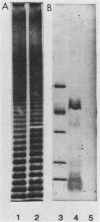
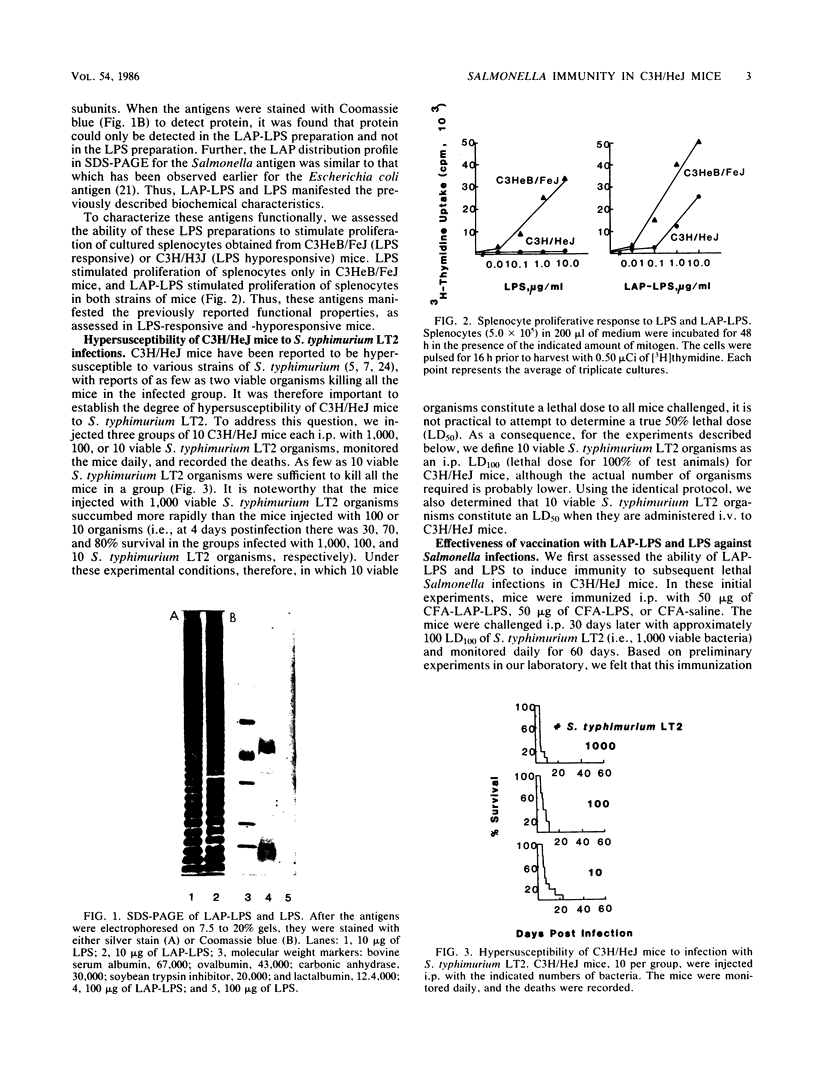
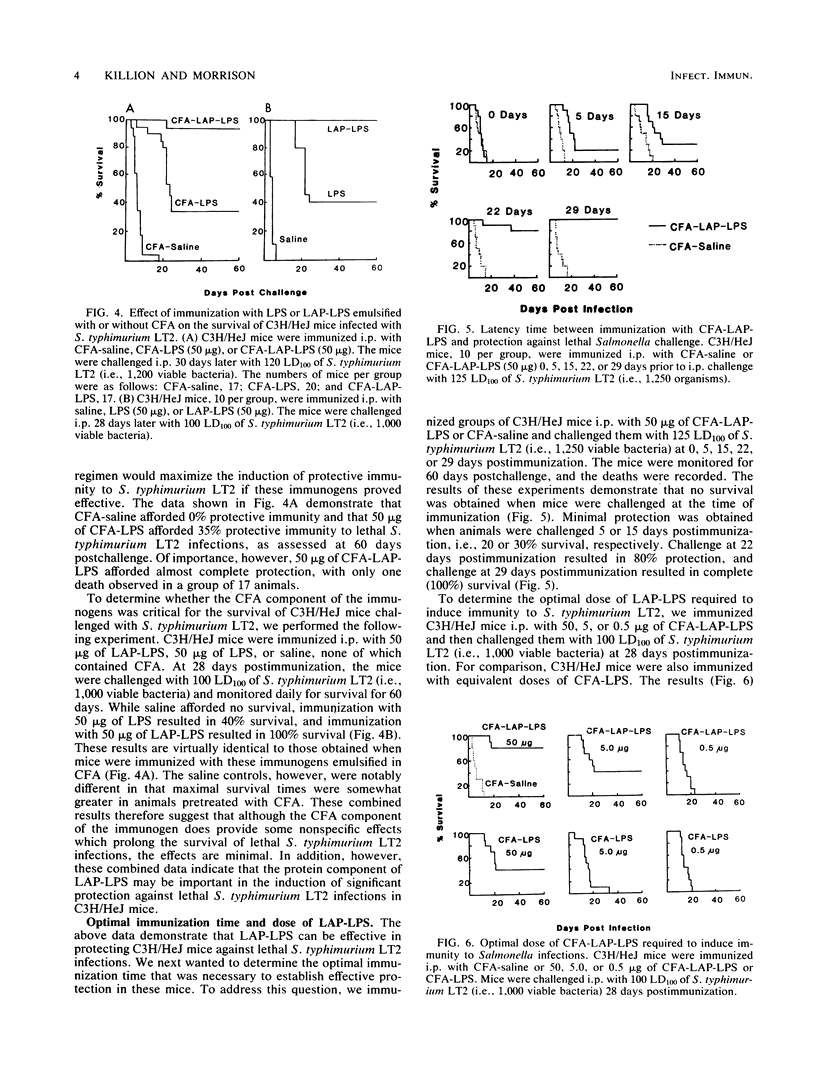
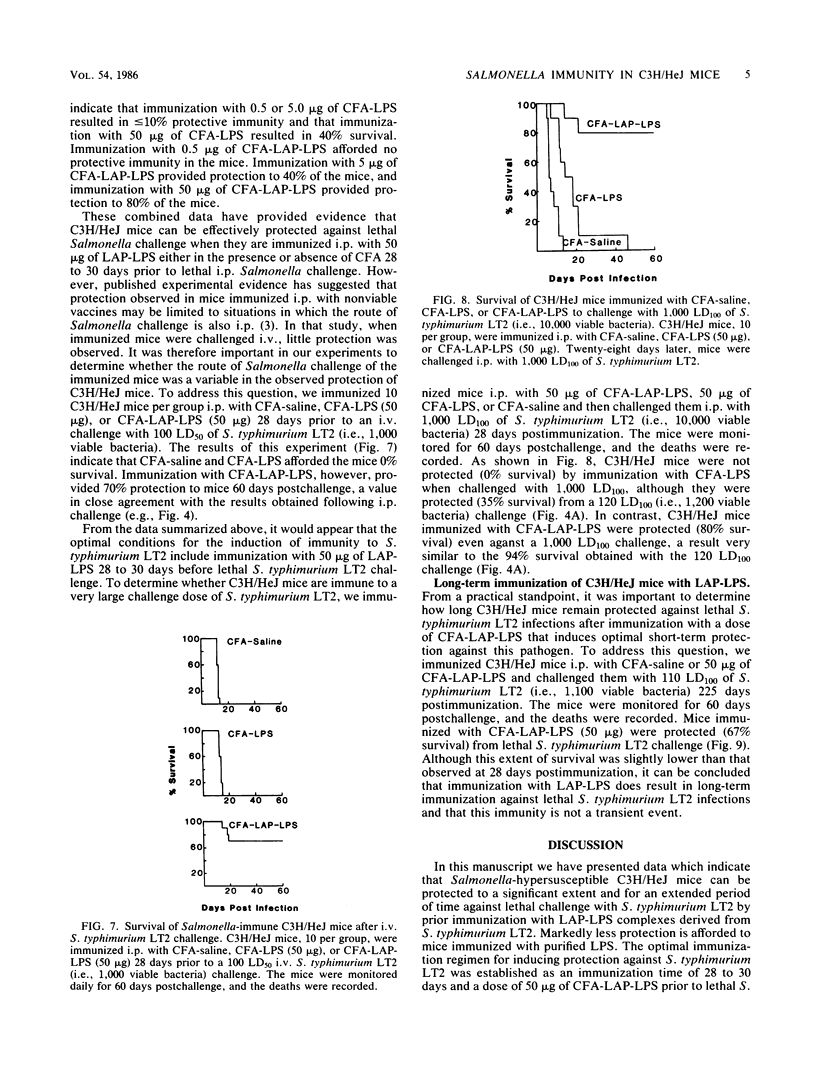
Abstract
C3H/HeJ mice were immunized intraperitoneally (i.p.) with lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-lipid A-associated protein (LAP) complexes or with purified protein-free LPS prior to lethal i.p. or intravenous Salmonella typhimurium LT2 challenge. Our results demonstrated that these Salmonella-hypersusceptible mice can be effectively protected against 1,000 100% lethal doses of S. typhimurium LT2 (i.e., 1,000 viable bacteria) administered by intravenous challenge when previously immunized with LAP-LPS complexes. In contrast to these results, immunization with LPS afforded markedly less protection regardless of the route of challenge, thus suggesting that the LAP portion of LAP-LPS complexes may be necessary for inducing protection against Salmonella infections. For most experiments, antigens were emulsified in complete Freund adjuvant (CFA); however, the CFA portion of the vaccine was suggested not to be an essential component for the induction of immunity to Salmonella infections, since equivalent levels of protection were obtained when it was omitted from the vaccine. The induction of immunity to murine salmonellosis by prior immunization with CFA-LAP-LPS was demonstrated not to be a transient phenomenon, since C3H/HeJ mice were still protected against lethal S. typhimurium LT2 challenge as late as 225 days postimmunization.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanden R. V., Mackaness G. B., Collins F. M. Mechanisms of acquired resistance in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):585–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in mice preimmunized with living or ethyl alcohol-killed vaccines. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):676–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.676-683.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in nonvaccinated mice challenged by various routes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):667–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.667-675.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Infection-immunity in experimental salmonellosis. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):601–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Vaccines and cell-mediated immunity. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Dec;38(4):371–402. doi: 10.1128/br.38.4.371-402.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell D. E., Michalek S. M., Briles D. E., Jirillo E., McGhee J. R. Monoclonal antibodies to Salmonella lipopolysaccharide: anti-O-polysaccharide antibodies protect C3H mice against challenge with virulent Salmonella typhimurium. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):950–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K., Angerman C. R. Immunity to experimental Salmonella infection: studies on the protective capacity and immunogenicity of lipopolysaccharide, acetone-killed cells, and ribosome-rich extracts of Salmonella typhimurium in C3H/HeJ and CD-1 mice. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1010–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K., Deakins L. W., Killar L., Saluk P. H., Sultzer B. M. Dissociation of innate susceptibility to Salmonella infection and endotoxin responsiveness in C3HeB/FeJ mice and other strains in the C3H lineage. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):696–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.696-703.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K., Killar L. M., Stocker B. A., Sultzer B. M. Cellular immunity induced by avirulent Salmonella in LPS-defective C3H/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):958–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K., Killar L. M., Sultzer B. M. Immunity to infection with Salmonella typhimurium: mouse-strain differences in vaccine- and serum-mediated protection. J Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;150(3):425–435. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., White D., Leive L. Identification of outer membrane proteins, including known lymphocyte mitogens, as the endotoxin protein of Escherichia coli 0111. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1290–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepper K. P., Garman R. D., Lyons M. F., Teresa G. W. Plaque-forming cell response in BALB/c mice to two preparations of LPS extracted from Salmonella enteritidis. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1290–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Morrison D. C., Curry B., Dixon F. J. Effect of lipid A-associated protein and lipid A on the expression of lipopolysaccharide activity. I. Immunological activity. Immunology. 1980 Jul;40(3):473–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxen H., Valtonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane proteins in experimental salmonellosis of mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):857–862. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.857-862.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt M. L., Johnson W. Protective ability of Salmonella ribosomal protein and RNA in inbred mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):286–291. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.286-291.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt M. L., Johnson W. Role of endotoxin contamination in ribiosomal vaccines prepared from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.98-104.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Betz S. J., Jacobs D. M. Isolation of a lipid A bound polypeptide responsible for "LPS-initiated" mitogenesis of C3H/HeJ spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):840–846. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Leive L. Fractions of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli O111:B4 prepared by two extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2911–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakoneczna I., Hsu H. S. The comparative histopathology of primary and secondary lesions in murine salmonellosis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1980 Feb;61(1):76–84. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Metcalf E. S., Rosenstreich D. L. Defect in macrophage effector function confers Salmonella typhimurium susceptibility on C3H/HeJ mice. Cell Immunol. 1982 Mar 1;67(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Rosenstreich D. L. Genetic control of the susceptibility of C3HeB/FeJ mice to Salmonella typhimurium is regulated by a locus distinct from known salmonella response genes. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2613–2615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Rosenstreich D. L., Taylor B. A. Control of natural resistance to Salmonella typhimurium and Leishmania donovani in mice by closely linked but distinct genetic loci. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):440–442. doi: 10.1038/287440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Scher I., Campbell G. H., MacDermott R. P., Formal S. B. Susceptibility of CBA/N mice to infection with Salmonella typhimurium: influence of the X-linked gene controlling B lymphocyte function. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):720–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Taylor B. A., Rosenstreich D. L. Genetic control of natural resistance to Salmonella typhimurium in mice during the late phase of infection. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3313–3318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Weinstein D. A., Soliman M. Y., Rosenstreich D. L. Additional evidence that the Lps gene locus regulates natural resistance to S. typhimurium in mice. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):2820–2823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Nurminen M., Lindberg A. A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines: O-antigenic oligosaccharide-protein conjugates induce protection against infection with Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):863–872. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.863-872.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Riblet R. Genetic control of responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharides in mice. I. Evidence for a single gene that influences mitogenic and immunogenic respones to lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1147–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]