Abstract
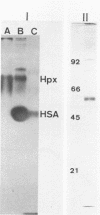
Although Haemophilus influenzae requires heme for growth, the source of heme during invasive infections is not known. We compared heme, lactoperoxidase, catalase, cytochrome c, myoglobin, and hemoglobin as sources of heme for growth in defined media. The minimum concentration of heme permitting unrestricted growth of strain E1a, an H. influenzae type b isolate from cerebrospinal fluid, was 0.02 micrograms/ml. Using molar equivalents of heme as lactoperoxidase, catalase, cytochrome c, myoglobin, and hemoglobin, we determined that myoglobin and hemoglobin permitted unrestricted growth at this concentration. To determine the ability of host defenses to sequester heme from H. influenzae, we used affinity chromatography to purify human haptoglobin and hemopexin, serum proteins which bind hemoglobin and heme. Plate assays revealed that 12 strains of H. influenzae acquired heme from hemoglobin, hemoglobin-haptoglobin, heme-hemopexin, and heme-albumin. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of outer membrane proteins of strain E1a grown in heme-replete and heme-restricted conditions revealed a heme-repressible outer membrane protein with an apparent molecular mass of 38 kilodaltons. These results demonstrated that, unlike Escherichia coli, H. influenzae may acquire heme from hemoglobin-haptoglobin. H. influenzae also may acquire heme from hemopexin and albumin, which have not been previously investigated. The role of outer membrane proteins in the acquisition of heme is not yet clear.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcoleo J. P., Greer J. Hemoglobin binding site and its relationship to the serine protease-like active site of haptoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10063–10068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Hancock R. E., Hantke K., Hartmann A. Functional organization of the outer membrane of escherichia coli: phage and colicin receptors as components of iron uptake systems. J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(1):37–58. doi: 10.1002/jss.400050105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J. The significance of iron in infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1127–1138. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Nutritional profiles of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Neisseria lactamica in chemically defined media and the use of growth requirements for gonococcal typing. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):178–194. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delers F., Lombart C., Domingo M., Musquera S. A novel and specific method for the purification of hemoglobin-binding proteins. Anal Biochem. 1981 Dec;118(2):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90593-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton J. W., Brandt P., Mahoney J. R., Lee J. T., Jr Haptoglobin: a natural bacteriostat. Science. 1982 Feb 5;215(4533):691–693. doi: 10.1126/science.7036344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann A., Braun V. Iron uptake and iron limited growth of Escherichia coli K-12. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Dec 2;130(5):353–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00414599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Sparling P. F. Haemophilus influenzae can use human transferrin as a sole source for required iron. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):248–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.248-251.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan K. M., Oski F. A. Anemia with Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. Pediatrics. 1980 Jun;65(6):1101–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka K., Bindereif A., Neilands J. B. Aerobactin-mediated utilization of transferrin iron. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6503–6508. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskelo P., Muller-Eberhard U. Interaction of porphyrins with proteins. Semin Hematol. 1977 Apr;14(2):221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Scolea L. J., Jr, Rosales S. V., Welliver R. C., Ogra P. L. Mechanisms underlying the development of meningitis or epiglottitis in children after Haemophilus influenzae type b bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1162–1165. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T. Porphyrin-binding proteins in serum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:624–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo G., Tecce M. F. A four- to sixfold enhancement in sensitivity for detecting trace proteins in dye or silver stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Oct 1;134(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. Preparation of blood hemoglobins of vertebrates. Methods Enzymol. 1981;76:5–29. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)76111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. G., Zwahlen A., Moxon E. R. Role of intravascular replication in the pathogenesis of experimental bacteremia due to Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):307–314. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seery V. L., Hathaway G., Eberhard U. M. Hemopexin of human and rabbit: molecular weight and extinction coefficient. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 May;150(1):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seery V. L., Muller-Eberhard U. Binding of porphyrins to rabbit hemopexin and albumin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3796–3800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurin S. B., Anderson P., Zollinger J., Rathbun R. K. Pathophysiology of hemolysis in infections with Hemophilus influenzae type b. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1340–1348. doi: 10.1172/JCI112439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Smith D. H., Averill D. R., Jr, Marino J., Moxon E. R. Production of Haemophilus influenzae b meningitis in infant rats by intraperitoneal inoculation. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):278–290. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.278-290.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., Jacobs R. F., Haas J. E., Roberts M. C., Wilson C. B., Smith A. L. Human serum bactericidal activity against Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Mar;130(3):665–672. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-3-665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., Mack K., Haas J. E., Smit J., Smith A. L. A comparison of techniques for isolation of the outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Anal Biochem. 1985 Nov 1;150(2):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., Mendelman P. M., Haas J. E., Schoenborn M. A., Mack K. D., Smith A. L. Characterization of Haemophilus influenzae type b fimbriae. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):787–796. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.787-796.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Ryan D., Levin W. An improved staining procedure for the detection of the peroxidase activity of cytochrome P-450 on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):168–176. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsui K., Mueller G. C. Affinity chromatography of heme-binding proteins: an improved method for the synthesis of hemin-agarose. Anal Biochem. 1982 Apr;121(2):244–250. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90475-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wejman J. C., Hovsepian D., Wall J. S., Hainfeld J. F., Greer J. Structure of haptoglobin and the haptoglobin-hemoglobin complex by electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 5;174(2):319–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Bindereif A., Paw B. H., Neilands J. B. Aerobactin biosynthesis and transport genes of plasmid ColV-K30 in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):570–578. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.570-578.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]