Abstract
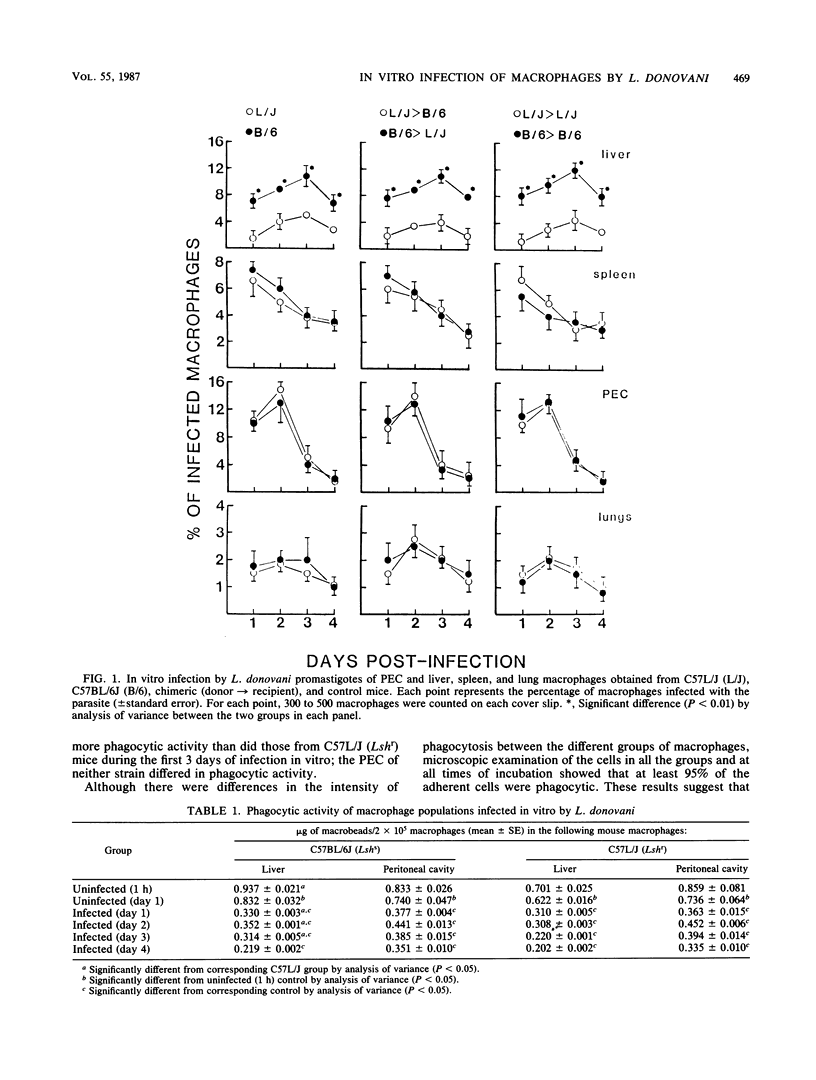
Many studies have demonstrated differences in the resistance of strains of mice to infection by Leishmania donovani, Salmonella typhimurium, and Mycobacterium bovis BCG; this resistance/susceptibility phenotype seems to be controlled by a single gene. The present study investigated the susceptibility of liver, lung, peritoneal, and spleen macrophages to infection by L. donovani promastigotes in vitro; the objective was to determine if the susceptibility of animals was expressed by their macrophages when infected in vitro. This study indicated that the Lsh phenotype was only expressed by liver macrophages. The liver macrophages of the susceptible C57BL/6J strain were significantly more phagocytic than those of the resistant C57L/J strain; infection affected the phagocytic activity of the macrophage population. These results indicated that only liver macrophages can express the Lsh gene. Recognition of expression is in part due to its effect on the phagocytic activity of the macrophages.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belosevic M., Faubert G. M. Comparative studies of inflammatory responses in susceptible and resistant mice infected with Giardia muris. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Sep;65(3):622–630. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J. M., Ezekowitz R. A., Roberts M. B., Channon J. Y., Sim R. B., Gordon S. Macrophage complement and lectin-like receptors bind Leishmania in the absence of serum. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):324–331. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Kirkley J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. I. the variable course of Leishmania donovani infections in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):119–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Kirkley J. Variation in susceptibility of mouse strains to Leishmania donovani infection. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1972;66(4):527–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Taylor B. A., Blackwell J., Evans E. P., Freeman J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. III. Mapping of the locus controlling susceptibility to visceral leishmaniasis in the mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):7–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray R. S., Heikal B., Kaye P. M., Bray M. A. The effect of parasitization by Leishmania mexicana mexicana on macrophage function in vitro. Acta Trop. 1983 Mar;40(1):29–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Blackwell J. M., Bradley D. J. Expression of the natural resistance gene Lsh in resident liver macrophages. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1033–1040. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1033-1040.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Blackwell J. M., Bradley D. J. Transfer of innate resistance and susceptibility to Leishmania donovani infection in mouse radiation bone marrow chimaeras. Immunology. 1984 Jul;52(3):417–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egwang T. G., Gauldie J., Befus D. Broncho-alveolar leucocyte responses during primary and secondary Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection in the rat. Parasite Immunol. 1984 May;6(3):191–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1984.tb00792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E., Maskell D. J., Harrington K., Joysey H., Brock J. Mechanisms of natural resistance to mouse typhoid. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1983 Mar-Apr;19(2):137–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E. The natural resistance of radiation chimeras to S. typhimurium C5. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):329–332. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Hale C., Liew F. Y. Genetically determined susceptibility to Leishmania tropica infection is expressed by haematopoietic donor cells in mouse radiation chimaeras. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):161–162. doi: 10.1038/288161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. R., Pappas M. G., Hansen B. D. Fluorogenic substrate detection of viable intracellular and extracellular pathogenic protozoa. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):435–438. doi: 10.1126/science.2578226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongshavn P. A., Sadarangani C., Skamene E. Genetically determined differences in antibacterial activity of macrophages are expressed in the environment in which the macrophage precursors mature. Cell Immunol. 1980 Aug 1;53(2):341–349. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepay D. A., Nathan C. F., Steinman R. M., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Murine Kupffer cells. Mononuclear phagocytes deficient in the generation of reactive oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1079–1096. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Metcalf E. S. Control of early Salmonella typhimurium growth in innately Salmonella-resistant mice does not require functional T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1349–1351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J. E., Blackwell J. M., O'Brien A. D., Bradley D. J., Glynn A. A. Are the Lsh and Ity disease resistance genes at one locus on mouse chromosome 1? Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):510–511. doi: 10.1038/297510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Genetics of resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):72–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Gros P., Forget A., Kongshavn P. A., St Charles C., Taylor B. A. Genetic regulation of resistance to intracellular pathogens. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):506–509. doi: 10.1038/297506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiger R. F., Black C. D. Simplified defined media for cultivating Leishmania donovani promastigotes. Acta Trop. 1980 Jun;37(2):195–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulczak O. M., Blackwell J. M. Immunoregulation of genetically controlled acquired responses to Leishmania donovani infection in mice: the effects of parasite dose, cyclophosphamide and sublethal irradiation. Parasite Immunol. 1983 Sep;5(5):449–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1983.tb00760.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


