Abstract
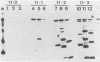
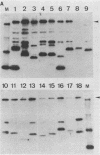
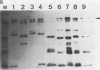
Mice immunized with live meningococci developed antibodies directed against various antigens of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis, as demonstrated by immunoblotting. An antigen of 70 kilodaltons appeared to be common and stable in all gonococcal strains tested and highly immunogenic in mice infected with N. meningitidis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A., Bennett K. M., Hermerath C. A., Roberts D. E. Monoclonal antibody analysis of lipopolysaccharide from Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):751–756. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.751-756.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell C. C., Law J. A. Typing of non-serogroupable Neisseria meningitidis by means of sensitivity to R-type pyocines of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect. 1981 Dec;3(4):370–378. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(81)91996-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Eschenbach D. A., Knapp J. S., Holmes K. K. Gonococcal salpingitis is less likely to recur with Neisseria gonorrhoeae of the same principal outer membrane protein antigenic type. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Dec 1;138(7 Pt 2):978–980. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)91091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Hildebrandt J. F. Antigen-specific serotyping of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: characterization based upon principal outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):985–994. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.985-994.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Pearce W. A., Schoolnik G. K., Arko R. J. Protection against infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae by immunization with outer membrane protein complex and purified pili. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S132–S137. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Swanson J., Holmes K. K., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Quantitative determination of antibody to gonococcal pili. Changes in antibody levels with gonococcal infection. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2896–2909. doi: 10.1172/JCI107486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Black W. J., Nachamkin I., Stewart P. W. Monoclonal antibody that recognizes an outer membrane antigen common to the pathogenic Neisseria species but not to most nonpathogenic Neisseria species. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):994–999. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.994-999.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremieux A. C., Puissant A., Ancelle R., Martin P. M. Bactericidal antibodies against Neisseria gonorrhoeae elicited by Neisseria meningitidis. Lancet. 1984 Oct 20;2(8408):930–930. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90687-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halter R., Pohlner J., Meyer T. F. IgA protease of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: isolation and characterization of the gene and its extracellular product. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1595–1601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02016.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P., Thornley M. J., Thompson R. J. A study by high-resolution two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of relationships between Neisseria gonorrhoeae and other bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Dec;130(12):3189–3201. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-12-3189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koomey J. M., Falkow S. Nucleotide sequence homology between the immunoglobulin A1 protease genes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):101–107. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.101-107.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E., James L. T., Watt P. J. Variations in surface protein composition associated with virulence properties in opacity types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):305–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Zollinger W. D. Use of a zwitterionic detergent for the restoration of the antibody-binding capacity of electroblotted meningococcal outer membrane proteins. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Feb 24;67(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. M., Patel P. V., Parsons N. J., Smith H. Induction of serum resistance in recent isolates of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by a low-molecular-weight fraction of guinea pig serum. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):334–334. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Parsons N. J., Veale D. R., Smith H. Correlation with different immunotypes of gonococcal antigens associated with growth in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Mar;105(1):153–157. doi: 10.1099/00221287-105-1-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Fernandez R., Schoolnik G. K. Strain-specific and common epitopes of gonococcal pili. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):208–221. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIV. Cell wall protein differences among color/opacity colony variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):292–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.292-302.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Sadoff J. C., Artenstein M. S. Cross-reactivity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis and the nature of antigens involved in the bactericidal reaction. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):240–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veale D. R., Penn C. W., Smith H. Factors affecting the induction of phenotypically determined serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae grown in media containing serum or its diffusible components. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Feb;122(2):235–245. doi: 10.1099/00221287-122-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M., Heckels J. E. Antigenic cross-reactivity of Neisseria pili: investigations with type- and species-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2761–2768. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Sparling P. F. Response of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to iron limitation: alterations in expression of membrane proteins without apparent siderophore production. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):388–394. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.388-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak K., Diaz J. L., Jackson D., Heckels J. E. Antigenic variation during infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae: detection of antibodies to surface proteins in sera of patients with gonorrhea. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):166–174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]