Abstract
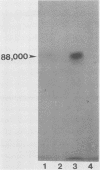
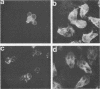
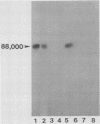
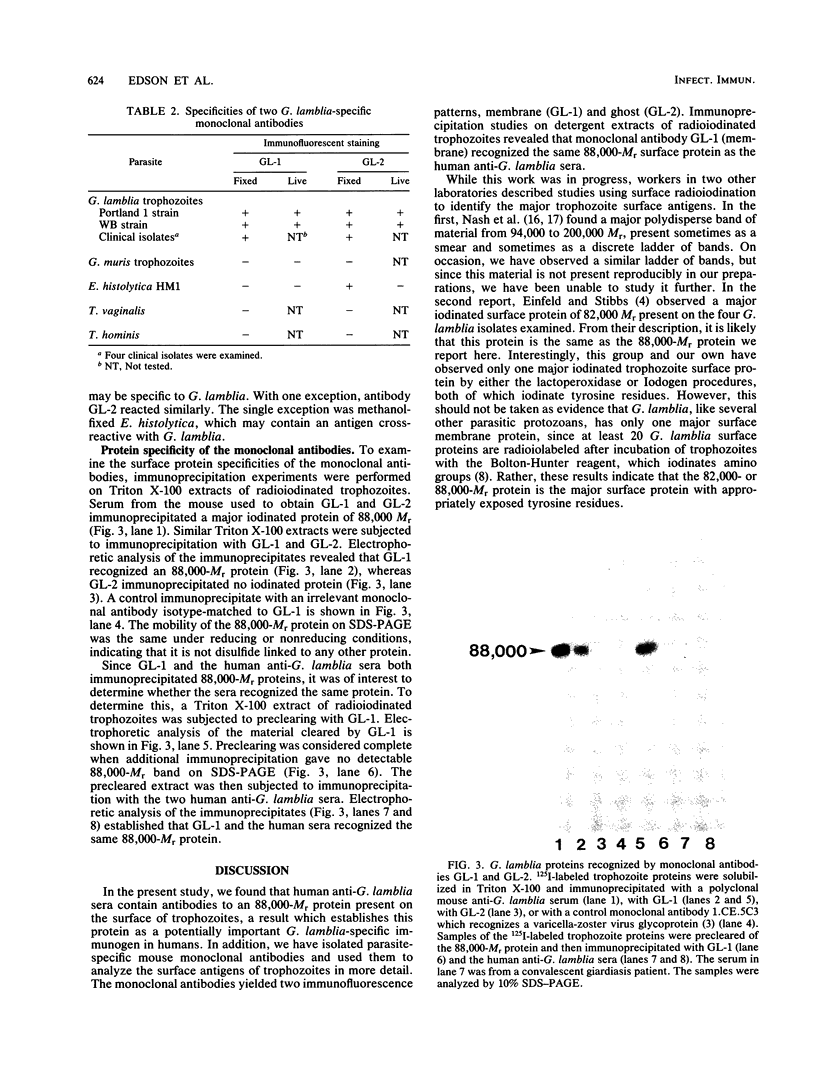
Human anti-Giardia lamblia sera specifically immunoprecipitated an 88,000-Mr surface protein from radioiodinated trophozoites, establishing this protein as a potentially important immunogen in humans. A mouse monoclonal antibody (GL-1) was isolated which immunoprecipitated the same 88,000-Mr surface protein recognized by the human sera. GL-1 gave uniform fluorescent staining of the cell surface and flagella of G. lamblia trophozoites from the Portland 1 and WB strains as well as fresh clinical isolates, but not of Giardia muris, suggesting that the surface antigen is specific to G. lamblia. Other human parasites, including Entamoeba histolytica, Trichomonas vaginalis, and Trichomonas hominis, were not stained. A second mouse monoclonal antibody (GL-2) gave weaker immunofluorescent staining of living G. lamblia trophozoites but intense staining of fixed cells. None of the other parasites tested were stained, with the exception of E. histolytica, which may contain a cross-reactive antigen. No proteins were recognized in immunoprecipitation studies with iodinated trophozoites.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ament M. E., Rubin C. E. Relation of giardiasis to abnormal intestinal structure and function in gastrointestinal immunodeficiency syndromes. Gastroenterology. 1972 Feb;62(2):216–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson C. M., Hosler B. A., Poodry C. A., Schooley R. T., Waters D. J., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Varicella-zoster virus envelope glycoproteins: biochemical characterization and identification in clinical material. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):62–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90201-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einfeld D. A., Stibbs H. H. Identification and characterization of a major surface antigen of Giardia lamblia. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):377–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.377-383.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlich J. H., Anders R. F., Roberts-Thomson I. C., Schrader J. W., Mitchell G. F. An examination of differences in serum antibody specificities and hypersensitivity reactions as contributing factors to chronic infection with the intestinal protozoan parasite, Giardia muris, in mice. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1983 Oct;61(Pt 5):599–615. doi: 10.1038/icb.1983.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farthing M. J., Pereira M. E., Keusch G. T. Description and characterization of a surface lectin from Giardia lamblia. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.661-667.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farthing M. J., Pereira M. E., Keusch G. T. Giardia lamblia: evaluation of roller bottle cultivation. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Dec;54(3):410–415. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farthing M. J., Varon S. R., Keusch G. T. Mammalian bile promotes growth of Giardia lamblia in axenic culture. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(4):467–469. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E., Santer V. Enzymic iodination. A probe for accessible surface proteins of normal and neoplastic lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(5):921–927. doi: 10.1042/bj1240921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer E. A. Giardia lamblia: isolation and axenic cultivation. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Feb;39(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Gillin F. D., Smith P. D. Excretory-secretory products of Giardia lamblia. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):2004–2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Keister D. B. Differences in excretory-secretory products and surface antigens among 19 isolates of Giardia. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1166–1171. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENDTORFF R. C. The experimental transmission of human intestinal protozoan parasites. II. Giardia lamblia cysts given in capsules. Am J Hyg. 1954 Mar;59(2):209–220. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley M. J., Ridley D. S. Serum antibodies and jejunal histology in giardiasis associated with malabsorption. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Jan;29(1):30–34. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson I. C., Mitchell G. F., Anders R. F., Tait B. D., Kerlin P., Kerr-Grant A., Cavanagh P. Genetic studies in human and murine giardiasis. Gut. 1980 May;21(5):397–401. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.5.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson I. C., Stevens D. P., Mahmoud A. A., Warren K. S. Acquired resistance to infection in an animal model of giardiasis. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):2036–2037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Gillin F. D., Brown W. R., Nash T. E. IgG antibody to Giardia lamblia detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jun;80(6):1476–1480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider D. P., Gordon J., McDermott M. R., Underdown B. J. Chronic Giardia muris infection in anti-IgM-treated mice. I. Analysis of immunoglobulin and parasite-specific antibody in normal and immunoglobulin-deficient animals. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4153–4162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A. Characterization of cross-reacting antigens on the Epstein-Barr virus envelope and plasma membranes of producer cells. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Edson C. M. Polypeptides of the Epstein-Barr virus membrane antigen complex. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):458–467. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.458-467.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Smith P. D., Healy G. R., Brown W. R. An immunofluorescence test to detect serum antibodies to Giardia lamblia. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Dec;93(6):802–805. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-6-802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]