Abstract
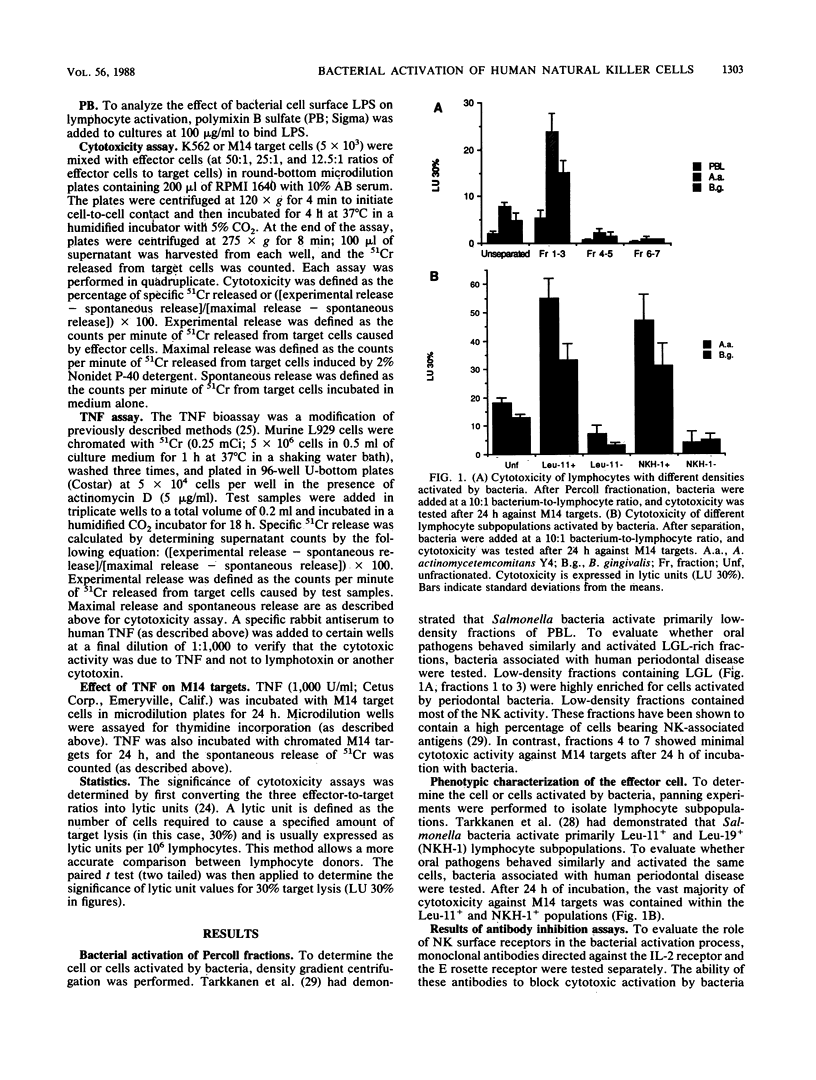
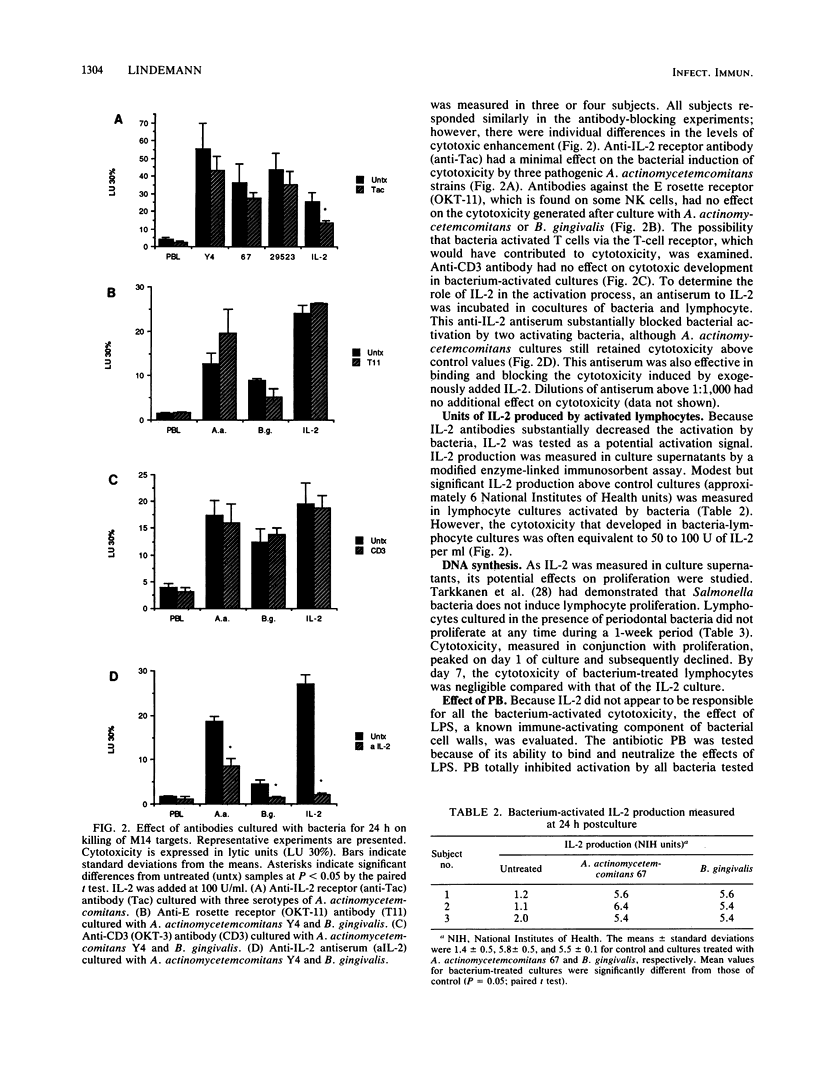
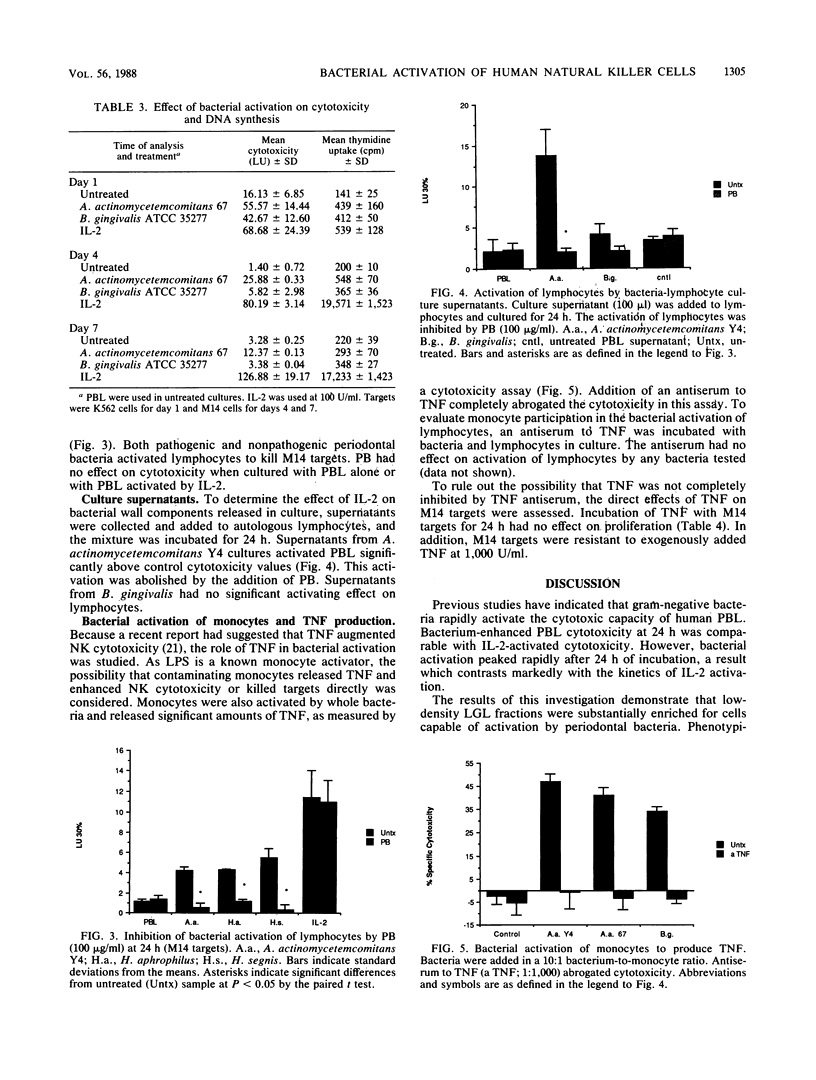
Culture of human peripheral blood lymphocytes with gram-negative bacteria associated with periodontal disease caused a rapid increase in the cytotoxic potential of natural killer (NK) cells. The NK cells were activated to kill NK-resistant targets, the peak cytotoxicity occurring on day 1 of culture. The addition of anti-Tac, anti-CD3, or anti-OKT-11 antibodies to block activation via the interleukin-2 (IL-2), T-cell, or E rosette receptors had a minimal effect on this inductive process. Anti-IL-2 antiserum was effective in blocking a significant amount, but not all, of the cytotoxicity in bacterium-activated cultures. Modest IL-2 production (5 to 6 National Institutes of Health units) was measured in lymphocyte cultures activated by bacteria, but proliferation was not induced during a 1-week period. When polymixin B sulfate was added to bind and block lipopolysaccharides, bacterium-induced cytotoxicity was completely abrogated for all activating bacteria. In addition, when culture supernatants from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans were tested, activation still occurred. However, again, this activation was totally inhibited by polymixin B sulfate. Monocytes were also activated by bacteria to produce tumor necrosis factor (TNF). To exclude the possibility that TNF was responsible for cytotoxicity, an antiserum to TNF was added to cocultures of bacteria and lymphocytes with adherent cells removed. The antiserum had no effect on the inductive process. In addition, exogenous TNF did not kill M14 targets. These results suggest that bacterial cell surface lipopolysaccharides provide a major activation signal for NK cells to enhance cytotoxicity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abruzzo L. V., Rowley D. A. Homeostasis of the antibody response: immunoregulation by NK cells. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):581–585. doi: 10.1126/science.6685343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banck G., Forsgren A. Many bacterial species are mitogenic for human blood B lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(4):347–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrigan J. J., Jr, Sieber O. E., Jr, Ratajczak H., Bennett B. B. Modification of human neutrophil response to endotoxin with polymyxin B sulfate. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):384–387. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amore P. J., Golub S. H. Detection of double target binders at the single cell level: an evaluation of the specificity of NK and MLC-induced NK-like cells. Cell Immunol. 1982 Jul 15;71(1):66–79. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90496-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukovich M., Wano Y., Le thi Bich Thuy, Katz P., Cullen B. R., Kehrl J. H., Greene W. C. A second human interleukin-2 binding protein that may be a component of high-affinity interleukin-2 receptors. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):518–522. doi: 10.1038/327518a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Mazumder A., Zhang H. Z., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. Lysis of natural killer-resistant fresh solid tumor cells by interleukin 2-activated autologous human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1823–1841. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Wilson D. J. The human lymphokine-activated killer cell system. V. Purified recombinant interleukin 2 activates cytotoxic lymphocytes which lyse both natural killer-resistant autologous and allogeneic tumors and trinitrophenyl-modified autologous peripheral blood lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1985 Sep;94(2):568–578. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Djeu J., Kay H. D., Ortaldo J. R., Riccardi C., Bonnard G. D., Holden H. T., Fagnani R., Santoni A., Puccetti P. Natural killer cells: characteristics and regulation of activity. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:43–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Tanner A. C., Socransky S. S. Morphology and ultrastructure of oral strains of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Haemophilus aphrophilus. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):588–600. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.588-600.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karavodin L. M., Golub S. H. Universal rosetting reagent for the detection of human cell surface markers. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jul 29;61(3):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90223-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindemann R. A., Golub S. H., Park N. H. HSV-1-infected oral epithelial cells are targets for natural killer cells. J Dent Res. 1987 Mar;66(3):770–773. doi: 10.1177/00220345870660031301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Fabbi M., Fox D., Acuto O., Fitzgerald K. A., Hodgdon J. C., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. An alternative pathway of T-cell activation: a functional role for the 50 kd T11 sheep erythrocyte receptor protein. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Gartner S., Kaplan H. S. Stimulation of mitogenic responses in human peripheral blood lymphocytes by lipopolysaccharide: serum and T helper cell requirements. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2160–2164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nencioni L., Villa L., Boraschi D., Berti B., Tagliabue A. Natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated activity against Salmonella typhimurium by peripheral and intestinal lymphoid cells in mice. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):903–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta M., Rothmann J., Kovats E., Pham P. H., Nowotny A. Biological activities of lipopolysaccharide fractionated by preparative acrylamide gel electrophoresis. Microbiol Immunol. 1985;29(1):1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1985.tb00797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostensen M. E., Thiele D. L., Lipsky P. E. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha enhances cytolytic activity of human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4185–4191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Dissection of the lymphokine-activated killer phenomenon. Relative contribution of peripheral blood natural killer cells and T lymphocytes to cytolysis. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):814–825. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pross H. F., Baines M. G., Rubin P., Shragge P., Patterson M. S. Spontaneous human lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor target cells. IX. The quantitation of natural killer cell activity. J Clin Immunol. 1981 Jan;1(1):51–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00915477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. W., Pace J. L., Varesio L., Akporiaye E., Blasi E., Celado A., Schreiber R. D., Schultz R. M., Stevenson A. P., Stewart C. C. Comparison of five short-term assays that measure nonspecific cytotoxicity mediated to tumor cells by activated macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1986 Dec;40(6):801–813. doi: 10.1002/jlb.40.6.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salata R. A., Kleinhenz M. E., Schacter B. Z., Ellner J. J. Augmentation of natural killer cell activity by lipopolysaccharide through separable effects on the binding of nonadherent lymphocytes to tumor targets and tumor killing. Cancer Res. 1984 Mar;44(3):1044–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley J. K., Golub S. H. Studies on cytotoxicity generated in human mixed lymphocyte cultures. I. Time course and target spectrum of several distinct concomitant cytotoxic activities. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1415–1422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkkanen J., Saksela E., Lanier L. L. Bacterial activation of human natural killer cells. Characteristics of the activation process and identification of the effector cell. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2428–2433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkkanen J., Saxén H., Nurminen M., Mäkelä P. H., Saksela E. Bacterial induction of human activated lymphocyte killing and its inhibition by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2662–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):569–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. A., Tracey D. E., Henney C. S. Introduction of "natural" killer' cells by BCG. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):584–586. doi: 10.1038/262584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. C., Weitzen M. L., Kahle R., Granger G. A., Bonavida B. Studies on the mechanism of natural killer cytotoxicity. II. coculture of human PBL with NK-sensitive or resistant cell lines stimulates release of natural killer cytotoxic factors (NKCF) selectively cytotoxic to NK-sensitive target cells. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2479–2483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


