Abstract
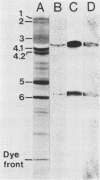
The erythrocyte receptors for S-fimbriated Escherichia coli, which causes sepsis and meningitis in newborn infants, were investigated. Neuraminidase and trypsin treatments of erythrocytes abolished the hemagglutination ability of the bacteria. To identify the receptor glycoproteins, we separated erythrocyte membrane proteins by gel electrophoresis, blotted them to nitrocellulose, and incubated them with 125I-labeled bacteria. The only bacterium-binding bands identified corresponded to glycophorin A dimer and monomer, and the binding was abolished by neuraminidase treatment of the blot. Radiolabeled bacteria also bound to purified glycophorin A adsorbed to polyvinyl chloride microwells, and the binding was inhibited by other sialoglycoproteins and isolated sialyloligosaccharides containing the NeuAc alpha 2-3Gal sequence. Oligosaccharides which contain the NeuAc alpha 2-3Gal beta 1-3GalNAc and NeuAc alpha 2-3Gal beta 1-3(NeuAc alpha 2-6)GalNAc sequence and which are identical to the O-linked saccharides of glycophorin A were twofold more effective inhibitors of binding than were other oligosaccharides containing the NeuAc alpha 2-3Gal sequence. The replacement of sialic acid in asialoerythrocytes with a purified Gal beta 1-3GalNAc alpha 2-3 sialyltransferase, which forms the O-linked NeuAc alpha 2-3Gal beta 1-3GalNAc sequence in asialoglycophorins, restored bacterial hemagglutination. These results indicated that the major erythrocyte receptor for S-fimbriated E. coli is the NeuAc alpha 2-3Gal beta 1-3GalNAc sequence of the O-linked oligosaccharide chains of glycophorin A.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartles J. R., Hubbard A. L. 125I-wheat germ agglutinin blotting: increased sensitivity with polyvinylpyrrolidone quenching and periodate oxidation/reductive phenylamination. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jul;140(1):284–292. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahr W., Uhlenbruck G., Janssen E., Schmalisch R. Different N-terminal amino acids in the MN-glycoprotein from MM and NN erythrocytes. Hum Genet. 1977 Mar 14;35(3):335–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00446624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzandu J. K., Deh M. E., Wise G. E. A re-examination of the effects of chymotrypsin and trypsin on the erythrocyte membrane surface topology. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):50–58. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90569-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén C. S., Hanson L. A., Jodal U., Lindberg U., Akerlund A. S. Variable adherence to normal human urinary-tract epithelial cells of Escherichia coli strains associated with various forms of urinary-tract infection. Lancet. 1976 Sep 4;1(7984):490–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. G., Silver R. P., Evans D. J., Jr, Chase D. G., Gorbach S. L. Plasmid-controlled colonization factor associated with virulence in Esherichia coli enterotoxigenic for humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):656–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.656-667.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J. Identification of the blood-group ABH-active glycoprotein components of human erythrocyte membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;104(1):181–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M. N., Fukuda M., Hakomori S. Cell surface modification by endo-beta-galactosidase. Change of blood group activities and release of oligosaccharides from glycoproteins and glycosphingolipids of human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5458–5465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H. Glycophorins A, B, and C: a family of sialoglycoproteins. Isolation and preliminary characterization of trypsin derived peptides. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(1):79–95. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Tomita M., Marchesi V. T. Fractionation of the major sialoglycopeptides of the human red blood cell membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):113–121. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., de Graaf F. K. Host-specific fimbrial adhesins of noninvasive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):129–161. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.129-161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Andersson L. C. Selective radioactive labeling of cell surface sialoglycoproteins by periodate-tritiated borohydride. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5888–5894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. C., Karlsson K. A., Larson G., Strömberg N., Thurin J. Carbohydrate-specific adhesion of bacteria to thin-layer chromatograms: a rationalized approach to the study of host cell glycolipid receptors. Anal Biochem. 1985 Apr;146(1):158–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Leffler H., Svanborg Edén C. Binding specificity of piliated strains of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium to epithelial cells, saccharomyces cerevisiae cells, and erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):796–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.796-804.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Valtonen M. V., Parkkinen J., Väisänen-Rhen V., Finne J., Orskov F., Orskov I., Svenson S. B., Mäkelä P. H. Serotypes, hemolysin production, and receptor recognition of Escherichia coli strains associated with neonatal sepsis and meningitis. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):486–491. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.486-491.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Väisänen-Rhen V., Rhen M., Pere A., Parkkinen J., Finne J. Escherichia coli fimbriae recognizing sialyl galactosides. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):762–766. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.762-766.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledeen R. W., Yu R. K. Gangliosides: structure, isolation, and analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:139–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisowska E., Duk M., Dahr W. Comparison of alkal-labile oligosaccharide chains of M and N blood-group glycopeptides from human erythrocyte membrane. Carbohydr Res. 1980 Feb;79(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)85135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomes L. M., Uemura K., Childs R. A., Paulson J. C., Rogers G. N., Scudder P. R., Michalski J. C., Hounsell E. F., Taylor-Robinson D., Feizi T. Erythrocyte receptors for Mycoplasma pneumoniae are sialylated oligosaccharides of Ii antigen type. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):560–563. doi: 10.1038/307560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A. A new solid-state reagent to iodinate proteins. I. Conditions for the efficient labeling of antiserum. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Finne J., Achtman M., Väisänen V., Korhonen T. K. Escherichia coli strains binding neuraminyl alpha 2-3 galactosides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):456–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Finne J. Isolation and characterization of novel phosphate-containing sialyloligosaccharides from normal human urine. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Apr 16;140(2):427–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Finne J. Isolation and structural characterization of five major sialyloligosaccharides and a sialylglycopeptide from normal human urine. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Nov 2;136(2):355–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. C., Sadler J. E., Hill R. L. Restoration of specific myxovirus receptors to asialoerythrocytes by incorporation of sialic acid with pure sialyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2120–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rearick J. I., Sadler J. E., Paulson J. C., Hill R. L. Enzymatic characterization of beta D-galactoside alpha2 leads to 3 sialyltransferase from porcine submaxillary gland. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4444–4451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers G. N., Paulson J. C. Receptor determinants of human and animal influenza virus isolates: differences in receptor specificity of the H3 hemagglutinin based on species of origin. Virology. 1983 Jun;127(2):361–373. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Yu J. Selective solubilization of proteins from red blood cell membranes by protein perturbants. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):220–232. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowell C. P., Lee R. T., Lee Y. C. Studies on the specificity of rabbit hepatic carbohydrate-binding protein using neoglycoproteins. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4904–4908. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. B., Winzler R. J. Structural studies on human erythrocyte glycoproteins. Alkali-labile oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5943–5946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita M., Furthmayr H., Marchesi V. T. Primary structure of human erythrocyte glycophorin A. Isolation and characterization of peptides and complete amino acid sequence. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4756–4770. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viitala J., Finne J. Specific cell-surface labeling of polyglycosyl chains in human erythrocytes and HL-60 cells using endo-beta-galactosidase and galactosyltransferase. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):393–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Väisänen-Rhen V., Korhonen T. K., Finne J. Novel cell-binding activity specific for N-acetyl-D-glucosamine in an Escherichia coli strain. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 8;159(1-2):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80453-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshima H., Furthmayr H., Kobata A. Structures of the asparagine-linked sugar chains of glycophorin A. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9713–9718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]