Abstract
Pathogen-specific membrane immunogens of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum (T. pallidum) have been identified previously by phase partitioning with the nonionic detergent Triton X-114. One of these antigens, a 15-kilodalton (kDa) polypeptide, is expressed in relatively small quantities in T. pallidum but is highly immunogenic in both human and experimental syphilis. The native T. pallidum antigen was purified to homogeneity from the mixture of Triton X-114 detergent-phase proteins by chromatofocusing. Recombinant Escherichia coli clones were selected from a T. pallidum genomic DNA library by using monoclonal antibodies specific to the 15-kDa antigen; immunoblotting and minicell analyses confirmed expression of the 15-kDa protein in the transformants. Southern hybridization with a 1.1-kilobase fragment of DNA encoding the 15-kDa-antigen gene indicated that the gene is probably present in a single copy within the genomes of both T. pallidum and T. pallidum subsp. pertenue (the agent of yaws), while it is absent from the genome of the nonpathogenic Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter. Cell fractionation studies with Triton X-114 demonstrated that the recombinant polypeptide possesses hydrophobic properties similar to those of the native antigen and localized the cloned 15-kDa antigen to the inner membrane of E. coli. Protein processing experiments in minicells revealed that a precursor appears to be processed to the mature 15-kDa polypeptide.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker-Zander S. A., Fohn M. J., Lukehart S. A. Development of cellular immunity to individual soluble antigens of Treponema pallidum during experimental syphilis. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4363–4369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Hook E. W., 3rd, Bonin P., Handsfield H. H., Lukehart S. A. Antigens of Treponema pallidum recognized by IgG and IgM antibodies during syphilis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):264–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., Brandt M. E., Erwin A. L., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Major integral membrane protein immunogens of Treponema pallidum are proteolipids. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2872–2877. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2872-2877.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., DeOgny L., Slaughter C., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Acylation of the 47-kilodalton major membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum determines its hydrophobicity. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2878–2885. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2878-2885.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., Radolf J. D., Hsu P. L., Sell S., Norgard M. V. Genetic and physicochemical characterization of the recombinant DNA-derived 47-kilodalton surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):71–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.71-78.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Ray P. H., Leong J., Benedict C. D., Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Identification and purification of a recombinant Treponema pallidum basic membrane protein antigen expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1106–1115. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1106-1115.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehniger T. E., Radolf J. D., Walfield A. M., Cunningham T. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Native surface association of a recombinant 38-kilodalton Treponema pallidum antigen isolated from the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):586–593. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.586-593.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Fehniger T. E., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Humoral immune response in human syphilis to polypeptides of Treponema pallidum. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1287–1291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Norris S. J., Lovett M. A., Miller J. N. Purification of Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain, by Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Sex Transm Dis. 1984 Oct-Dec;11(4):275–286. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198410000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., McCaslin D. R., Fries E., Tanford C. Properties of detergents. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:734–749. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
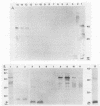
- Hensel U., Wellensiek H. J., Bhakdi S. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis immunoblotting as a serological tool in the diagnosis of syphilitic infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.82-87.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
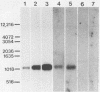
- Hussain M., Ichihara S., Mizushima S. Accumulation of glyceride-containing precursor of the outer membrane lipoprotein in the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli treated with globomycin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3707–3712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. A., Marchitto K. S., Miller J. N., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody with hemagglutination, immobilization, and neutralization activities defines an immunodominant, 47,000 mol wt, surface-exposed immunogen of Treponema pallidum (Nichols). J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1404–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Baker-Zander S. A., Gubish E. R., Jr Identification of Treponema pallidum antigens: comparison with a nonpathogenic treponeme. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):833–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooi F. R., Harms N., Bakker D., de Graaf F. K. Organization and expression of genes involved in the production of the K88ab antigen. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1155–1163. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1155-1163.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation in Escherichia coli: cryogenic preservation of competent cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):349–351. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.349-351.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Miller J. N. Cloning and expression of Treponema pallidum (Nichols) antigen genes in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):435–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.435-445.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Falkow S. Nucleotide sequence of pilA, the gene encoding the structural component of type 1 pili in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):454–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.454-457.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Hirst T. R., Hardy S. J., Holmgren J., Randall L. Synthesis of a precursor to the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):325–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.325-330.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Chamberlain N. R., Clausell A., Norgard M. V. Identification and localization of integral membrane proteins of virulent Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum by phase partitioning with the nonionic detergent triton X-114. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):490–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.490-498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Pathogen specificity of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum integral membrane proteins identified by phase partitioning with Triton X-114. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1825–1828. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1825-1828.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V., Schulz W. W. Outer membrane ultrastructure explains the limited antigenicity of virulent Treponema pallidum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2051–2055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. M., Kettman J. R., Miller J. N., Norgard M. V. Murine monoclonal antibodies specific for virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols). Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1076–1085. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1076-1085.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E., Brown K., Yanofsky C. Mitomycin C-induced expression of trpA of Salmonella typhimurium inserted into the plasmid ColE1. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):388–394. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.388-394.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Hodinka R. L., Wyrick P. B., Bassford P. J., Jr Changes in the cell surface properties of Treponema pallidum that occur during in vitro incubation of freshly extracted organisms. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2255–2261. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2255-2261.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swancutt M. A., Twehous D. A., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody selection and analysis of a recombinant DNA-derived surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):110–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.110-119.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg R. W., Baseman J. B. Comparison of major protein antigens and protein profiles of Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):623–627. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.623-627.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Tokunaga M. Biogenesis of lipoproteins in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:127–157. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]