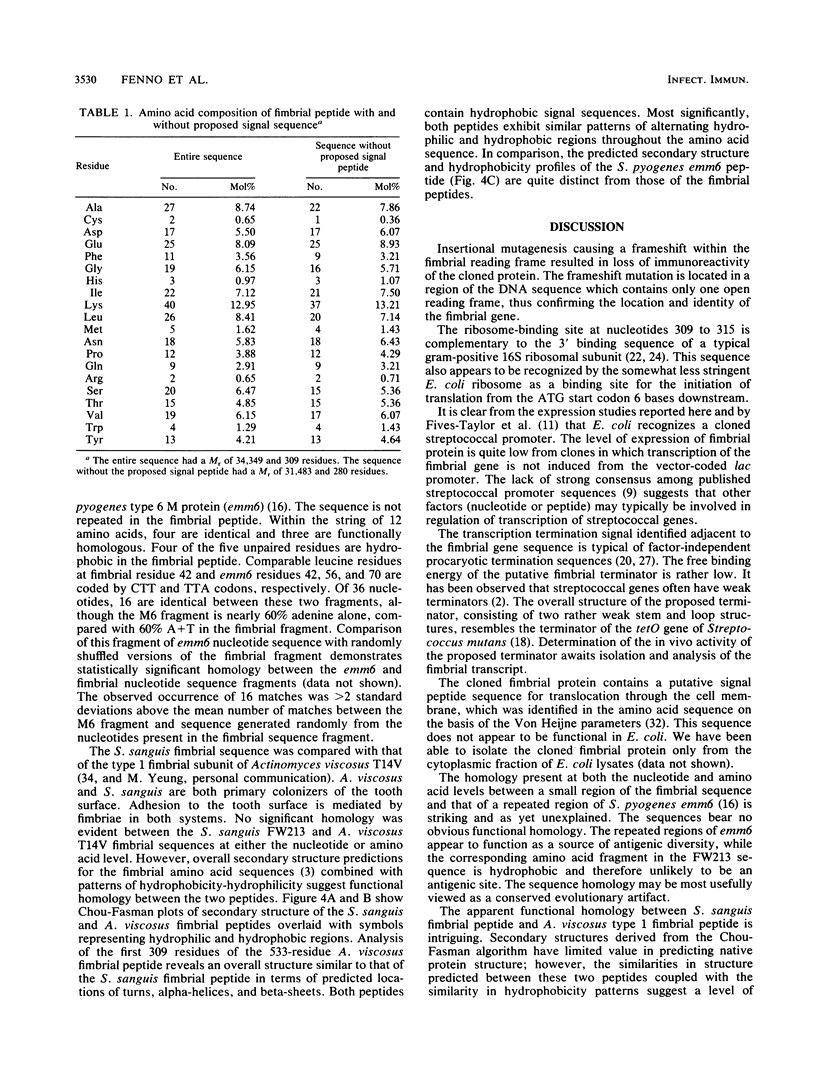
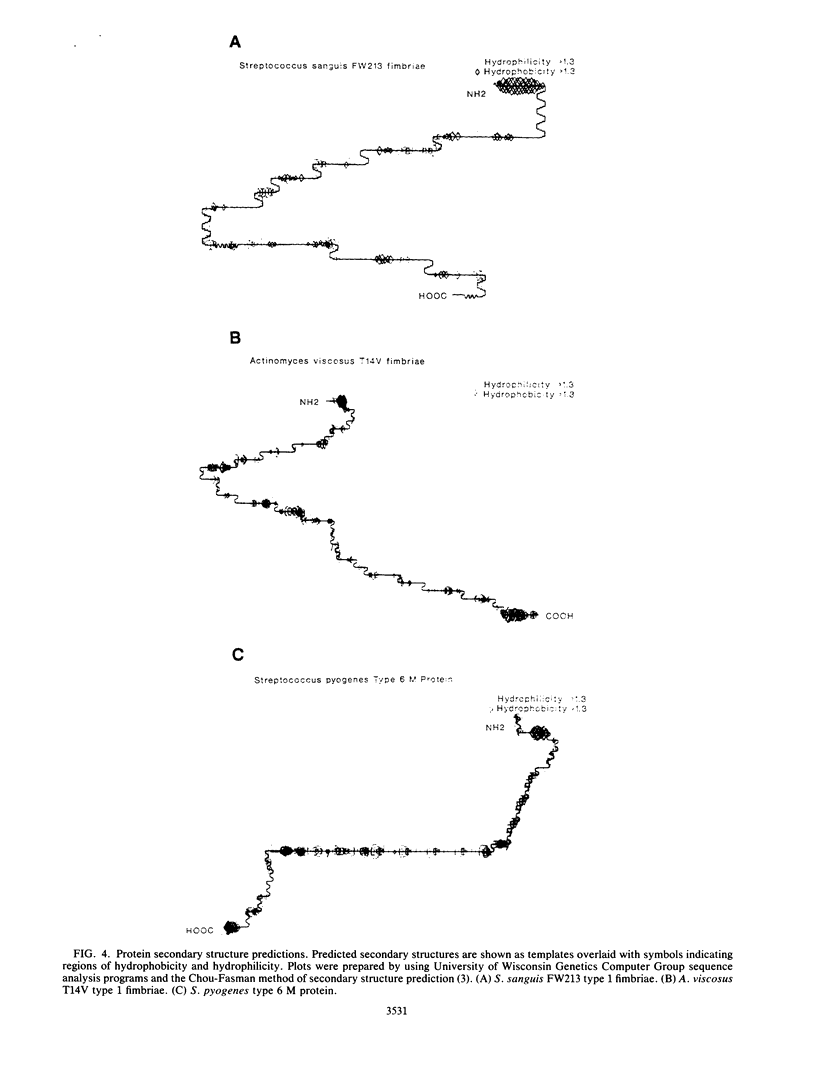
Abstract
A structural gene for type 1 fimbriae of Streptococcus sanguis FW213 was located within a 6-kilobase fragment cloned in Escherichia coli. A 1.6-kilobase internal fragment contains an open reading frame of 927 bases coding for an immunoreactive peptide of 34,349 daltons, which corresponds in size with an observed cytoplasmic form of fimbrial peptide (P. M. Fives-Taylor, F. L. Macrina, T. J. Pritchard, and S. J. Peene, Infect. Immun. 55:123-128, 1987). Disruption of the reading frame by insertional mutagenesis results in loss of immunoreactivity. Consensus sequences for initiation of transcription and translation were identified 5' to the coding region. Transcription terminator-like sequences were found downstream of the coding region. The deduced amino acid sequence of the cloned fimbrial peptide shows a strongly hydrophobic signal sequence at the amino terminus. The carboxyl-terminal region does not include a hydrophobic membrane anchor sequence such as has been reported for other gram-positive surface structures. A hydrophobic region of 12 to 14 amino acids downstream from the putative signal sequence cleavage site exhibits homology with the Streptococcus pyogenes type 6 M protein repetitive region A (S. K. Hollingshead, V. A. Fischetti, and J. R. Scott, J. Biol. Chem., 261:1677-1686, 1986). Functional homology at the level of protein secondary structure with Actinomyces viscosus T14V type 1 fimbriae (M. K. Yeung, B. M. Chassy, and J. O. Cisar, J. Bacteriol., 169:1678-1683, 1987) is proposed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brendel V., Trifonov E. N. A computer algorithm for testing potential prokaryotic terminators. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4411–4427. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. D., Morrison D. A. Cloning of Streptococcus pneumoniae DNA fragments in Escherichia coli requires vectors protected by strong transcriptional terminators. Gene. 1987;55(2-3):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder B. L., Fives-Taylor P. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for adhesion: isolation of an adhesin of Streptococcus sanguis FW213. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):421–427. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.421-427.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fachon-Kalweit S., Elder B. L., Fives-Taylor P. Antibodies that bind to fimbriae block adhesion of Streptococcus sanguis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):617–624. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.617-624.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahnestock S. R., Alexander P., Nagle J., Filpula D. Gene for an immunoglobulin-binding protein from a group G streptococcus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):870–880. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.870-880.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fives-Taylor P. M., Macrina F. L., Pritchard T. J., Peene S. S. Expression of Streptococcus sanguis antigens in Escherichia coli: cloning of a structural gene for adhesion fimbriae. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):123–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.123-128.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fives-Taylor P. M., Thompson D. W. Surface properties of Streptococcus sanguis FW213 mutants nonadherent to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):752–759. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.752-759.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganeshkumar N., Song M., McBride B. C. Cloning of a Streptococcus sanguis adhesin which mediates binding to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1150–1157. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1150-1157.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I., Skobe Z. Association of fimbriae with the hydrophobicity of Streptococcus sanguis FC-1 and adherence to salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):414–417. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.414-417.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingshead S. K., Fischetti V. A., Scott J. R. Complete nucleotide sequence of type 6 M protein of the group A Streptococcus. Repetitive structure and membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1677–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont R. J., Rosan B., Baker C. T., Nelson G. M. Characterization of an adhesion antigen of Streptococcus sanguis G9B. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2417–2423. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2417-2423.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Lee L. N., Titmas B. M., Smith C. J., Tenover F. C. Nucleotide sequence analysis of tetracycline resistance gene tetO from Streptococcus mutans DL5. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3618–3626. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3618-3626.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinus M. G. DNA methylation in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:113–131. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Tinoco I., Jr DNA-RNA hybrid duplexes containing oligo(dA:rU) sequences are exceptionally unstable and may facilitate termination of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2295–2299. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R. Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:171–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. R., Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Unique features in the ribosome binding site sequence of the gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus beta-lactamase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11283–11291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Skorupa E. S., Kemper B. Single stranded DNA SP6 promoter plasmids for engineering mutant RNAs and proteins: synthesis of a 'stretched' preproparathyroid hormone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1103–1118. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., Ganeshkumar N., Song M., McBride B. C. Identification and preliminary characterization of a Streptococcus sanguis fibrillar glycoprotein. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.164-171.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouw A. R., Beachey E. H., Burdett V. Molecular evolution of streptococcal M protein: cloning and nucleotide sequence of the type 24 M protein gene and relation to other genes of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):676–684. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.676-684.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B., Baker C. T., Nelson G. M., Berman R., Lamont R. J., Demuth D. R. Cloning and expression of an adhesin antigen of Streptococcus sanguis G9B in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Mar;135(3):531–538. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-3-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Benson S. A., Emr S. D. Mechanisms of protein localization. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):313–344. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.313-344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén M., Guss B., Nilsson B., Gatenbeck S., Philipson L., Lindberg M. Complete sequence of the staphylococcal gene encoding protein A. A gene evolved through multiple duplications. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1695–1702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung M. K., Chassy B. M., Cisar J. O. Cloning and expression of a type 1 fimbrial subunit of Actinomyces viscosus T14V. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1678–1683. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1678-1683.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




