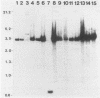
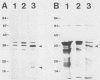
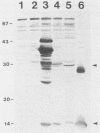
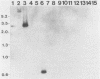
Abstract
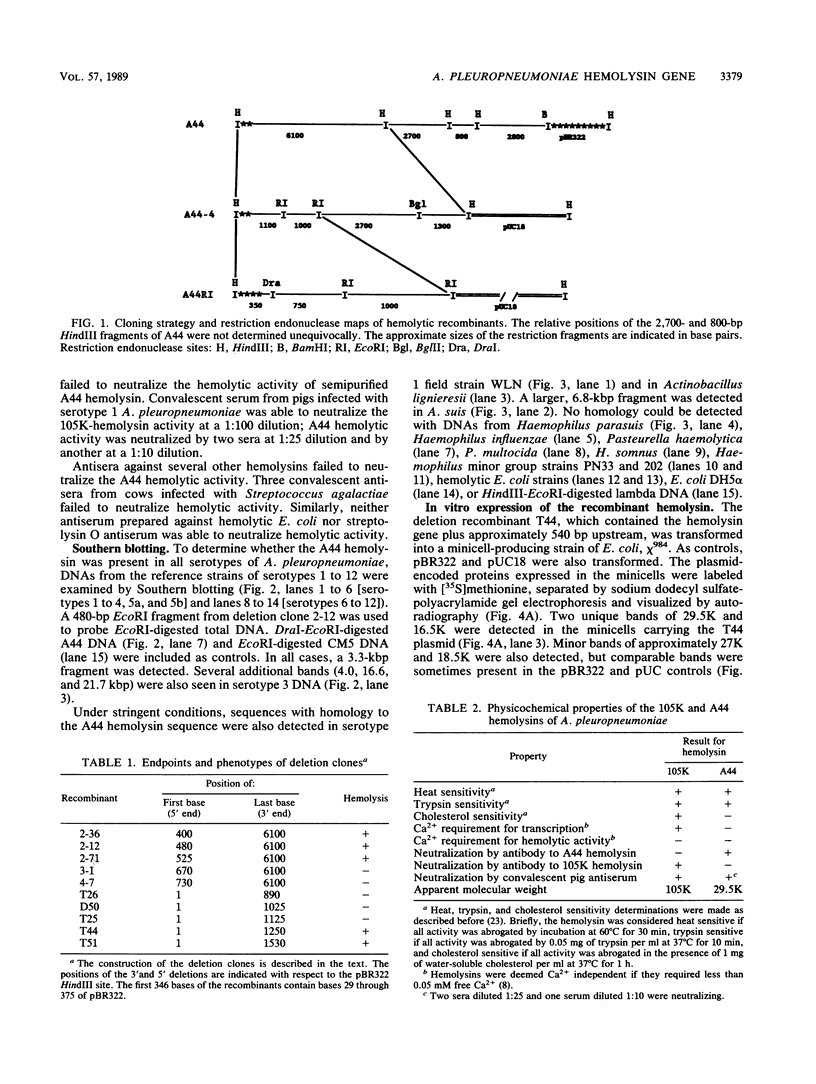
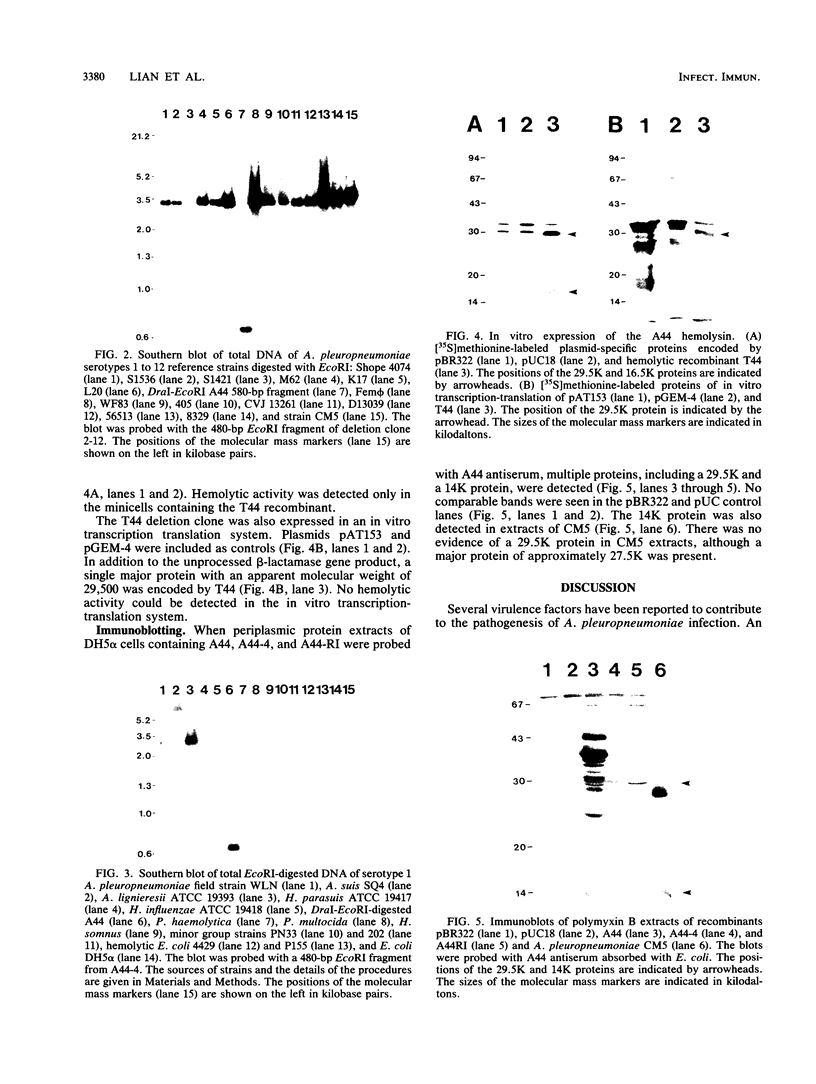
This article describes the molecular cloning and expression of a hemolysin gene from a serotype 1 strain of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. The hemolysin was a thermolabile protein with an apparent molecular weight of 29,500 (29.5K hemolysin). Unlike expression of the recently described 105K hemolysin of A. pleuropneumoniae (J. Frey and J. Nicolet, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 55:41-46, 1988), expression of this hemolysin was not regulated by Ca2+. Antiserum prepared against the 105K hemolysin did not neutralize the activity of the 29.5K hemolysin; conversely, antiserum prepared against the 29.5K hemolysin did not neutralize the activity of the 105K hemolysin. The hemolytic activity was not neutralized with antisera against hemolytic Escherichia coli, Streptococcus agalactiae, or purified streptolysin O, but antisera prepared against recombinants containing the 29.5K gene and convalescent pig sera abrogated hemolytic activity. Although hemolytic activity could be detected in several strains of E. coli K-12 and in minicells expressing several different constructs encoding the 29.5K hemolysin, we could not rigorously exclude the possibility that the gene which we have isolated encodes a regulator of hemolytic activity rather than a hemolysin per se.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernheimer A. W., Rudy B. Interactions between membranes and cytolytic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 12;864(1):123–141. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertram T. A. Pathobiology of Acute Pulmonary Lesions in Swine Infected with Haemophilus (Actinobacillus) pleuropneumoniae. Can Vet J. 1988 Jul;29(7):574–577. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Kathariou S., Hacker J., Hof H., Huhle B., Wagner W., Kuhn M., Goebel W. Molecular analysis of bacterial cytolysins. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9 (Suppl 5):S456–S466. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_5.s456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J., Rosendal S. Identification of the heat-labile hemolysin of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 1. Can J Vet Res. 1989 Apr;53(2):251–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick B. W., Cullor J. S., Osburn B. I., Olander H. J. Mechanisms involved in protection provided by immunization against core lipopolysaccharides of Escherichia coli J5 from lethal Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infections in swine. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):298–304. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.298-304.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Nicolet J. Regulation of hemolysin expression in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 1 by Ca2+. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2570–2575. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2570-2575.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen A. E., Bertram T. A. Morphological and biochemical comparison of virulent and avirulent isolates of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae serotype 5. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):419–424. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.419-424.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M. A., Miller L., Walker J. A., Boulnois G. J. Nucleotide sequence of the streptolysin O (SLO) gene: structural homologies between SLO and other membrane-damaging, thiol-activated toxins. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3228–3232. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3228-3232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume K., Nakai T., Sawata A. Interaction between heat-stable hemolytic substance from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae and porcine pulmonary macrophages in vitro. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):563–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.563-570.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacInnes J. I., Rosendal S. Analysis of major antigens of Haemophilus (Actinobacillus) pleuropneumoniae and related organisms. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1626–1634. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1626-1634.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. G., Lachance P., Niven D. F. Production of RNA-dependent haemolysin by Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Can J Microbiol. 1985 May;31(5):456–462. doi: 10.1139/m85-085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley J. R., Kadis S., Mayberry W. R. Isolation, purification, and partial characterization of a lipopolysaccharide from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):501–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.501-506.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Sawata A., Kume K. Characterization of the hemolysin produced by haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Feb;44(2):344–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Sawata A., Kume K. Pathogenicity of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae for laboratory animals and possible role of its hemolysin for production of pleuropneumonia. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1984 Dec;46(6):851–858. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.46.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson K., Michalski J., Kaper J. B. Hemolysin production and cloning of two hemolysin determinants from classical Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):415–420. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.415-420.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Boyd D. A., Gilbride K. A. Comparative virulence of porcine Haemophilus bacteria. Can J Comp Med. 1985 Jan;49(1):68–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Devenish J., MacInnes J. I., Lumsden J. H., Watson S., Xun H. Evaluation of heat-sensitive, neutrophil-toxic, and hemolytic activity of Haemophilus (Actinobacillus) pleuropneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;49(7):1053–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebunya T. N., Saunders J. R. Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infection in swine: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1983 Jun 15;182(12):1331–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart N. L., Miniats O. P., MacInnes J. I. Analysis of Haemophilus parasuis isolates from southern Ontario swine by restriction endonuclease fingerprinting. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;52(3):319–324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udeze F. A., Latimer K. S., Kadis S. Role of haemophilus pleuropneumoniae lipopolysaccharide endotoxin in the pathogenesis of porcine Haemophilus pleuropneumonia. Am J Vet Res. 1987 May;48(5):768–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. A., Allen R. L., Falmagne P., Johnson M. K., Boulnois G. J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for pneumolysin, the sulfhydryl-activated toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1184–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1184-1189.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]