Abstract
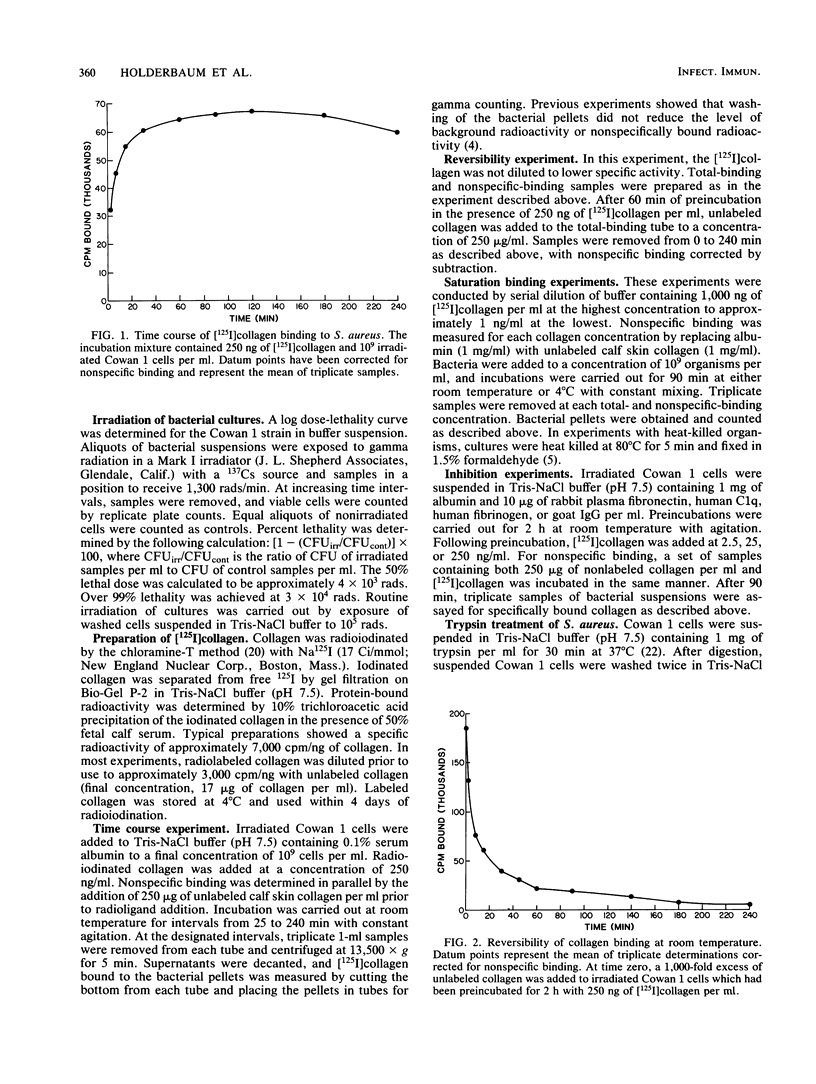
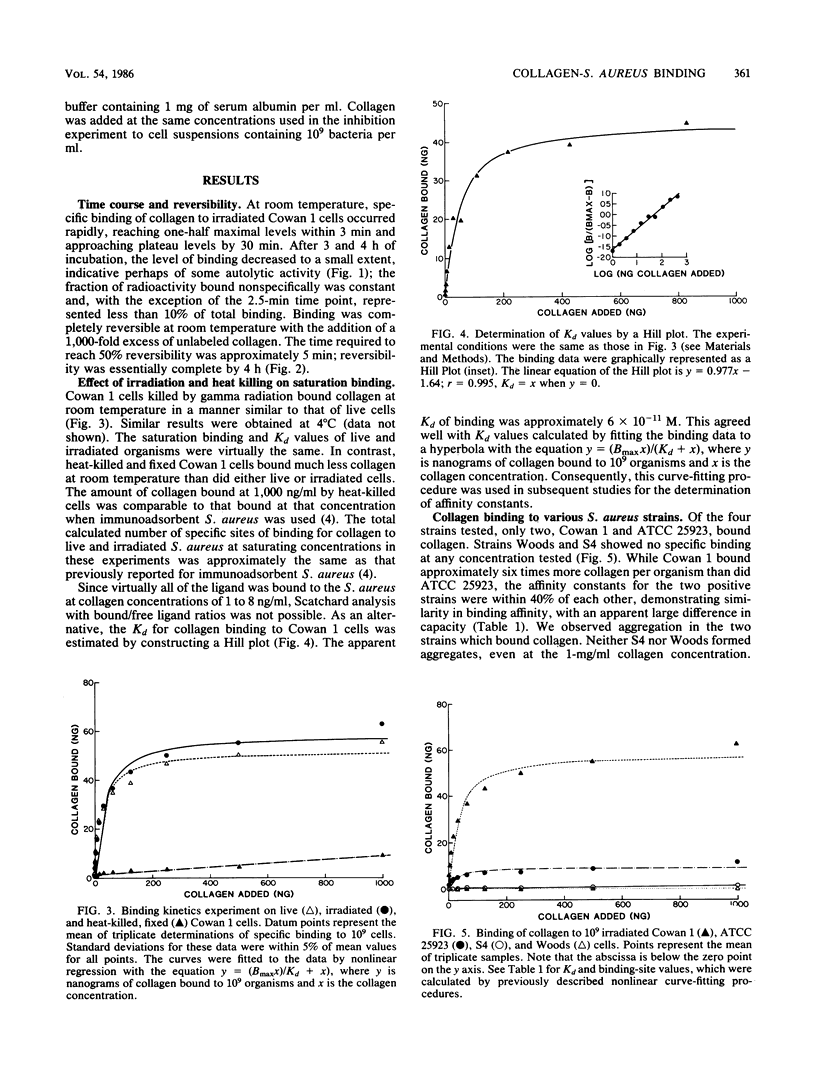
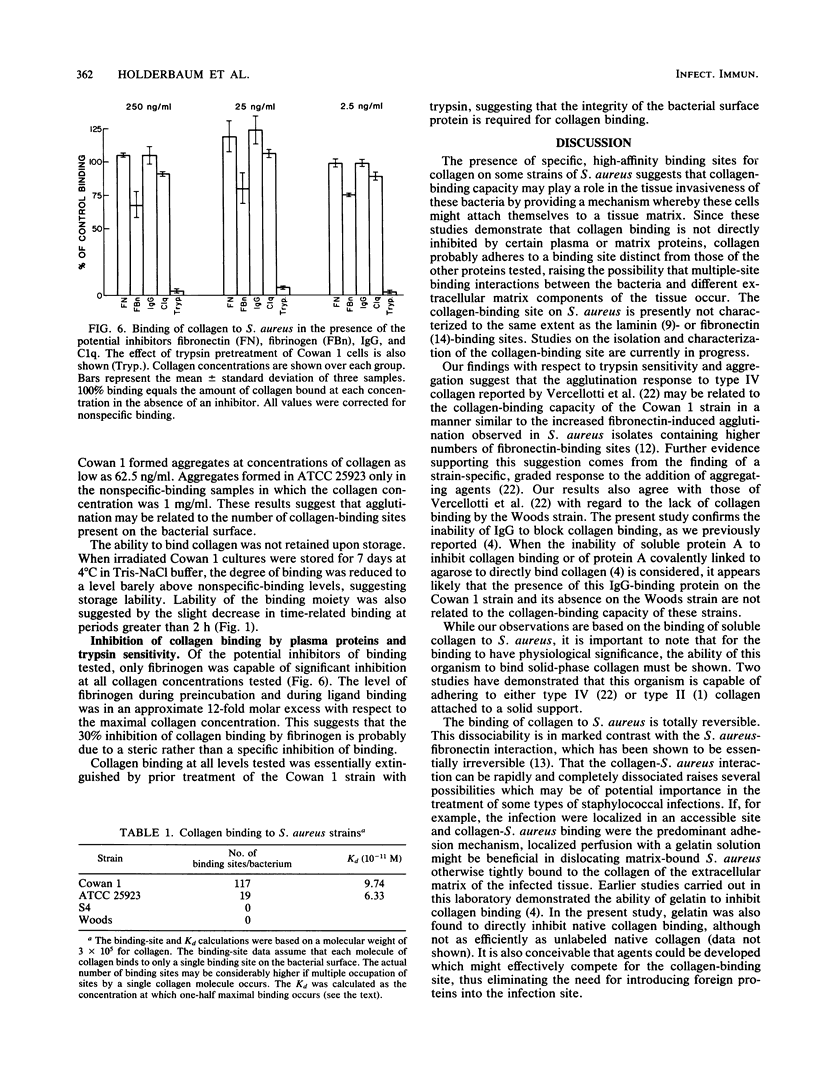
Staphylococcus aureus can bind soluble collagen in a specific, saturable manner. We have previously shown that some variability exists in the degree of collagen binding between different strains of heat-killed, formaldehyde-fixed S. aureus which are commercially available as immunologic reagents. The present study demonstrates that live S. aureus of the Cowan 1 strain binds amounts of collagen per organism equivalent to those demonstrated previously in heat-killed, formaldehyde-fixed bacteria but has an affinity over 100 times greater, with Kd values of 9.7 X 10(-11) M and 4.3 X 10(-8) M for live and heat-killed organisms, respectively. Studies were also carried out with S. aureus killed by ionizing radiation, since this method of killing the organism seemed less likely to alter the binding moieties on the surface than did heat killing. Bacteria killed by exposure to gamma radiation bound collagen in a manner essentially indistinguishable from that of live organisms. Binding of collagen to irradiated cells of the Cowan 1 strain was rapid, with equilibrium reached by 30 min at 22 degrees C, and was fully reversible. The binding was not inhibited by fibronectin, fibrinogen, C1q, or immunoglobulin G, suggesting a binding site for collagen distinct from those for these proteins. Collagen binding was virtually eliminated in trypsin-treated organisms, indicating that the binding site has a protein component. Of four strains examined, Cowan 1 and S. aureus ATCC 25923 showed saturable, specific binding, while strains Woods and S4 showed a complete lack of binding. These results suggest that some strains of S. aureus contain high-affinity binding sites for collagen. While the number of binding sites per bacterium varied sixfold in the two collagen-binding strains, the apparent affinity was similar. The ability of S. aureus to bind collagen with high affinity may provide a mechanism for bacterial adhesion to host tissue and thereby play a role in the invasive characteristics of this organism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carret G., Emonard H., Fardel G., Druguet M., Herbage D., Flandrois J. P. Gelatin and collagen binding to Staphylococcus aureus strains. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1985 Mar-Apr;136A(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(85)80063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkle L. M., Blair L. L., Fortune K. P. Transformation of a plasmid encoding an adhesin of Staphylococcus aureus into a nonadherent staphylococcal strain. J Infect Dis. 1986 Apr;153(4):670–675. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holderbaum D., Spech R. A., Ehrhart L. A. Specific binding of collagen to Staphylococcus aureus. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Jun;5(3):261–271. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Quie P. G., Williams R. C., Jr Quantitation of staphylococcal protein A: Determination of equilibrium constant and number of protein A residues on bacteria. J Immunol. 1970 Feb;104(2):273–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):718–720. doi: 10.1038/276718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Vartio T., Vuento M., Myhre E. B. Attachment of staphylococci and streptococci on fibronectin, fibronectin fragments, and fibrinogen bound to a solid phase. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.77-81.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J. D., dos Reis M., Brentani R. R. Presence of laminin receptors in Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):275–277. doi: 10.1126/science.3160113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miekka S. I., Ingham K. C., Menache D. Rapid methods for isolation of human plasma fibronectin. Thromb Res. 1982 Jul 1;27(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Binding and factor XIIIa-mediated cross-linking of a 27-kilodalton fragment of fibronectin to Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):927–929. doi: 10.1126/science.7403857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Christman G., Mosher D. F. Fibronectin-induced agglutination of Staphylococcus aureus correlates with invasiveness. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Oct;104(4):455–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Mosher D. F., Olbrantz P. J. Fibronectin binding to Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14788–14794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén C., Rubin K., Speziale P., Hök M., Lindberg M., Wadström T. Fibronectin receptors from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3396–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R., Braun W. E. Purification of anti-fibrinogen antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):206–211. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorvillo J. M., Pearlstein E. C1q, a subunit of the first component of complement, enhances binding of plasma fibronectin to bacteria. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):664–669. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.664-669.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Raucci G., Visai L., Switalski L. M., Timpl R., Hök M. Binding of collagen to Staphylococcus aureus Cowan 1. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.77-81.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski L. M., Rydén C., Rubin K., Ljungh A., Hök M., Wadström T. Binding of fibronectin to Staphylococcus strains. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):628–633. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.628-633.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti G. M., Lussenhop D., Peterson P. K., Furcht L. T., McCarthy J. B., Jacob H. S., Moldow C. F. Bacterial adherence to fibronectin and endothelial cells: a possible mechanism for bacterial tissue tropism. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Jan;103(1):34–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti G. M., McCarthy J. B., Lindholm P., Peterson P. K., Jacob H. S., Furcht L. T. Extracellular matrix proteins (fibronectin, laminin, and type IV collagen) bind and aggregate bacteria. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jul;120(1):13–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


