toxin aerolysin by extracellular processing. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):336–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.336-340.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard S. P., Buckley J. T. Membrane glycoprotein receptor and hole-forming properties of a cytolytic protein toxin. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 30;21(7):1662–1667. doi: 10.1021/bi00536a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard S. P., Buckley J. T. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the structural gene for the hemolytic toxin aerolysin from Aeromonas hydrophila. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Aug;204(2):289–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00425512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard S. P., Garland W. J., Green M. J., Buckley J. T. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the hole-forming toxin aerolysin of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2869–2871. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2869-2871.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugo F., Reichwein J., Arvand M., Krämer S., Bhakdi S. Use of a monoclonal antibody to determine the mode of transmembrane pore formation by streptolysin O. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):641–645. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.641-645.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maharaj I., Fackrell H. B. Rabbit erythrocyte band 3: a receptor for staphylococcal alpha toxin. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Apr;26(4):524–531. doi: 10.1139/m80-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Andrews E. P. Glycoproteins: isolation from cellmembranes with lithium diiodosalicylate. Science. 1971 Dec 17;174(4015):1247–1248. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4015.1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silversmith R. E., Nelsestuen G. L. Assembly of the membrane attack complex of complement on small unilamellar phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 25;25(4):852–860. doi: 10.1021/bi00352a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]