Abstract
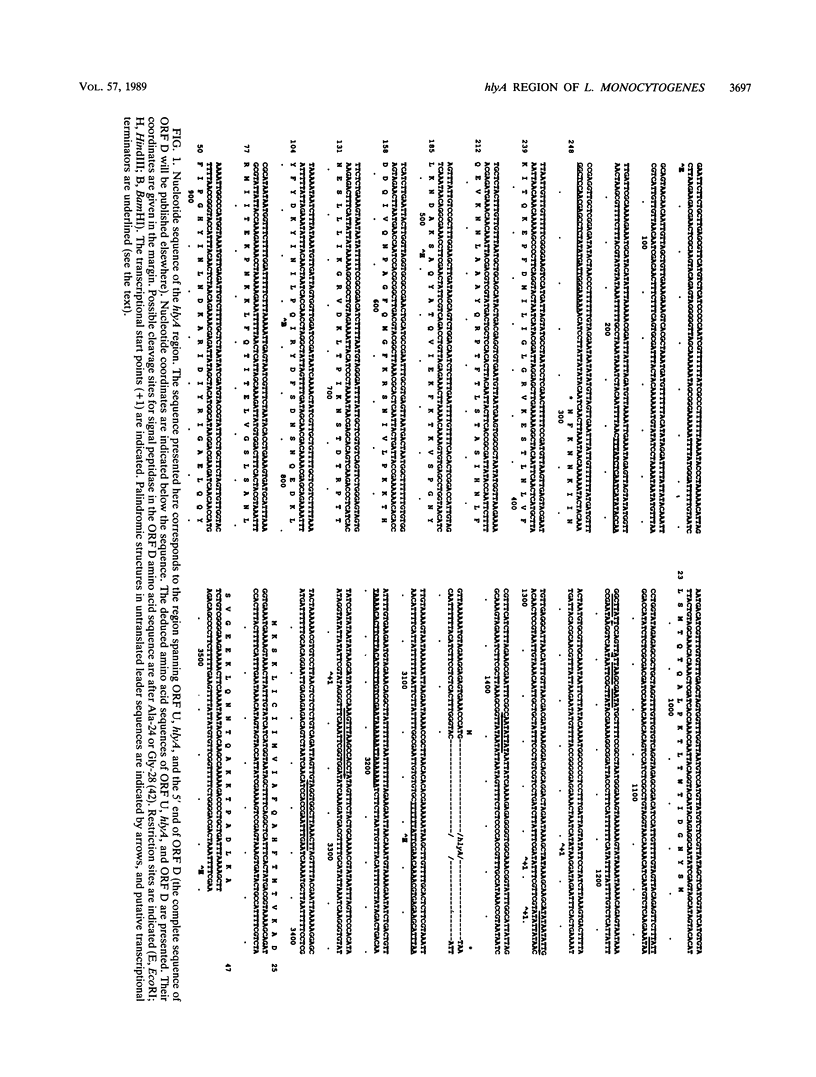
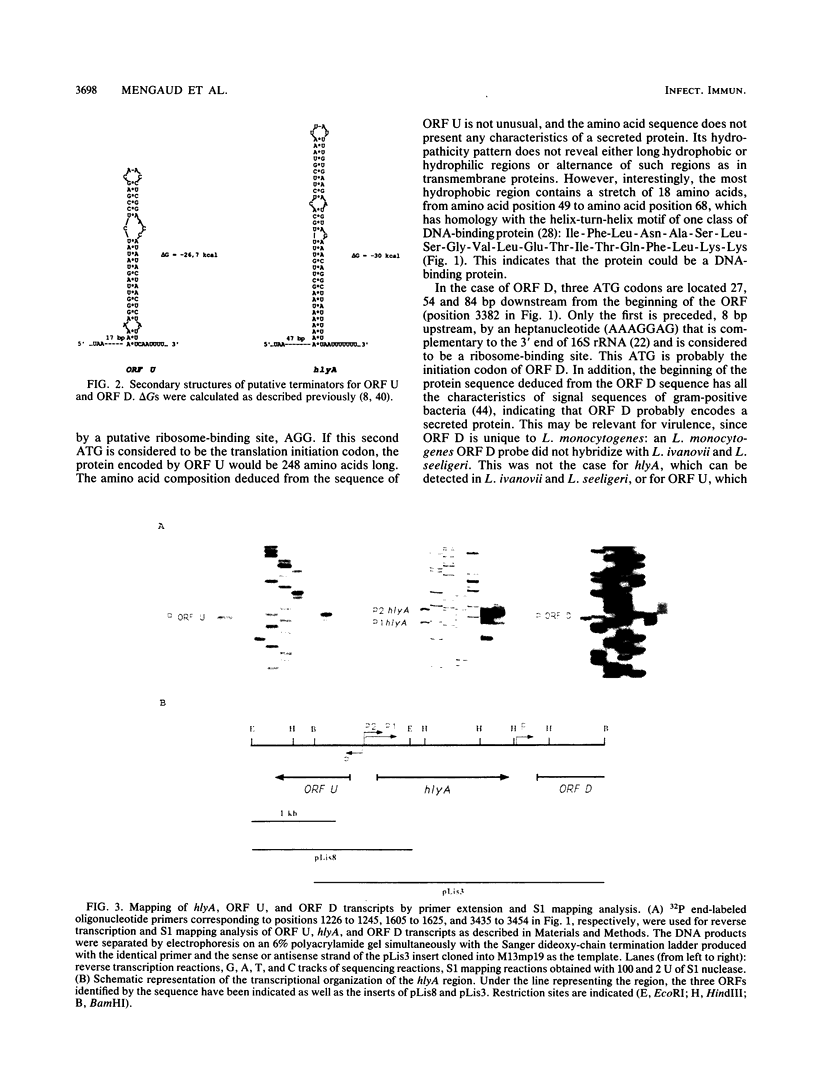
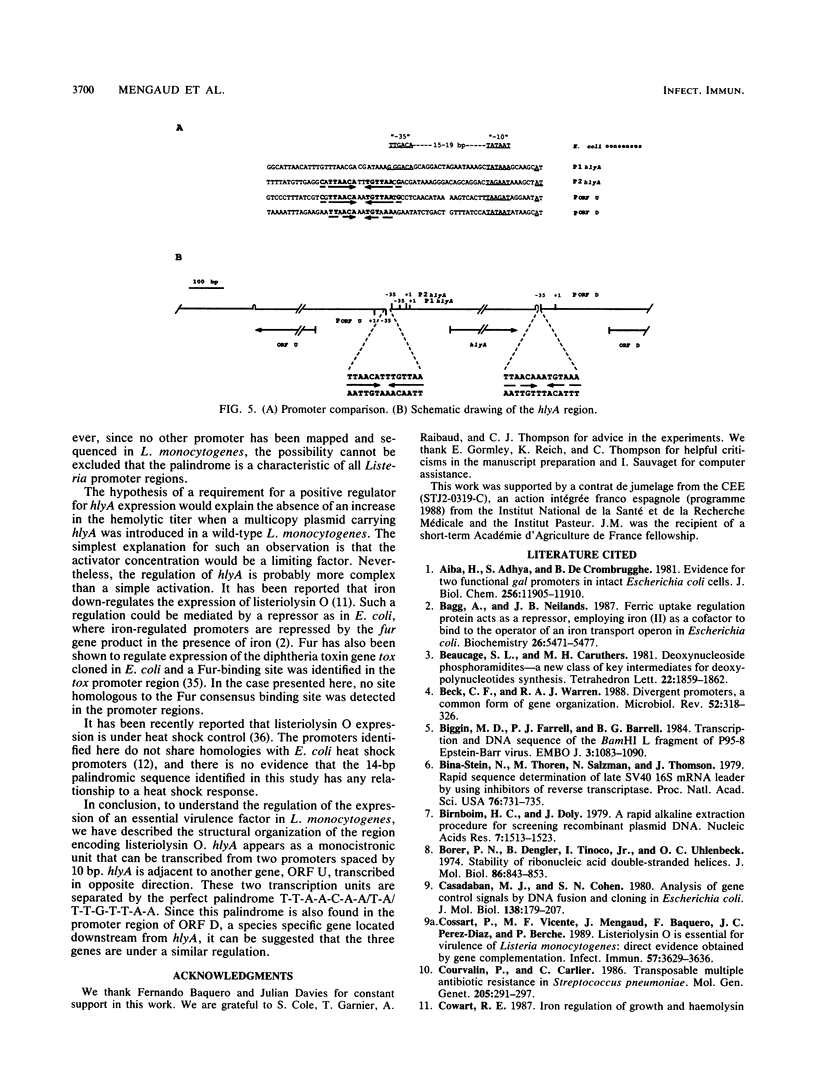
DNA sequence analysis of the regions adjacent to the hlyA gene, which encodes listeriolysin O, an essential virulence factor of Listeria monocytogenes, revealed the presence of two open reading frames (ORFs): ORF D located 304 base pairs downstream from hlyA, and ORF U located 224 base pairs upstream from and in opposite direction to hlyA. Promoter mapping performed with RNAs extracted from cells growing exponentially in rich medium showed that the three ORFs are independently transcribed. hlyA is transcribed from two promoters separated by 10 base pairs (P1 hlyA and P2 hlyA). ORF U is transcribed in the opposite direction from an adjacent promoter. These two promoter regions are separated by a palindromic sequence T-T-A-A-C-A-A/T-T-G-T-T-A-A. This palindrome was also found upstream from the ORF D promoter, suggesting that all three genes are similarly regulated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagg A., Neilands J. B. Ferric uptake regulation protein acts as a repressor, employing iron (II) as a cofactor to bind the operator of an iron transport operon in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 25;26(17):5471–5477. doi: 10.1021/bi00391a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C. F., Warren R. A. Divergent promoters, a common form of gene organization. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Sep;52(3):318–326. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.3.318-326.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M., Farrell P. J., Barrell B. G. Transcription and DNA sequence of the BamHI L fragment of B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1083–1090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bina-Stein M., Thoren M., Salzman N., Thomspon J. A. Rapid sequence determination of late simian virus 40 16S mRNA leader by using inhibitors of reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):731–735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borer P. N., Dengler B., Tinoco I., Jr, Uhlenbeck O. C. Stability of ribonucleic acid double-stranded helices. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 15;86(4):843–853. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Vicente M. F., Mengaud J., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Berche P. Listeriolysin O is essential for virulence of Listeria monocytogenes: direct evidence obtained by gene complementation. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3629–3636. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3629-3636.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P., Carlier C. Transposable multiple antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):291–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00430441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowing D. W., Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A., Woolford C., Hendrix R. W., Gross C. A. Consensus sequence for Escherichia coli heat shock gene promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Georges E., Orth G., Yaniv M. Fine structure of the cottontail rabbit papillomavirus mRNAs expressed in the transplantable VX2 carcinoma. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):735–741. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.735-741.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus M. What constitutes the signal for the initiation of protein synthesis on Escherichia coli mRNAs? J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):79–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke A. E., Clewell D. B. Evidence for conjugal transfer of a Streptococcus faecalis transposon (Tn916) from a chromosomal site in the absence of plasmid DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):77–80. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier T., Cole S. T. Studies of UV-inducible promoters from Clostridium perfringens in vivo and in vitro. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):607–614. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. Immunity against intracellular bacteria: biological effector functions and antigen specificity of T lymphocytes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;138:141–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Chenevert J., Geoffroy C., Gaillard J. L., Cossart P. Identification of the structural gene encoding the SH-activated hemolysin of Listeria monocytogenes: listeriolysin O is homologous to streptolysin O and pneumolysin. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3225–3227. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3225-3227.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Chenevert J., Pereira J. M., Geoffroy C., Gicquel-Sanzey B., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Cossart P. Expression in Escherichia coli and sequence analysis of the listeriolysin O determinant of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):766–772. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.766-772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Schwartz M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:173–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Siegele D. A., Cowing D. W., Gross C. A. The regulation of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:355–387. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovic Z., Goebel W. Synthesis of listeriolysin in Listeria monocytogenes under heat shock conditions. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):295–298. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.295-298.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai S. P., Holmes R. K. Iron regulation of the cloned diphtheria toxin promoter in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2430–2436. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2430-2436.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]