Abstract
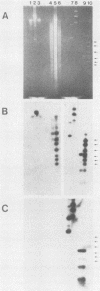
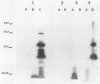
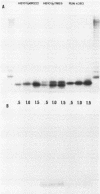
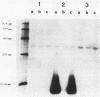
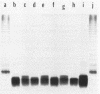
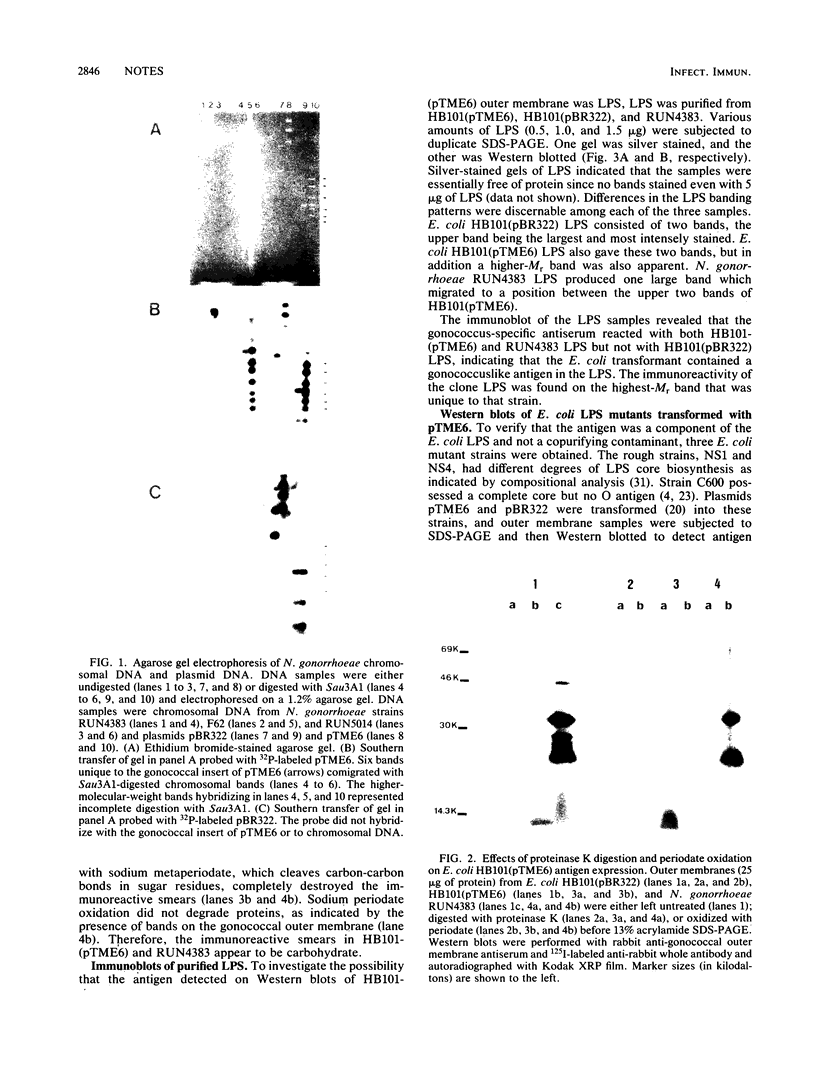
A gonococcal gene bank maintained in Escherichia coli K-12 was screened by colony immunoblotting, and a transformant expressing a surface antigen reactive to anti-gonococcal outer membrane antiserum was isolated. The isolate carried a recombinant plasmid, pTME6, consisting of approximately 9 kilobases of Neisseria gonorrhoeae DNA inserted into the BamHI site of pBR322. Surface labeling of E. coli HB101(pTME6) confirmed that the antigen was expressed on the E. coli cell surface. The antigenic material was resistant to proteinase K digestion and sensitive to periodate oxidation, indicating that the material was carbohydrate. Purified lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from HB101(pTME6) produced a unique band on silver-stained polyacrylamide gels that contained immunoreactive material as seen on Western blots of LPS samples. Only two of three E. coli LPS mutant strains carrying pTME6 reacted with the antigonococcal antiserum, suggesting that a certain E. coli core structure is necessary for antigen expression. We conclude that pTME6 contains one or more gonococcal genes encoding an LPS core biosynthetic enzyme(s) which can modify E. coli core LPS to produce a gonococcuslike epitope(s).
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A., Dudas K. C., Campagnari A., Rice P., Mylotte J. M., Murphy T. F. Antigenic heterogeneity of lipid A of Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.9-14.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apicella M. A., Gagliardi N. C. Antigenic heterogeneity of the non-serogroup antigen structure of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):870–874. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.870-874.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apicella M. A. Serogrouping of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: identification of four immunologically distinct acidic polysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1976 Oct;134(4):377–383. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark V. L., Campbell L. A., Palermo D. A., Evans T. M., Klimpel K. W. Induction and repression of outer membrane proteins by anaerobic growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1359–1364. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1359-1364.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly M. C., Allen P. Z. Antigenic specificity and heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharides from pyocin-sensitive and -resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1046–1055. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1046-1055.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guymon L. F., Esser M., Shafer W. M. Pyocin-resistant lipopolysaccharide mutans of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: alterations in sensitivity to normal human serum and polymyxin B. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):541–547. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.541-547.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koomey J. M., Gill R. E., Falkow S. Genetic and biochemical analysis of gonococcal IgA1 protease: cloning in Escherichia coli and construction of mutants of gonococci that fail to produce the activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7881–7885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Mlawer N., So M. Pilus expression in Neisseria gonorrhoeae involves chromosomal rearrangement. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz C. S., Apicella M. A., Morse S. A. Electrophoretic and serological characterization of the lipopolysaccharide produced by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):544–552. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Nikaido K., Rapin A. M. Biosynthesis of thymidine diphosphate L-rhamnose in Escherichia coli K-12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Dec 16;111(2):548–551. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrod E. P., Burnham J. S., Williams R. P., Ding M. J. Induced changes in the surface of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Can J Microbiol. 1983 May;29(5):584–592. doi: 10.1139/m83-091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Griffiss J. M., Williams G. D., Pier G. B. Immunological basis of serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Jan;128(1):13–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Hale T. L., Zollinger W. D., Seid R. C., Jr, Hammack C. A., Griffiss J. M. Heterogeneity of molecular size and antigenic expression within lipooligosaccharides of individual strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.544-549.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead A., Main J. S., Ward M. E., Watt P. J. Studies on lipopolysaccharides isolated from strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):123–131. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Sato T., Matsuhashi M. Role of lipopolysaccharides in antibiotic resistance and bacteriophage adsorption of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):968–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.968-975.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M., Caird J. D. Composition of the lipopolysaccharide of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):550–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.550-556.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]