Abstract
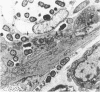
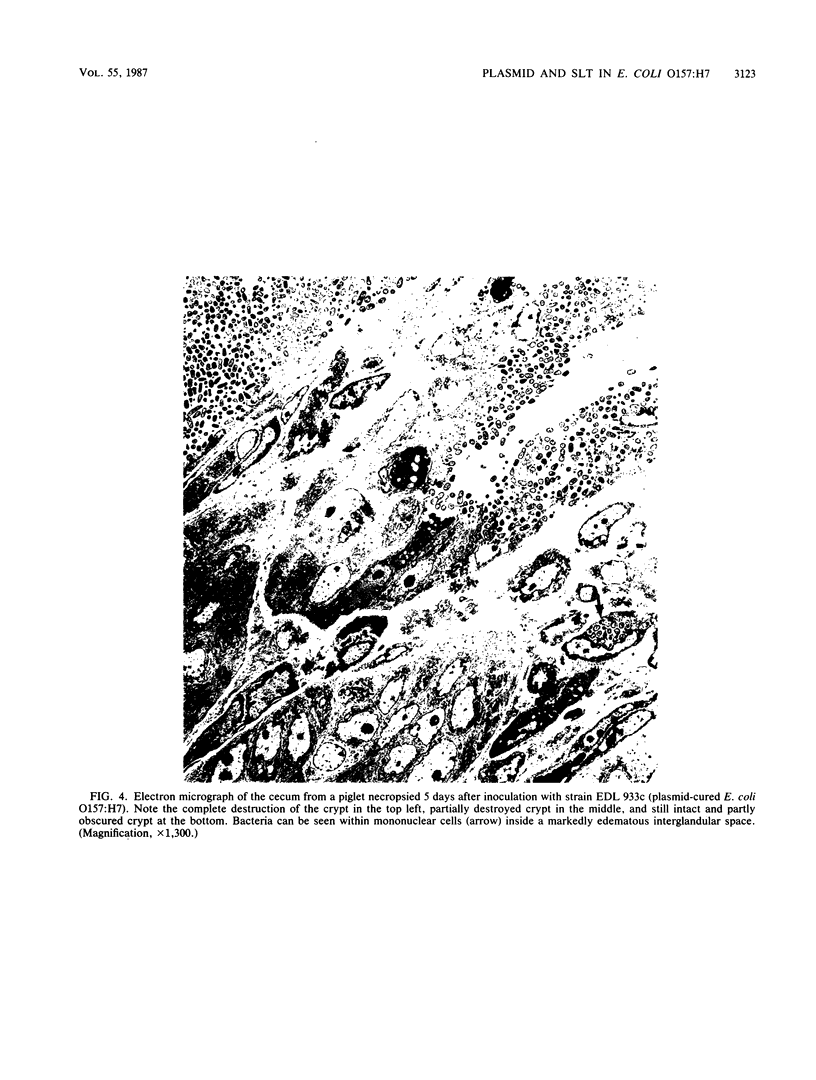
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) of serotype O157:H7 has two putative virulence factors: (i) a fimbrial adhesin, specified by a 60-megadalton (MDa) plasmid, and (ii) bacteriophage-specified cytotoxin(s), known as Shiga-like toxin (SLT) or verotoxin. The contribution of these factors to the pathogenesis of EHEC-induced disease in gnotobiotic piglets was examined. The bacterial strains included the following: two EHEC strains and their corresponding plasmid-cured derivatives; another EHEC isolate and its derivative which had spontaneously lost the ability to produce SLT; one E. coli K-12 transconjugatant containing a 60-MDa plasmid from an EHEC strain; two K-12 strains into which an SLT-producing phage had been transduced (one of these strains also carried a 60-MDa EHEC-derived plasmid); and the parent K-12 strain. Each strain was fed to four piglets, which were observed for diarrhea and examined for development of characteristic mucosal lesions 3 or 5 days after inoculation. All 24 piglets inoculated with the three EHEC strains and their respective derivatives (two plasmid cured and one SLT negative) showed the typical mucosal lesions of bacterial attachment: effacement of microvillous border and cell membrane dissolution culminating in destruction of surface and glandular epithelium in the cecum and colon. No such lesions were observed in 12 piglets inoculated with three strains of E. coli K-12, including the strain which carried both the 60-MDa plasmid and a phage which specified production of SLT. Moderate to severe diarrhea was observed in 16 piglets inoculated with two EHEC strains and their derivatives (one plasmid cured and one SLT negative). The third EHEC strain and its plasmid-cured derivative produced fewer typical mucosal lesions and no diarrhea. The reason for the reduced virulence of this strain was not clear. These results demonstrate that neither the 60-MDa plasmid nor the capacity to produce SLT is essential for expression of virulence by E. coli O157:H7 in gnotobiotic piglets.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M., Candy D. C., Moon H. W. Plasmid-mediated adhesion in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2(3):534–538. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198302030-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Pierce N. F. Differences in the response of rabbit small intestine to heat-labile and heat-stable enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.873-880.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. H., Collins J. E., Duimstra J. R. Infection of gnotobiotic pigs with an Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain associated with an outbreak of hemorrhagic colitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):953–956. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.953-956.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Heesemann J., Laufs R., O'Brien A. D., Tacket C. O., Levine M. M. A plasmid of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 is required for expression of a new fimbrial antigen and for adhesion to epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):455–461. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.455-461.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Cheung R., Arbus G. S. Sensitive method for detecting low numbers of verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in mixed cultures by use of colony sweeps and polymyxin extraction of verotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):614–619. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.614-619.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai G. J., Burrows W. The titration of cholera toxin and antitoxin in the rabbit ileal loop. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):606–614. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., DuPont H. L., Formal S. B., Hornick R. B., Takeuchi A., Gangarosa E. J., Snyder M. J., Libonati J. P. Pathogenesis of Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga) dysentery. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):261–270. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Edelman R. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of classic serotypes associated with infant diarrhea: epidemiology and pathogenesis. Epidemiol Rev. 1984;6:31–51. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Xu J. G., Kaper J. B., Lior H., Prado V., Tall B., Nataro J., Karch H., Wachsmuth K. A DNA probe to identify enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli of O157:H7 and other serotypes that cause hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):175–182. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makin T. J., Tzipori S. Inexpensive techniques for the production and maintenance of gnotobiotic piglets, calves and lambs. Aust Vet J. 1980 Aug;56(8):353–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1980.tb09558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Argenzio R. A., Levine M. M., Giannella R. A. Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1340–1351. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1340-1351.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nataro J. P., Baldini M. M., Kaper J. B., Black R. E., Bravo N., Levine M. M. Detection of an adherence factor of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with a DNA probe. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):560–565. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill M. A., Agosti J., Rosen H. Hemorrhagic colitis with Escherichia coli O157:H7 preceding adult hemolytic uremic syndrome. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Dec;145(12):2215–2217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., LaVeck G. D., Thompson M. R., Formal S. B. Production of Shigella dysenteriae type 1-like cytotoxin by Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):763–769. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old D. C., Crichton P. B., Maunder A. J., Wilson M. I. Discrimination of urinary strains of Escherichia coli by five typing methods. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Aug;13(3):437–444. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-3-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Kelly J. K., Meyers G. L. Experimental infection of infant rabbits with verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):16–23. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.16-23.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. K., Bennett P. M., Falkow S., Dodd H. M. Isolation of a temperature-sensitive derivative of RP1. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Green P., Parsell Z. Vero cell toxins in Escherichia coli and related bacteria: transfer by phage and conjugation and toxic action in laboratory animals, chickens and pigs. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3121–3137. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spika J. S., Parsons J. E., Nordenberg D., Wells J. G., Gunn R. A., Blake P. A. Hemolytic uremic syndrome and diarrhea associated with Escherichia coli O157:H7 in a day care center. J Pediatr. 1986 Aug;109(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Newland J. W., Smith H. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Two toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 933 encode antigenically distinct toxins with similar biologic activities. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.135-140.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Robins-Browne R. M., Gonis G., Hayes J., Withers M., McCartney E. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli enteritis: evaluation of the gnotobiotic piglet as a model of human infection. Gut. 1985 Jun;26(6):570–578. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.6.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S., Wachsmuth I. K., Chapman C., Birden R., Brittingham J., Jackson C., Hogg J. The pathogenesis of hemorrhagic colitis caused by Escherichia coli O157:H7 in gnotobiotic piglets. J Infect Dis. 1986 Oct;154(4):712–716. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.4.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]