Abstract
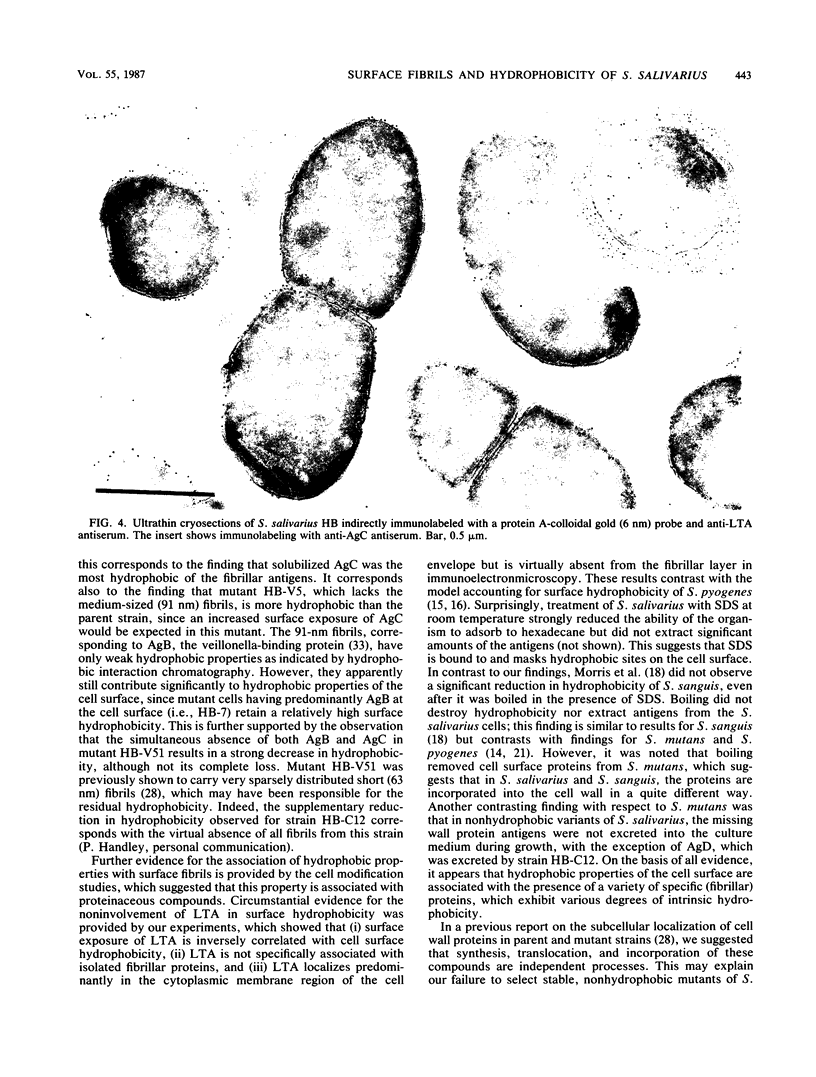
The cell surfaces of a range of variants of Streptococcus salivarius HB, altered in cell wall antigen composition, were compared with those of the parent with respect to adherence, ability to adsorb to hexadecane, morphology, and exposure of lipoteichoic acid (LTA). Adherence to host surfaces was measured by using both saliva-coated hydroxyapatite beads and tissue-cultured HeLa cells, and interbacterial adherence was measured by using Veillonella alcalescens V1 cells. Progressive loss of the protease-sensitive fibril classes was generally associated with decreasing ability to adsorb to hexadecane. However, increased exposure of protein antigen C (AgC) increased the apparent hydrophobicity of the cell. This correlated with the finding that AgC was the most hydrophobic of the solubilized fibrillar cell wall antigens. Collectively, this demonstrates that adsorption to hydrophobic ligands is directly related to the density of the fibrillar layer on the cells and the properties and surface exposure of specific fibril classes. The involvement of hydrophobic interactions in AgC-associated attachment was suggested by its sensitivity to low levels of the hydrophobic bond-breaking agent tetramethyl urea, although the reduction was not to the level of adherence observed with strains lacking AgC. However, hydrophobicity was less essential to other adherence reactions. Circumstantial evidence, including immunoelectron microscopy, showing that LTA was virtually absent from the fibrillar layer, whole-cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, suggesting that surface exposure of LTA related inversely to the density of the fibrillar layer, and agarose gel electrophoresis, showing that LTA was not specifically associated with protein fibrillar antigens, strongly suggested that LTA does not confer hydrophobic properties to these cells and is not involved in adherence reactions associated with the cell wall protein antigens.
Full text
PDF

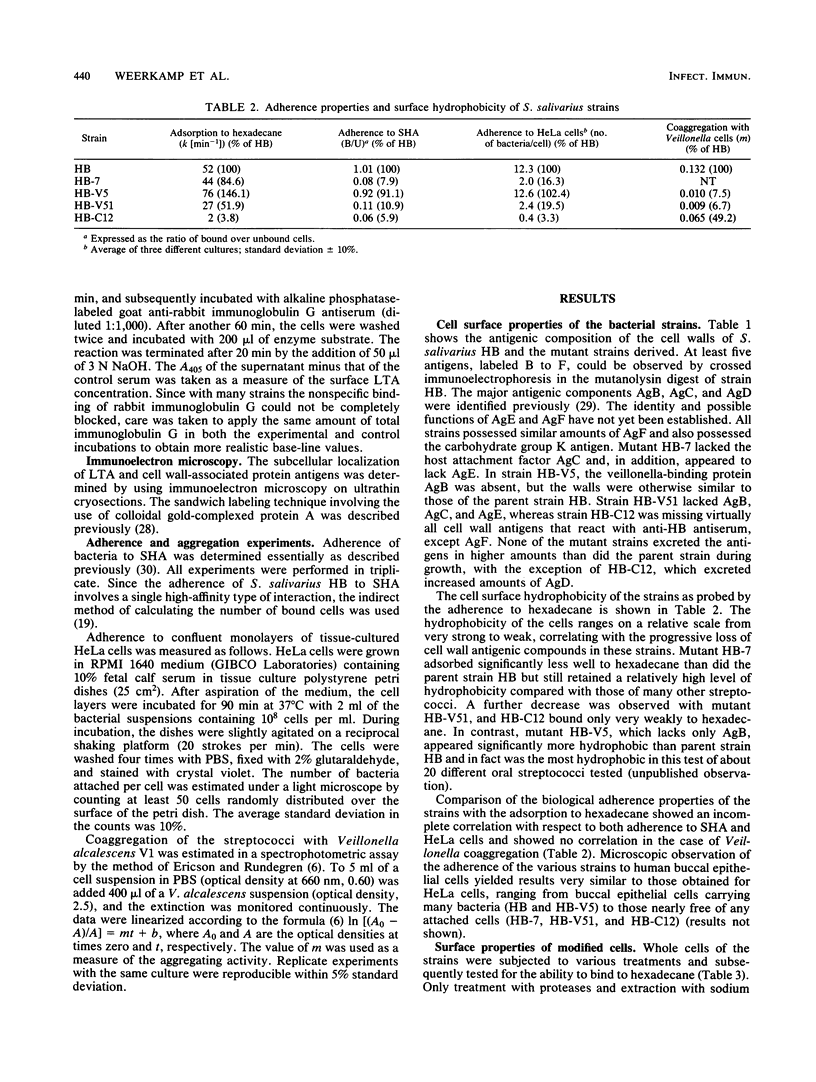
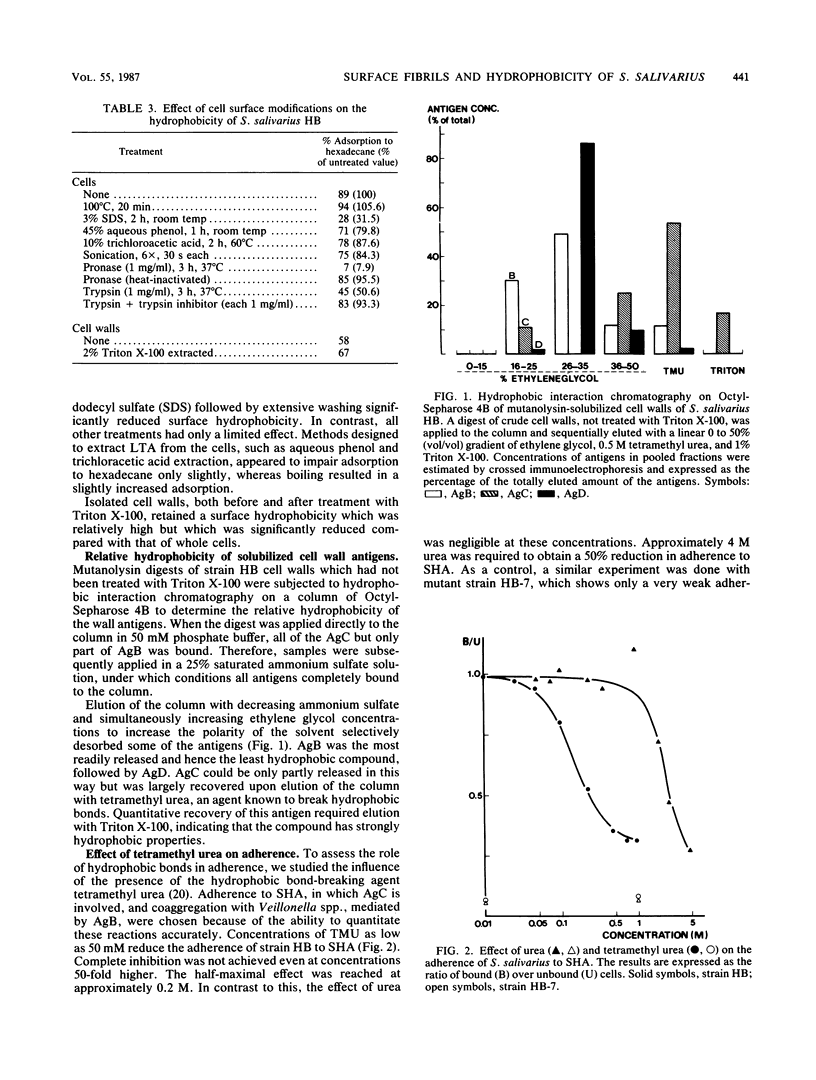



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H., Ofek I. Epithelial cell binding of group A streptococci by lipoteichoic acid on fimbriae denuded of M protein. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):759–771. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busscher H. J., Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., van Pelt A. W., de Jong H. P., Arends J. Measurement of the surface free energy of bacterial cell surfaces and its relevance for adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):980–983. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.980-983.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. B., Lane M. D., Beem J. E., Bragg S. L., Wheeler T. T. Relative hydrophobicities of Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii strains and their adsorption to saliva-treated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):730–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.730-736.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. M protein-associated adherence of Streptococcus pyogenes to epithelial surfaces: prerequisite for virulence. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):826–830. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.826-830.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson T., Rundegren J. Characterization of a salivary agglutinin reacting with a serotype c strain of Streptococcus mutans. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fives-Taylor P. M., Thompson D. W. Surface properties of Streptococcus sanguis FW213 mutants nonadherent to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):752–759. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.752-759.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I. Comparative hydrophobicities of oral bacteria and their adherence to salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1190–1196. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1190-1196.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Etherden I., Skobe Z. Association of fimbriae with the hydrophobicity of Streptococcus sanguis FC-1 and adherence to salivary pellicles. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):414–417. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.414-417.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson S. L., Stinson M. W., Millar S. J., Cohen R. E. Purification of lipoteichoic acid by chromatography in water-organic solvent systems. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):378–384. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.378-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Hardy L. N., Markevics L. J., Evans J. D., Wicken A. J. Comparative studies on the effect of growth conditions on adhesion, hydrophobicity, and extracellular protein profile of Streptococcus sanguis G9B. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):545–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.545-554.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Song M., Krasse B., Olsson J. Biochemical and immunological differences between hydrophobic and hydrophilic strains of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):68–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.68-75.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miörner H., Havlícek J., Kronvall G. Surface characteristics of group A streptococci with and without M-protein. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1984 Feb;92(1):23–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb02789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miörner H., Johansson G., Kronvall G. Lipoteichoic acid is the major cell wall component responsible for surface hydrophobicity of group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):336–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.336-343.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moeremans M., Daneels G., Van Dijck A., Langanger G., De Mey J. Sensitive visualization of antigen-antibody reactions in dot and blot immune overlay assays with immunogold and immunogold/silver staining. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Nov 30;74(2):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90303-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., Ganeshkumar N., McBride B. C. Cell surface components of Streptococcus sanguis: relationship to aggregation, adherence, and hydrophobicity. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):255–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.255-262.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris E. J., McBride B. C. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite: evidence for two binding sites. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):656–663. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.656-663.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt W. E., Doyle R. J., Taylor K. G. Hydrophobic interactions and the adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to hydroxylapatite. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):637–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.637-644.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Whitnack E., Beachey E. H. Hydrophobic interactions of group A streptococci with hexadecane droplets. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):139–145. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.139-145.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., Handley P. S., Baars A., Slot J. W. Negative staining and immunoelectron microscopy of adhesion-deficient mutants of Streptococcus salivarius reveal that the adhesive protein antigens are separate classes of cell surface fibril. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):746–755. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.746-755.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., Jacobs T. Cell wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus salivarius: purification, properties, and function in adherence. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):233–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.233-242.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., McBride B. C. Adherence of Streptococcus salivarius HB and HB-7 to oral surfaces and saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):150–158. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.150-158.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., McBride B. C. Characterization of the adherence properties of Streptococcus salivarius. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):459–468. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.459-468.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., McBride B. C. Identification of a Streptococcus salivarius cell wall component mediating coaggregation with Veillonella alcalescens V1. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):723–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.723-730.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., Busscher H. J. The surface free energy of oral streptococci after being coated with saliva and its relation to adhesion in the mouth. J Dent Res. 1985 Oct;64(10):1204–1210. doi: 10.1177/00220345850640100501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., Liem R. S. Structural properties of fibrillar proteins isolated from the cell surface and cytoplasm of Streptococcus salivarius (K+) cells and nonadhesive mutants. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):756–762. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.756-762.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergren G., Olsson J. Hydrophobicity and adherence of oral streptococci after repeated subculture in vitro. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):432–435. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.432-435.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. T., Clark W. B. Fibril-mediated adherence of Actinomyces viscosus to saliva-treated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):577–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.577-584.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]