Abstract
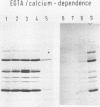
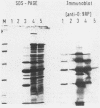
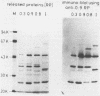
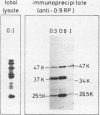
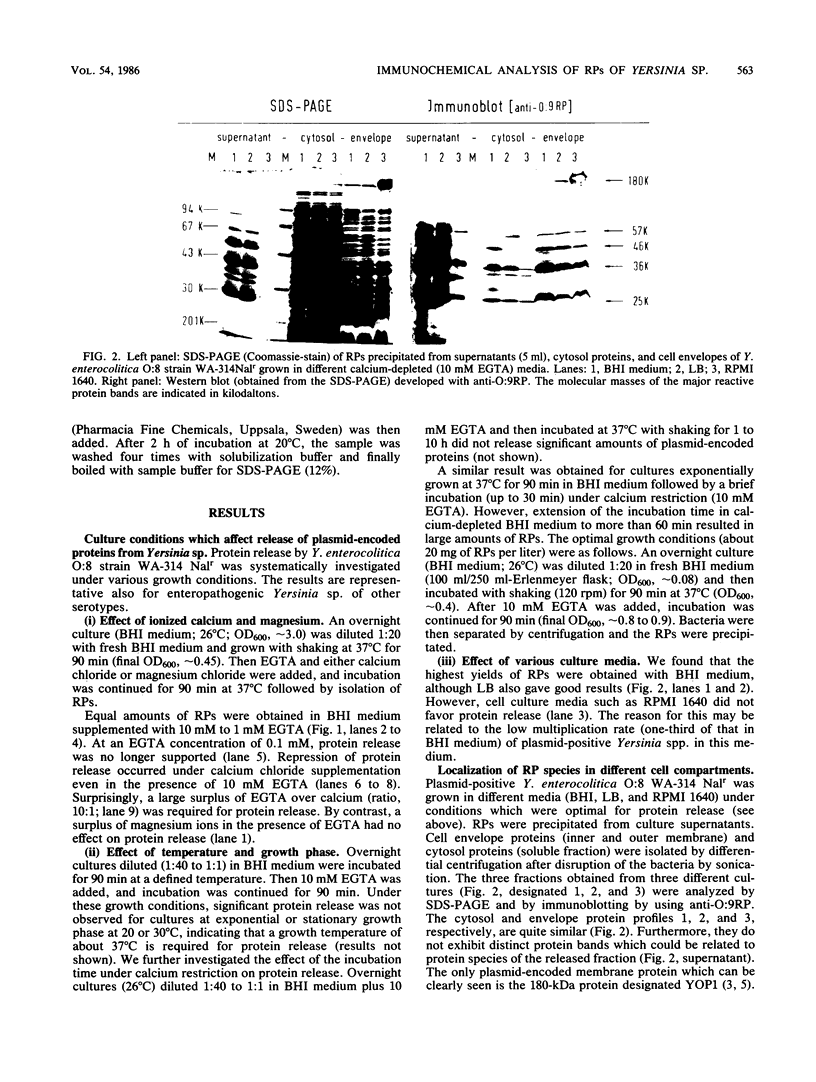
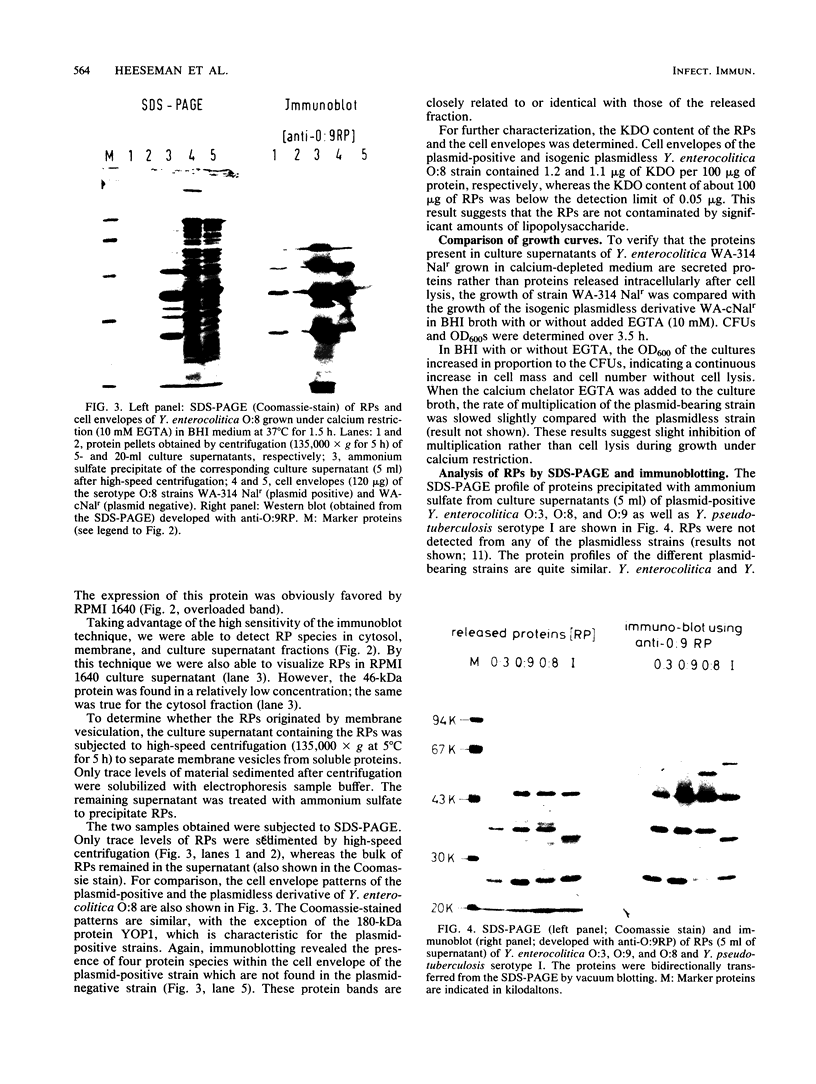
Enteropathogenic Yersinia sp. releases plasmid-associated proteins of low molecular mass (26-67 kilodaltons) at 37 degrees C. In this study, the optimum conditions for the release of proteins were assessed and the released proteins (RPs) were analyzed for the manner of release, immunochemical characteristics, and the location of the genes necessary for their synthesis. Protein release was strongly enhanced when growth media were markedly depleted of calcium ions by precipitation with oxalate or chelation with EGTA [ethylene glycol-bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid]. RP yields were greatest when Yersinia spp. were in the exponential growth phase. The RPs appeared to be released from the Yersinia spp. by secretion rather than by pinching off of membrane vesicles, because the RPs did not sediment during high-speed centrifugation nor were they contaminated to any significant degree with lipopolysaccharide. Moreover, immunoblot analysis revealed only traces of protein species related to RPs within the outer membranes of plasmid-positive Yersinia spp. grown at 37 degrees C under calcium-restricted conditions. Immunoblot studies also showed that the RPs of Y. enterocolitica serotypes O:3, O:8, and O:9 and the RP of Y. pseudotuberculosis serotype I are highly cross-reactive. Finally, the immunoprecipitates of the products of minicells which harbor Yersinia plasmids were used to demonstrate that at least three proteins immunochemically related to the released fraction were plasmid encoded. These results suggest that at least three of the RPs may be related to or identical with previously described plasmid-encoded Yersinia outer membrane proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Mercer A., Kusecek B., Pohl A., Heuzenroeder M., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Silver R. P. Six widespread bacterial clones among Escherichia coli K1 isolates. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):315–335. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.315-335.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: a panoramic view of a charismatic microorganism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):211–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H. Expression of the temperature-inducible outer membrane proteins of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):234–240. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.234-240.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Wolf-Watz H. Molecular cloning of the temperature-inducible outer membrane protein 1 of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):72–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.72-78.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T., Wohlhieter J. A. Presence of a virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1044–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1044-1047.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. VI. A differential plating medium for the estimation of the mutation rate to avirulence. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:605–608. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.605-608.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Algermissen B., Laufs R. Genetically manipulated virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.105-110.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Keller C., Morawa R., Schmidt N., Siemens H. J., Laufs R. Plasmids of human strains of Yersinia enterocolitica: molecular relatedness and possible importance for pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):107–115. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Laufs R. Construction of a mobilizable Yersinia enterocolitica virulence plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):761–767. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.761-767.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Laufs R. Double immunofluorescence microscopic technique for accurate differentiation of extracellularly and intracellularly located bacteria in cell culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):168–175. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.168-175.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNAPP W. Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis unter besonderer Berücksichtigung ihrer humanmedizinischen Bedeutung. Ergeb Mikrobiol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1959;32:196–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B. A., Wachsmuth K., Gemski P. New virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia enterocolitica. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jun;15(6):1161–1163. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.6.1161-1163.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWTON W. D., ERDMAN R. L., SURGALLA M. J. BIOSYNTHESIS AND PURIFICATION OF V AND W ANTIGEN IN PASTEURELLA PESTIS. J Immunol. 1963 Aug;91:179–184. doi: 10.21236/ad0299868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Smith R. E., Damaré J. M., Harris M. E., Johnston R. W. Evaluation of virulence test procedures for Yersinia enterocolitica recovered from foods. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;50(3):529–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb04255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazigh D., Quilici M. L., Mollaret H. H. Role of the virulence-associated plasmids of Yersinia enterocolitica on its immunogenicity against Y. pestis. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1984 Nov-Dec;135B(3):283–290. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(84)80095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., DeStephano L. Serum resistance associated with virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):605–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.605-611.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Martinez R. J. Role of a plasmid in the pathogenicity of Yersinia species. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:29–51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Bowmer W. S. Virulence genes regulated at the transcriptional level by Ca2+ in Yersinia pestis include structural genes for outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):445–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.445-454.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Cytoplasmic and membrane proteins of yersiniae cultivated under conditions simulating mammalian intracellular environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1224–1228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Barrera O. Immunological characteristics of gonococcal outer membrane protein II assessed by immunoprecipitation, immunoblotting, and coagglutination. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1405–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Nurmi T., Mäki M., Skurnik M., Sundqvist C., Granfors K., Grönroos P. Plasmids in Yersinia enterocolitica serotypes O:3 and O:9: correlation with epithelial cell adherence in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):870–876. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.870-876.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winblad S., Niléhn B., Sternby N. H. Yersinia enterocolitica (Pasteurella x) in human enteric infections. Br Med J. 1966 Dec 3;2(5526):1363–1366. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5526.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]